The iBoxx ChinaBond Asian High Yield is designed to reflect the performance of high yield bonds from Asian issuers, denominated in USD, CNY and SGD. This index is a joint initiative between S&P Dow Jones Indices (S&P DJI) and ChinaBond Pricing Center Co., Ltd. (CBPC). The index seeks to combine the bond valuation data and domestic market expertise of CBPC with S&P DJI’s award-winning global fixed income index expertise that provides investors with accurate and objective indices to assess the performance of the respective underlying markets and investments.
1. Why was the iBoxx ChinaBond Asian High Yield launched?
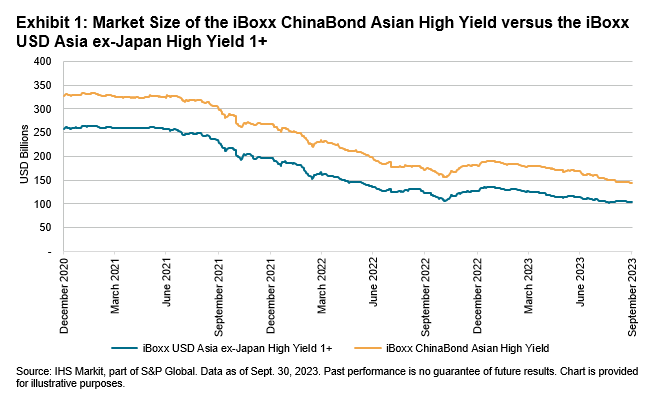
S&P DJI: Historically, the Asian high yield market has been mostly dedicated to the U.S. dollar (USD) space, where Real Estate bonds from Chinese issuers made up close to half of the market prior to the beginning of China’s Real Estate shift in 2021. Since then, the aggregate market size of Asian USD high yield bonds has declined significantly, as represented by iBoxx USD Asia ex-Japan High Yield 1+ (see Exhibit 1). The declining market size presents challenges for Asian high yield fund managers, including the ability to continue to allocate and find liquidity in the remaining Asian high yield bonds in the index.
At the same time, Asian local currencies have continued to gather interest from investors as a diversifier from traditional hard currency exposures. Asian local currency bond markets, as a whole, have also grown in size and depth over the past few years. These factors drove us to evaluate the accessible local currency bond markets with significant high yield exposure, and as a result, we partnered with CBPC to develop the iBoxx ChinaBond Asian High Yield, which tracks Asian-issued USD, CNY and SGD bonds. As seen in Exhibit 1, with the inclusion of Asian local currency bonds, the iBoxx ChinaBond Asian High Yield consistently provided a larger market size (capacity) compared to the iBoxx USD Asia ex-Japan 1+ from Dec. 31, 2020, to Sept. 30, 2023.
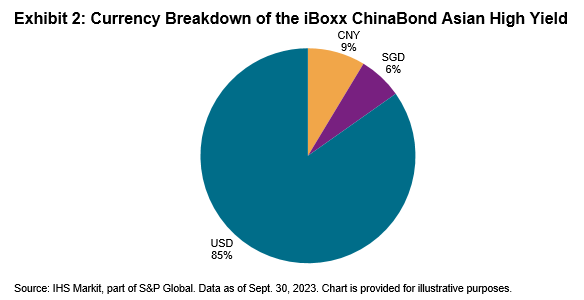
The goal of this index is to provide a measure for investable high yield bonds in the Asian market beyond USD-denominated bonds, as well as to give a broader perspective of the Asian high yield space as local bond markets continue to develop in the years to come. Exhibit 2 shows the breakdown of bonds in the index by currency, as of Sept. 30, 2023.
2. What are some of the considerations in the methodology of the iBoxx ChinaBond Asian High Yield?
S&P DJI: When we designed the index, the intention was to produce a view of the Asian high yield market that investors were familiar with (i.e., USD bonds), yet, at the same time, expand that view to introduce elements of local currency exposure to broaden the index universe.
As a result, from an index methodology perspective, we have implemented an overall issuer cap of 2%. Additionally, non-USD issuers are subject to a cap of 0.5% of the overall index. This approach seeks to address three concerns. First, it aims to minimize accessibility issues to local currency bonds for investors who might be concerned about liquidity. Second, for index funds, this rule allows investors to gradually become accustomed to local currency bond markets without a need to purchase large amounts of local currency bond exposure instantaneously. Third, this serves to provide greater diversification across issuers in the index.
Determining which local markets would be eligible for inclusion into the index was another consideration. From that perspective, we looked at the general liquidity, accessibility and size of the local markets, especially those with larger high yield issuances. As a result, we have had CNY and SGD local markets represented in the index from the onset. In the long term, the aim is to periodically review the eligibility of other Asian local currency markets as regional bond markets continue to grow.