Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Case Study — 2 Sep, 2022
By Yashi Yadav
This article is written and published by S&P Global Market Intelligence; a division independent from S&P Global Ratings. S&P Global Ratings does not contribute to or participate in the creation of credit scores generated by S&P Global Market Intelligence. Lowercase nomenclature is used to differentiate S&P Global Market Intelligence PD credit model scores from the credit ratings issued by S&P Global Ratings.
Avianca Holdings S.A.is a Colombia-based airline, founded in 1919, with years of success in the industry, defaulted in the spring of 2020. The company provided passenger and cargo transportation internationally with support from its subsidiaries. Throughout the firm’s history, they have had 231 public and private investors on the equity side along with numerous others on their debt side. For now, let’s focus on the debt side of their business.
The Evolution of Credit Risk
In Figure 1 below you can see that S&P Global Ratings issued its first credit rating for Avianca Airlines in April 2013, ‘B+’[1], which the company maintained for approximately three years until it was downgraded to ‘B’ early in 2016.[2] There was strong consistency in the rating, maintaining the expectation that a rating should be a resilient risk indicator.
Figure 1: S&P Global Ratings Issuer Credit Rating Transition
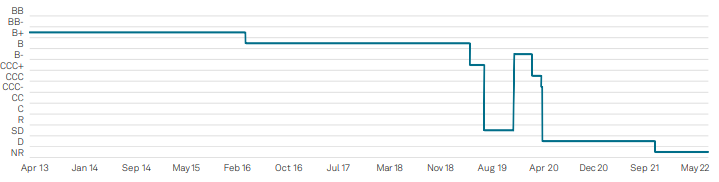
Source: RatingsDirect®, S&P Global Market Intelligence. Data as of August 15, 2022, for illustrative purposes only.
In July 2019 Avianca Holdings went into Selective Default (SD) due to missed payments which began the period of instability and credit uncertainty for the firm – see Figure 1 above.[3] After some lease renegotiations and successful completion of their debt restructuring plan at the end of 2019, the company was upgraded to a ‘B-‘ in December 2019, with expectations of stable financial and operational recovery.[4]
However, five months later the Coronavirus pandemic shook the global economy, striking particularly hard in the airline industry. This coincided with an already prominent liquidity crunch making the company’s debt coverage capacity very low.
Tracking the Early-Warning Signals of Credit Risk
There are a variety of ways you can measure credit risk, some are shorter-term indicators and others tend to look at longer durations of risk, such as credit ratings.
While credit ratings provide a long-term view of risk, Credit Analytics provides a suite of quantitative models that can give you access to different duration perspectives on credit risk. S&P Global Market Intelligence’s Probability of Default (PD) Model Market Signal uses equity market values and asset volatility to generate a PD score, updating daily to give users an early warning indicator on the credit performance of an entity. Comparatively, the PD Model Fundamentals looks at key business and financial risk factors, calibrating and running the analysis over 39+ years of default history to generate a one-year implied PD credit score.[5]
To compare the credit rating trajectory to the credit scores generated by Credit Analytics, we took a look at the different performance histories.
In Figures 2 and 3 below you can see how the Credit Analytics models pinpointed the red flags of credit quality deterioration prior to an official ratings downgrade. The PD Model Fundamentals, as shown in Figure 3 below, did not show strong signs of credit recovery, the Q4 2019 credit score went up to a ‘ccc’, and in Q12020 shows as ‘ccc-‘, right before the rating agency officially moved them into Default on May 11th . The PD Model Market Signal score tells a similar story, gaining some recovery in alignment with share pricing, however a very quick deterioration from ‘b+’ to ‘cc’ , the volatility itself being a clear indicator of credit pressures.
Figure 2: PD Model Market Signal Score Transition
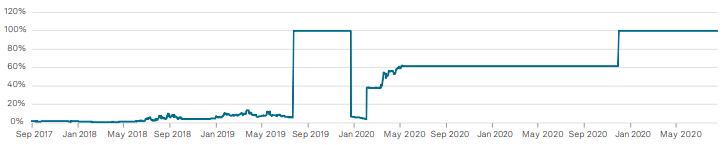
Source: S&P Capital IQ®, S&P Global Market Intelligence. Data as of August 15, 2022, for illustrative purposes only.
Figure 3: PD Model Fundamental Score Transition
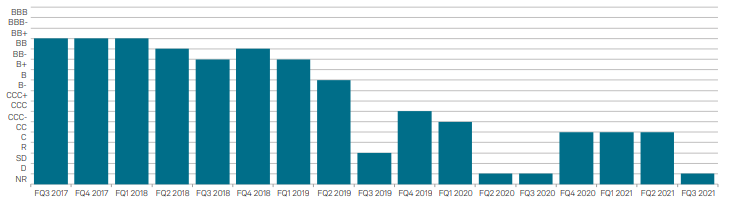
Source: S&P Capital IQ®, S&P Global Market Intelligence. Data as of August 15, 2022, for illustrative purposes only.
Being able to spot the early warning signals of credit quality deterioration before it’s too late is critical. If you would like more information on the solutions we have used to conduct this analysis, please contact us here
[1] Research Update – RatingsDirect “Avianca Holdings S.A. Rated 'B+' And Its Proposed Senior Unsecured Notes Rated 'B', Outlook Stable”, S&P Global Ratings. April 25, 2013.
[2] Research Update – RatingsDirect “Avianca Holdings S.A. Downgraded To 'B' From 'B+' On Higher Leverage And Weak Operating Performance; Outlook Stable”, S&P Global Ratings. April 13, 2016.
[3] Research Update – RatingsDirect “Avianca Rating Cut To 'SD' On Missed Principal Payments, 'CCC' Debt Ratings Still On Watch; LifeMiles Downgraded To 'B-'”, S&P Global Ratings. July 24, 2019.
[4] Research Update – RatingsDirect “Avianca Holdings Upgraded To 'B-' From 'SD' And LifeMiles To 'B+' From 'B-' On Debt Restructuring Completion”, S&P Global Ratings. December 20, 2019.
[5] S&P Global Ratings does not contribute or participate in the creation of credit scores generated by S&P Global Market Intelligence. Lowercase nomenclature is used to differentiation PD and credit model scores from the credit ratings issued by S&P Global Ratings.
Theme
Products & Offerings