Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
09 Apr, 2025
By John Wu and Marissa Ramos
China's biggest state-owned banks posted stronger fourth-quarter earnings, but their 2025 outlook is increasingly uncertain amid rising tariff risks.
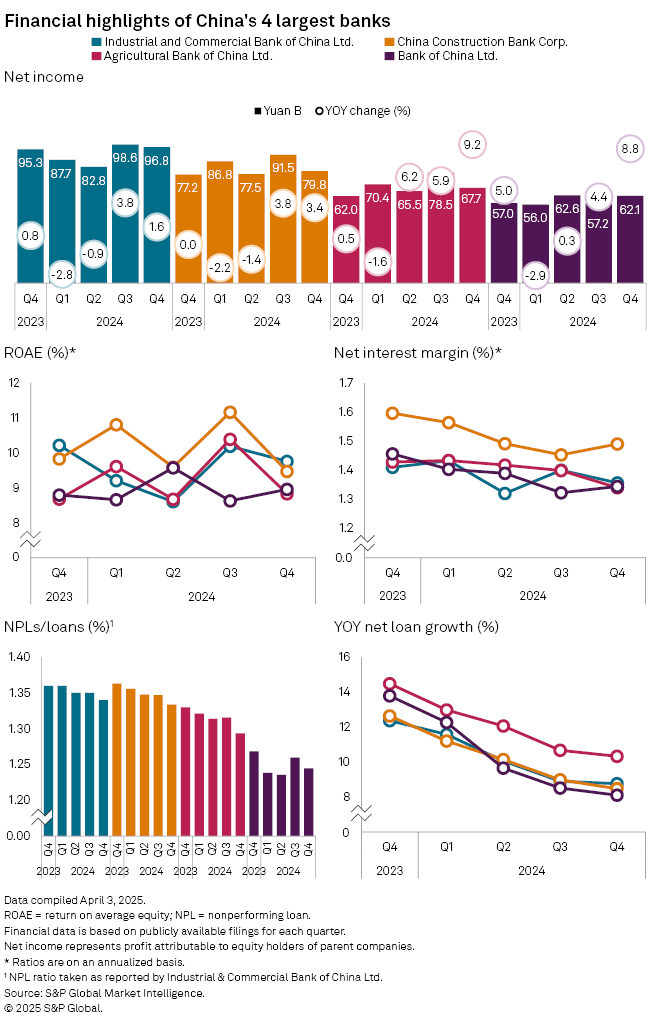
Agricultural Bank of China Ltd. posted a 9.2% year-over-year increase in net income to 67.71 billion yuan in the October-December quarter of 2024, according to S&P Global Market Intelligence data. Bank of China Ltd. reported an 8.8% gain to 62.08 billion yuan. Industrial and Commercial Bank of China Ltd., the world's largest lender by assets, recorded a 1.6% increase, while China Construction Bank Corp. rose 3.4%.
"The sequential improvement in fourth-quarter performance was due to stabilizing net interest margin (NIM), a rebound in noninterest income and lower provision expense," said Iris Tan, senior equity analyst at Morningstar, in a March 31 email. "Whether these trends will continue into 2025 is uncertain, depending on the potential recovery of consumer confidence," Tan said, adding, "near-term earnings growth may face pressure from an industrywide worsening credit cycle."
Growth drag
China has set a 2025 GDP growth target of about 5%, matching its 2024 goal. But the outlook is complicated by a prolonged real estate slump and escalating trade tensions. The latest round of tariffs, initiated by US President Donald Trump and met with countermeasures from Chinese President Xi Jinping's administration, threatens to further weigh on economic activity.
On April 9, the US increased tariffs on Chinese imports to 125%, leading China to respond with an 84% tariff on US goods.
"The drag on China's economy from higher tariffs will transmit to banks," said Ming Tan, director at S&P Global Ratings, in an April 3 note. "Strains will incrementally come from micro and small enterprises and unsecured consumer credit."
"We expect significant additional policy support … in the next couple of quarters," UBS Investment Bank said in an April 7 note. "We also see [that the] policy rate and reserve requirement ratio may be cut starting from April-May, with total policy rate cuts of at least 30 to 40 basis points," UBS said.
Falling interest rates
China's one-year loan prime rate is 3.1%, while the five-year rate, a benchmark for mortgages, is 3.6%. Both are at record lows following cuts in October 2024.
In the fourth quarter of 2024, NIMs at China Construction Bank and Bank of China rose slightly from the prior quarter, while margins declined at Agricultural Bank of China and Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, according to Market Intelligence data. Nonperforming loan ratios, a key measure of asset quality, declined at all four banks.
"We expect smaller NIM contractions of 10 to 15 basis points in 2025 due to deposit rate cuts, slowing migration to term deposits, and the People's Bank of China's measures to curb pricing competition," said Morningstar's Tan.
The average NIM for China's commercial banks fell to 1.52% at the end of 2024, down 17 basis points from a year earlier and 1 basis point from the prior quarter, according to the National Financial Regulatory Administration. The systemwide nonperforming loan ratio declined 9 basis points year over year to 1.50%.
"We expect the overall weak revenue trend to continue, and potential improvement hinges on the recovery of credit demand from both corporates and households," analysts at Ping An Securities Co. Ltd. said in an April 1 note.
Asset-side pricing is likely to remain under pressure in 2025 due to the repricing of existing mortgages and the continued decline in loan prime rates, the note said.