EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
This paper provides transparency around the S&P PACT Indices (S&P Paris-Aligned & Climate Transition Indices), a sophisticated index solution to align with a 1.5°C trajectory (EU PAB and CTB Aligned). The indices mitigate a multifaceted range of potential financial risks, while providing exposure to opportunities companies may face from climate change, as laid out by the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). This paper examines four core universes, including the S&P 500®, S&P Eurozone LargeMidCap, S&P Developed LargeMidCap and S&P Japan LargeMidCap.
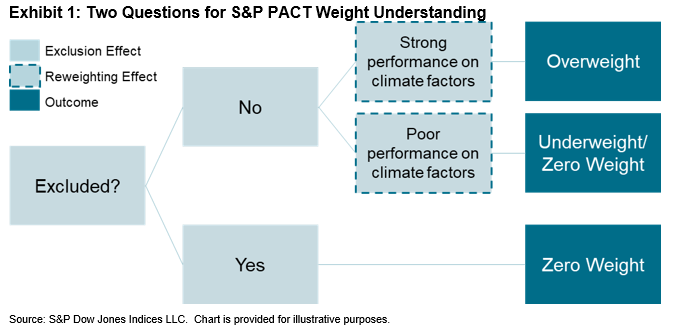
- The S&P PACT Index weights, relative to the benchmark index, are attributable to an exclusion effect (whether a stock is eligible for the index) or reweighting effect (how a stock performs from a climate perspective), as seen in Exhibit 1.
- The exclusion effect accounts for around 20% of active weights for the S&P Climate Transition (CT) Indices across most universes, while for the more ambitious S&P Paris-Aligned Climate (PA) Indices, exclusions account for 35%-65% of deviations from benchmark weights. The reweighting effect explains the remaining active share.
- The reweighting effect is driven by climate and index construction factors, which are affected by the strength of constraint, climate datasets distributions and climate factor correlations.
- A company’s transition pathway, sustainability performance score (as measured by the S&P DJI ESG Score), physical risk exposure, carbon intensity and high climate impact revenues are all key drivers of weighting S&P PACT Index constituents.
- Climate considerations can be appraised through different lenses, and so we use a range of different datapoints within S&P PACT Indices to capture climate in a holistic way. The high quality climate factors show low correlations between each other, hence explicitly controlling for each of them within the PACT Indices ensures a holistic approach to climate risks and opportunities.
- Eligible companies can be allocated a higher weight in the S&P PACT Indices by significantly reducing their carbon intensity year-on-year, disclosing more information regarding sustainability policies and metrics, improving performance against sustainability metrics, divesting assets in locations highly exposed to physical risks, and reducing assets’ physical risk sensitivity factors.