Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Research — 10 Nov, 2022
451 Research is part of S&P Global Market Intelligence. For more about 451 Research, please contact 451ClientServices@spglobal.com.
Introduction
The term ESG emerged in the 2000s as investors examined the role of environmental, social and governance value drivers in asset management and financial research. The ESG phenomenon has since morphed into one of the most significant agendas across all sectors of the economy, with implications well beyond asset value and financial impact. Major commitments are being made in company boardrooms, but the ESG mandate is challenging to embrace, both from reporting/technical and commercial/strategic perspectives.
While the concept of holistic ESG data capture and reporting has been thrust to the forefront relatively recently, initiatives focusing on corporate social responsibility and sustainability have been widely pursued for decades, albeit with varying levels of enthusiasm. As companies grapple with the process of capturing and exposing data to showcase their broader ESG commitments and progress, investors, consumers, technology buyers, end users and suppliers are making a case for visibility across industries by increasingly making ESG variables components in their decision-making, conferring a competitive advantage to companies with more attractive ESG and sustainability metrics.

Organizations are increasingly focusing on the impact they have on the environment and how the environment is affecting their business activities. S&P Global ESG Scores assess sustainability based on the risks and opportunities represented by key environmental, social and governance/economy public disclosures. 451 Research's Market Monitor employed S&P Global Sustainable1 ESG metrics to score IT infrastructure providers. Resulting data indicates that cloud infrastructure vendors are producing higher environmental scores compared with their hosting and colocation peers as cloud servers are much more efficient, in general, and are much more highly utilized than enterprise servers. For most organizations, running IT infrastructure is not a core business competency, and cloud service providers can be instrumental in helping them increase energy efficiency and reduce waste. As more jurisdictions require organizations to publish reports on ESG factors, S&P Global ESG Scores can shed light on an organization's impact on the environment when assessing ESG performance.

Importance of ESG initiatives
Organizations around the world are increasingly focusing on how their business activities affect the environment and vice versa. Confirmation of the commercial importance of ESG variables can be found in our Voice of the Enterprise: Digital Pulse, Environmental Impact 2022 study, in which 76% of respondents indicate that the environmental impact of potential technology purchases is very important or somewhat important to their organization's decisions. This sentiment is most pronounced for businesses in the financial and software IT services verticals, as well as among digital transformation leaders.
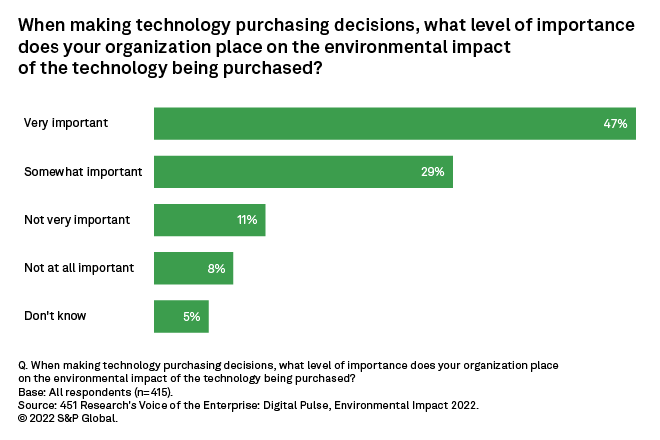
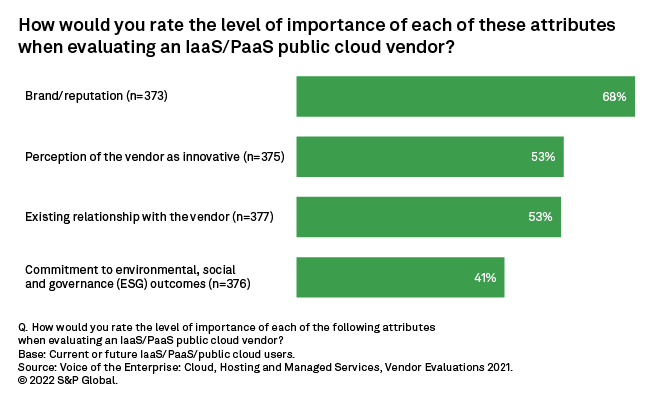
Additional survey data points to the importance of ESG initiatives in evaluating infrastructure/platform-as-a-service public cloud providers. In our Voice of the Enterprise: Cloud, Hosting & Managed Services study, over 40% of public cloud IaaS/PaaS buyers indicated that ESG outcomes represented a "very important" variable in selecting a cloud service provider.
Cloud infrastructure ESG performance to date
Cloud infrastructure providers, especially hyperscalers, have been active in developing plans and initiatives focusing on the environmental impact of their service offerings, primarily through datacenter efficiency efforts (to reduce greenhouse gas emissions), power consumption and increased renewable energy use. Examples of specific efficiency initiatives include the aggregation of workloads to increase server utilization and drive economies of scale, the incorporation of newer efficient servers, and the utilization of recycled or reclaimed water to cool cloud datacenters.
Leveraging S&P Global Sustainable1 ESG metrics, we are able to showcase the impact of these initiatives on the aggregate scores for public companies across the sector. Sustainable1 represents a centralized group within S&P Global's integrated sustainability offerings that provides comprehensive views and metrics on sustainability, including key ESG and climate topics. Sustainable1 brings together S&P Global's resources and full product suite of benchmarking, analytics, evaluations and indices that provide customers with a 360-degree view of ESG metrics across industries. ESG Scores are measured on a scale of 0-100, where 100 represents the maximum score.
Of the 306 cloud infrastructure providers we track in 451 Research's Market Monitor service, 98 have ESG variables in the S&P Global Sustainable1 database. The average 2021 ESG score of the 98 cloud infrastructure providers by dimension paints a picture of progress across the industry, with significantly higher scores for environmental metrics compared with governance and economic and social variables. Given the focus on environmental factors, the overperformance of the "E" relative to the "SG" components is not a surprise but indicates weak spots in the aggregate ESG initiatives across the sector.
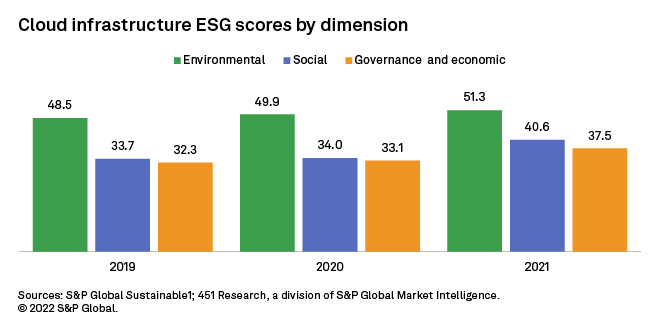
Cloud infrastructure ESG Scores by dimension
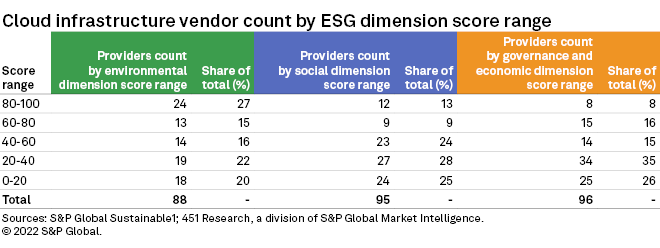
Examining the vendor count by ESG Score range in total and for each dimension, the dispersion of scores for environmental metrics compared with governance and economic and social variables is more evident. This also highlights the impact of public commitments and investments in environmental initiatives, such as datacenter efficiency and sustainable energy, and the need for more progress on governance and economic and social variables across the industry. Forty-two percent of the vendors within the cloud infrastructure market have a score of 60 and above for environmental dimensions of ESG, with another 42% of vendors having a score of 40 or below. Turning to social variables — e.g., labor practice indicators, talent attraction and retention, social reporting — only 22% of vendors have a score of 60 and over, with 54% posting a score of 40 or lower. Homing in on governance and economic variables — including corporate governance, privacy protection, and risk and crisis management — 61% have scores of 40 and below, and just 24% score at 60 or above.
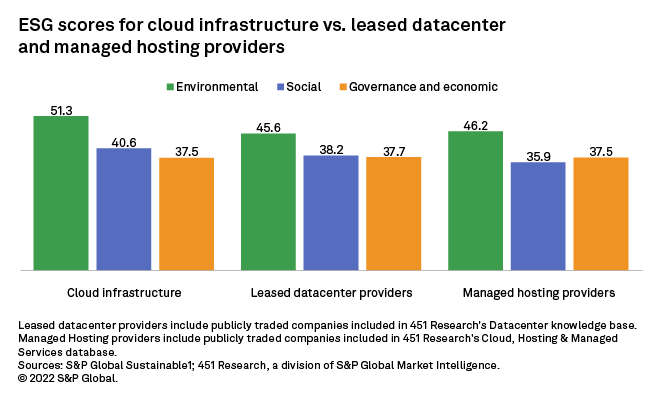
Cloud infrastructure providers vs. leased datacenter, managed hosting providers
Cloud infrastructure vendors are producing higher environmental scores compared with their peers in the leased datacenter and managed hosting businesses. According to 451 Research's datacenter team, cloud servers are much more efficient, in general, and are much more highly utilized than enterprise servers. This means that by moving workloads to the cloud, enterprises can dramatically reduce their energy use by up to 60%. When it comes to governance and economic dimensions, the sectors are close to parity with cloud infrastructure, and cloud infrastructure vendors have moderately higher scores than leased datacenter and managed hosting providers on social dimensions.
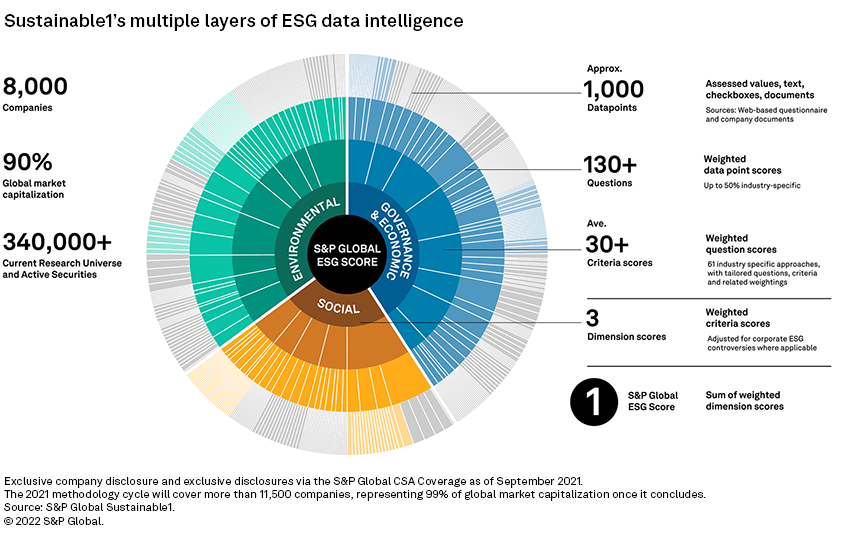
Sustainable1 methodology
S&P Global ESG scores provide multilayered ESG insight based on data intelligence captured by the S&P Global Corporate Sustainability Assessment, or CSA. Sustainable1 provides transparency to drill down into material ESG criteria scores for up to 30 focus areas across sub-industries, question-level scores covering 130 sustainability topics and up to 1,000 additional underlying data points per company. A more detailed discussion of S&P Global's ESG evaluation process is available.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.