Introduction
In recent years, the world has recognized the immense potential of artificial intelligence (AI), given the compelling and revolutionary advancements made in the field over the past decade. AI is moving from being able to only perform programmed tasks to being able to produce previously increasingly creative content, including text, images and videos. The global AI industry, along with its impact is growing. According to Fortune Business Insights, the global AI market value is expected to expand from USD 515.31 billion in 2023 to USD 2,740.46 billion by 2032, demonstrating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.4% during the forecast period. Moving forward, AI’s rapid pace of development and potential impact appear to be significant. In 2023, S&P Dow Jones Indices (S&P DJI) launched the S&P Kensho Artificial Intelligence Enablers Index, which seeks to measure the performance of companies that develop and enable AI technology, infrastructure and services. In this paper, we will introduce the AI technology and value chain, and we will elaborate on how we use an indexing approach designed to measure the opportunity they provide.
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
AI has seamlessly woven itself into our daily lives, from the technology in our smartphones to chatbots powered by generative AI. The first AI system, a robotic mouse that could find its way out of a labyrinth and remember its course, was built by Claude Shannon in 1950. Today, AI systems can perform tasks that closely mimic certain human abilities. So, what exactly is AI, and what technology is behind it?
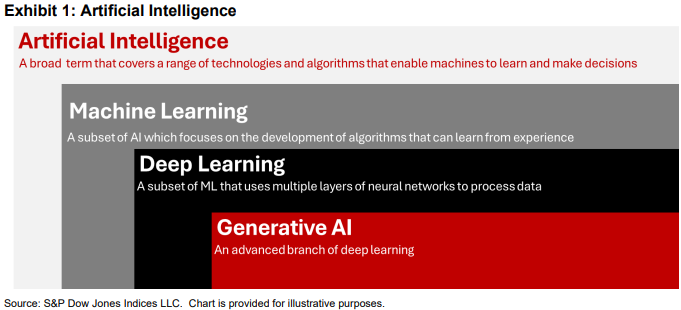
While definitions may vary, AI generally refers to the ability of machines to exhibit human-like intelligence and a degree of autonomous learning. It is an umbrella term that encompasses a wide variety of technologies, including machine learning, deep learning and generative AI.
Machine Learning
Machine learning, a subfield of AI, employs algorithms trained on diverse inputs such as historical data, synthesized data or human input. These algorithms identify patterns and learn to make predictions and recommendations by processing data rather than relying on explicit programming instructions Machine learning can be found in various domains. Common examples of machine learning include personalized product recommendations based on past purchases, voice memo translation to text and fraud detection in banking systems.
Deep Learning
Deep learning is a type of machine learning that uses neural networks to ingest and process data through multiple layers. These networks recognize progressively intricate features, simulating the complex decision-making power of the human brain. Deep learning drives many AI applications that improve the way systems and tools deliver services, such as self-driving cars and facial recognition.
Generative AI
Generative AI refers to AI systems that can create original content, such as text, images, videos or other data, in response to a user’s prompt or request. These systems often utilize large neural networks, such as large language models (LLMs), to learn patterns and generate content that closely aligns with the data they were trained on. Generative AI tools like ChatGPT and DALL-E3 are gaining global popularity, and their impact extends to potentially reshaping how various tasks are performed.