Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Case Study — 6 Mar, 2024
Highlights
Climate risks cannot be ignored given their potential impact on supply chains. More firms are assessing potential supplier vulnerabilities and accessing associated data via the cloud.
Recent and intensifying natural disasters underscore the reality of climate change. Dozens of billion-dollar weather events occurred in 2022, including three mega-disasters costing at least $20 billion and a heat wave that killed over 40,000 people in Europe.
Climate risks have severe consequences for supply chains. They can affect raw material yield, damage power plants and warehouses, impact storage and disrupt trade routes resulting in increased shipment delays. Companies are projected to face up to US$120 billion in costs from these climate-related supply chain risks within the next five years.[1]
Sustainability teams at U.S.-based apparel retailers are tasked with assessing the potential risks to company suppliers from a wide range of climate events, including hurricanes, droughts and wildfires. A significant portion of raw and finished fabric used in a company's manufacturing processes comes from offshore providers. As a result, sustainability teams need access to a range of capabilities to better understand their supply chain networks and climate-related vulnerabilities.[2]

Pain Points
Members of sustainability teams often lack the data and analytical tools needed to fully understand their company's supply chain risks from climate-related events. They need information providers that can help them:
Many of these teams are familiar with work that S&P Global Market Intelligence (“Market Intelligence”) does in this area, specifically related to climate solutions.
The Solution
Specialists from Market Intelligence illustrated how they could assist by pulling information from their datasets for a similar-sized firm in the same apparel industry. As shown in the example below, Gap, Inc. ("Gap") was chosen to show how these data services can help uncover climate-related supply chain risks. Looking at Gap's revenue by region revealed that 85% was U.S.-based for the period chosen (Table 1).
Table 1: Revenue by Region
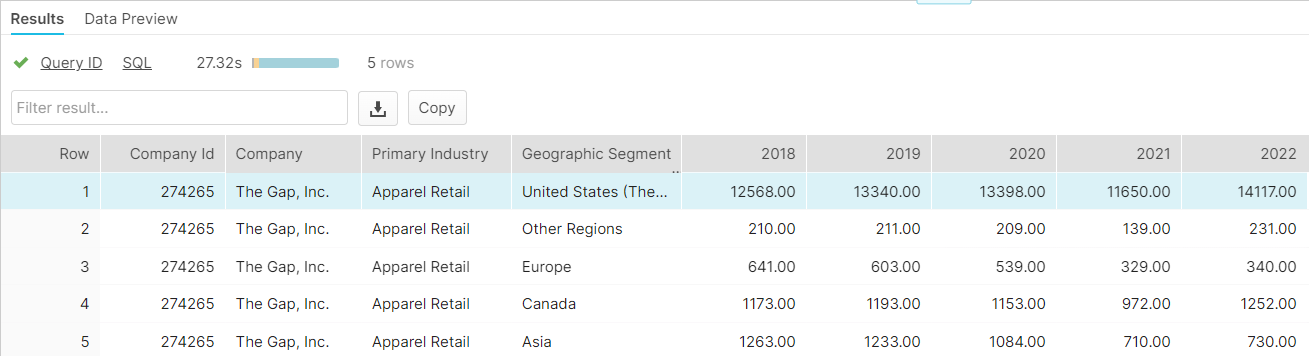
Source: Market Intelligence July 19, 2023. For Illustrative purposes only.
Next, data was pulled from the Business Relationships dataset on the suppliers that Gap was using for textile products (Table 2), a critical input in the manufacturing process, pointing out that 50% were based in India.
Table 2: Textile Suppliers
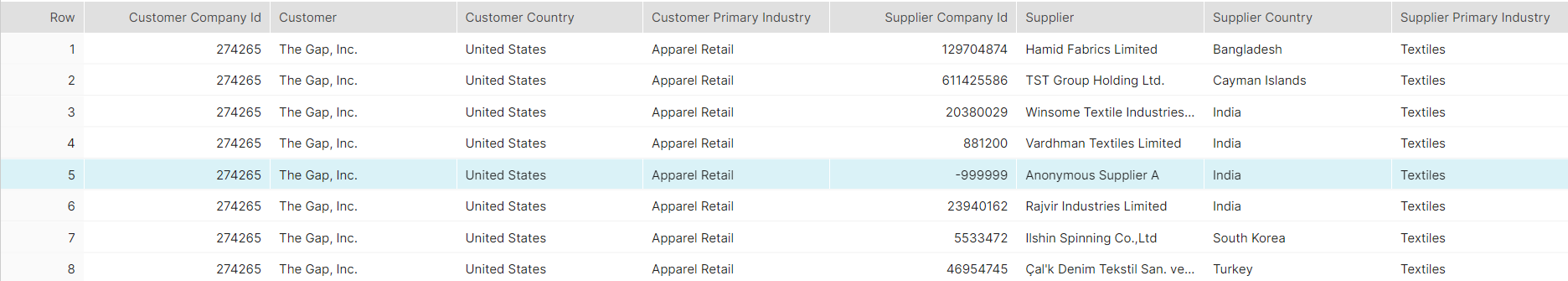
Source: Market Intelligence July 19, 2023. For Illustrative purposes only.
Next, an analysis of export data (Table 3) to the Gap from India-based 'Anonymous Supplier A' was complied, revealing that:
Table 3: Export Data
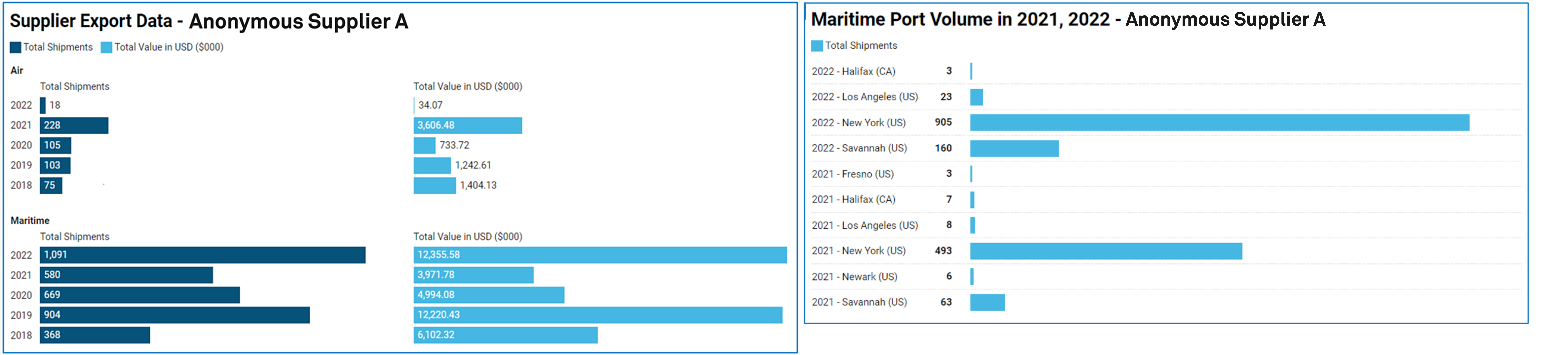
Source: Market Intelligence, as of August 31, 2023. For Illustrative purposes only.
Finally, an analysis of climate risk (Table 4) was conducted that showed that 'Anonymous Supplier A' is at a significantly high risk for water stress, with water being crucial for fabric dyeing. In addition, the risk for extreme heat is expected to be two times higher by 2040 and fluvial flood risk almost two times higher by 2090.
Table 4: Physical Climate Risks by Company
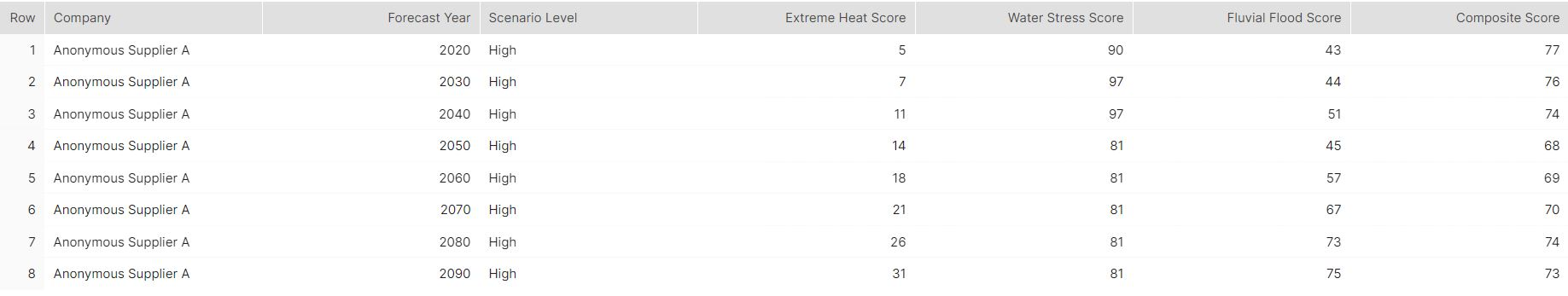
Source: Market Intelligence, as of August 31, 2023. For Illustrative purposes only.
The analysis is based on the following S&P Global datasets that enable sustainability teams to:
 |
Gain deep supply chain intelligence | Panjiva is a supply chain intelligence platform that brings transparency to trade through global coverage, powerful machine-learning technologies and dynamic data visualizations. It provides comprehensive international trade and commercial freight traffic data with annual forecasts up to 2040 and quarterly forecasts for eight quarters ahead, including data broken down by transportation modes and cargo types. 1,000+ daily insights are provided on pricing and risk across 200+ countries and territories. |
 |
Understand climate-related physical risks | The Physical Risk dataset provides asset and company-level physical risk exposure scores and financial impact metrics to help organizations assess the impact of climate change on their portfolios, operational assets and supply chains. The dataset covers eight climate hazards, four scenarios and eight time periods for 20,000+ companies and 870,000+ asset locations. The dataset includes:
|
 |
Access data through an efficient cloud-based offering | Snowflake enables users to directly access and query S&P Global and select third-party data, eliminating the data ingestion process and significantly improving productivity and efficiency. Snowflake's unique cloud-based architecture supports scalability for faster queries at lower costs. Accessing data from S&P Global via Snowflake provides live, ready-to-query datasets that are always up-to-date and do not require transformation before use. Snowflake lets users combine external and internal data for faster and better business decisions. |
Key Benefits
Sustainability teams can utilize these broad and deep datasets and analytical capabilities to take a deep look at their company's supply chain and potential areas of weakness and risk. Access to these services enables:
Click here to explore S&P Global datasets available via Cloud.
[1] Environmental supply chain risks to cost companies $120 billion by 2026", CDP, February 2021, www.cdp.net/en/articles/supply-chain/environmental-supply-chain-risks-to-cost-companies-120-billion-by-2026.
[2] This is a hypothetical example for illustrative purposes only.