Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Research — 20 Mar, 2024
By Nick Patience, Melissa Incera, and Alexander Johnston
The start of the year has seen a robust pipeline for releases from the largest generative AI technology providers, with Google particularly prolific over the past few weeks. It has also brought us a bundle of funding announcements, with a set of early-stage funding rounds setting the scene for a new set of generative AI giants. Other updates explored in this month's report include further progress with the EU AI Act, Jasper AI's acquisition of Clipdrop, Microsoft Corp. partnering with Mistral AI and an accord on AI election interference.

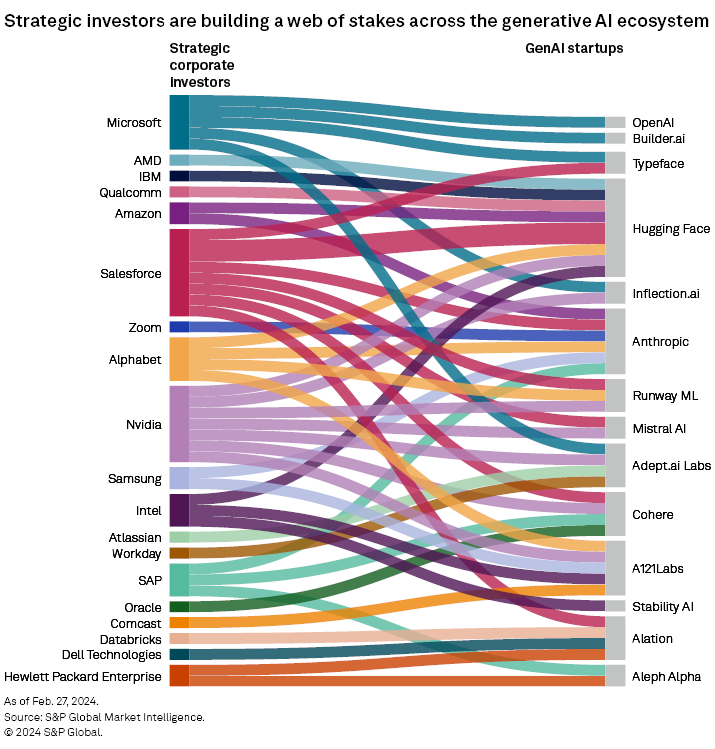
The popularity of ChatGPT spawned an ecosystem of startups, initially in text generation. This was followed by a wave of image-generation specialists building out from the open-source Stable Diffusion model. Early-stage funding is starting to separate the wheat from the chaff, and it is tempting to use these funding announcements to forecast a new set of market leaders. While a valuable indicator, many of these startups are highly reliant on established technology companies, which often emerge as their strategic investors, rather than a disruptive market presence. In addition, many of the startups we engage with are keenly aware that there is a risk in taking on too much funding too early. Several have suggested that some highly capitalized generative AI startups are already straining under inflated targets and unsustainable business models.

Product releases and updates
Google grabbed many of the generative AI headlines over the past few weeks, with a rebranding and product updates. Chat tool Bard is now known as Gemini, reflecting its model upgrade — the tool is now able to generate images. A Gemini app has been released for mobile devices, and an upgraded version of Gemini — Gemini Advanced, which leverages the company's Ultra 1.0 model — is now available. The company also released a new generation of open text-to-text models, Gemma, with 7 billion- and 2 billion-parameter size options.
Google also released ImageFX, an AI image creator powered by Imagen 2, a model Google released in December 2023. The capability joins music generator MusicFX and text generator TextFX as part of the company's AI test kitchen, with the image generator available for users in the US, Kenya, New Zealand and Australia. The company also announced a strategic partnership with open-source giant Hugging Face, which provides a collaboration platform for data, models and applications. The partnership appears to center on making AI research and innovations more accessible, as well as the ability to more easily train and deploy models from Hugging Face using Google Cloud services.
OpenAI LLC unveiled Sora, a video-generation model that can transform text instructions into vivid video scenes. The tool is currently in beta, being tested by a limited group of creators and red teamers — safety experts in areas such as misinformation, hateful content and bias. Sora is a diffusion model that can generate high-definition videos up to a minute long, including complex scenes with multiple characters and specific types of motion. It can also generate videos from still images and "extend" existing videos by filling in missing frames, for example. The company acknowledges Sora's current weaknesses, which include difficulty with continuity and distinguishing left from right. OpenAI is also focusing on safety measures, such as building tools to detect videos generated by Sora and rejecting prompts that request violence, sex, hateful imagery, celebrity likeness and third-party-owned IP. The company plans to engage with policymakers, educators and artists to understand their concerns and identify positive use cases for Sora.
Nokia Oyj announced MX Workmate, a large language model capability designed for edge operational technology environments. The company suggests MX Workmate will work as an assistant that can provide real-time information to the workforce, integrated with AI auditing capabilities to address operational technology standards. The company plans to make Nokia MX Workmate available by year-end 2024.
Slack AI was announced in February with initial capabilities focusing on summarization and search. Conversational enterprise search, the ability to summarize "threads," and updates to "channels" were featured for the team communication platform. A native integration with Salesforce Inc.'s Einstein Copilot is also apparently in the works. Slack AI is available as a paid add-on for Enterprise plans.
On Feb. 1, Tim Cook hinted that Apple Inc. had some notable announcements to make. He suggested that Apple had some projects that the business was "incredibly excited about, that we'll be talking about later this year," and noted that, "we have a lot of work going on internally" as part of the same response. The company contributed the code for open-source instruction-based image editing model MGIE to GitHub on Feb. 3, which could be a sign of some of this work.
Stable Diffusion 3 has been released in early preview. The text-to-image model suite, which will be available at a number of parameter sizes, ranging from 800 million to 8 billion parameters, promises better performance in depicting text within images and addressing more complex multi-subject prompts.
Paris-based Mistral has released a new series of models, including its newest flagship model, Mistral Large, which will be available via API, and Mistral Small, an intermediary option between its open-weight offering and flagship model optimized for latency and cost. Mistral seems to be taking an open-source approach to small models and an "open-ish" approach to its large ones, which it calls "open and commercial." The announcement also includes a new commercial partnership with Microsoft that reportedly includes minority investment from the hyperscaler (alongside NVIDIA Corp. and Salesforce). Mistral is the second company, apart from OpenAI, whose language models will be made available via Microsoft's cloud computing platform.
Funding and M&A
On Feb. 22, Jasper AI agreed to buy Init ML SAS from Stability AI Ltd. Jasper AI provides an AI marketing copilot, with text- and image-generation capabilities that can help with content creation. By acquiring the company, which does business as Clipdrop, from Stability AI, Jasper will enhance its image editing capabilities and its strategy for a multimodal offering. Stability AI bought Clipdrop in March 2023, after it had raised $1.5 million in seed and accelerator funding.
Chinese startup Beijing Dark Side of the Moon Technology, which does business as Moonshot AI, raised $1 billion in a new funding round led by Alibaba Group Holding Ltd. and VC HongShan. The Haidian, China-headquartered company's post-money valuation is $2.5 billion. The generative AI startup offers an intelligent assistant that is advertised to have a large memory — supporting the input of 200,000 Chinese characters.
Code generator Magic AI announced that it will be receiving $117 million in series B funding led by new investor NFDG Ventures. This takes the company's total funding since incorporation in March 2022 to $186.4 million. The company suggests it plans to use the funds to further develop its AI programmer. Investors in the company's series B include CapitalG Management Company, formerly known as Google Capital. As the chart illustrates, Alphabet Inc. has already made a number of investments in generative AI startups.
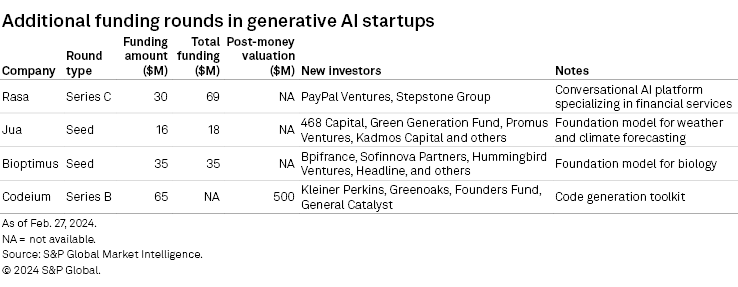
Generative assistant Mindy, positioned as an email-first chief of staff, raised $6 million in a seed round led by new investors Roelof Botha of Sequoia Capital Operations and The Founders Fund.
Bria Artificial Intelligence announced $24 million in series A funding in a round jointly led by GFT Ventures, Intel Capital and Entree Capital. Additional investors include Publicis Groupe SA, Getty Images Holdings Inc., Samsung Next, IN Venture (Sumitomo Corp., Japan), Atinum Investment Co. Ltd. (South Korea) and Z Venture Capital (LY Corp., Japan). The image generator had previously received $2.5 million in seed funding in 2020.
Langchain announced a $25 million series A round led by Sequoia Capital, bringing the total raised to $36 million following an $11 million seed round in March 2023 led by Benchmark Capital. The series A round also saw contributions from Amplify Partners, Conviction and Lux Capital. Additionally, the San Francisco-based company announced general availability of Langsmith, its tool for developing, monitoring and testing LLM-based applications.
Together AI officially joins the growing pack of GenAI unicorns, announcing another $100 million in venture funding from new investors Coatue Management and Salesforce Ventures, just three months after raising its $102 million series A in November 2023. This brings its total funding to $222 million. Together AI operates a decentralized cloud platform through which companies can train, fine-tune and run open-source generative AI models.
Conversational intelligence startup Kore.ai has raised another $150 million in series D funding led by NVIDIA, FTV Capital, Vistara Growth, Sweetwater PE and others. The company, which last raised in 2021, will slate this injection toward product development and go-to-market support to capitalize on market enthusiasm for AI-powered assistants. The round brings its total funding to $226 million. Its valuation was undisclosed.
Politics and regulations
The EU AI Act received the endorsement of the 27 country ambassadors to the EU. This marks the next step in its progress, following political agreement by the European Parliament in December 2023 and adoption by the Committee of Permanent Representatives in early February. The next stage will be a European Parliament plenary vote scheduled for April 10-11, after which the act will be endorsed at the ministerial level. However, the provisions that ban certain practices won't come into effect for a further six months, and the obligations on AI models, such as transparency of training data sets and energy consumption, won't come into effect for another six months after that (i.e., around the second quarter of 2025).
An accord was struck at the Munich Security Conference by major technology companies seeking to address the risk of AI-generated content interfering with elections. The 20 signatories at the event included cloud providers Microsoft, Google, Amazon.com Inc.'s AWS and International Business Machines Corp., as well as generative AI specialists Anthropic, OpenAI, ElevenLabs, Stability AI, Inflection AI and Nota. Other signatories included social media companies TikTok, Meta Platforms Inc., Snap Inc., X and LinkedIn. Adobe Inc., Arm Holdings PLC, McAfee, Trend Micro Inc. and Truepic were the other signatories.
The UK House of Lords Communications and Digital Committee published its report on large language models and generative AI, and made recommendations in three main areas. It says the UK government should rebalance from its current "narrow focus on high-stakes AI safety" toward a "greater focus on supporting commercial opportunities and academic excellence." Second, the government should "guard against regulatory capture" (i.e., the race between closed and open model developers in seeking regulations that benefit them over the alternative). Third, the government (which faces a general election this year) should bolster copyright, changing the law if needed, while empowering rights holders to determine if their data has been used without permission. The UK government should also "invest in large, high-quality training datasets to encourage tech firms to use licensed material."
The US Patent and Trademark Office rejected OpenAI's request to trademark "GPT" on the grounds that it is "merely descriptive," citing evidence from numerous other sources on the web where the term had been used. It added that the evidence "establishes that 'GPT' is a widely used acronym which means 'generative pre-trained transformers,' which are neural network models that 'give applications the ability to create human-like text and content (images, music and more), and answer questions in a conversational manner.'" OpenAI applied for the trademark in 2023, and it was initially rejected on the same grounds. The ruling in early February was final — even though it can be appealed within a three-month window.
The US AI Safety Institute Consortium was announced on Feb. 8 as part of the US AI Safety Institute being established at the National Institute for Standards and Technology. The inaugural cohort of 200 members includes technology companies, education institutions and nonprofits. The AI Safety Institute has a mandate to develop AI guidelines and evaluation approaches.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
451 Research is a technology research group within S&P Global Market Intelligence. For more about 451 Research, please contact .