S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Our Services
Investment Themes
Explore new territories with greater confidence
Equity
Fixed Income
Commodities
Multi-Asset
Sustainability
Dividends & Factors
Thematics
Our Exchange Relationships
S&P DJI combines global reach with local expertise, working with exchanges around the world to build indices for both the local and international investment communities.
Education
SPIVA®
For over 20 years, our renowned SPIVA research has measured actively managed funds against their index benchmarks worldwide.
Events & Webinars
Register to attend complimentary webinars and deepen your knowledge of current trends and issues impacting the index universe today.
Governance
Methodologies
SPICE
Your Gateway to Index Data
Our Services
Professional Resources
Equity
Fixed Income
Commodities
Multi-Asset
Sustainability
Dividends & Factors
Thematics
Digital Assets
Indicators
Other Strategies
By Region
Our Exchange Relationships
S&P DJI combines global reach with local expertise, working with exchanges around the world to build indices for both the local and international investment communities.
Research & Insights
Education
Performance Reports
SPIVA®
For over 20 years, our renowned SPIVA research has measured actively managed funds against their index benchmarks worldwide.
Events & Webinars
Register to attend complimentary webinars and deepen your knowledge of current trends and issues impacting the index universe today.
Methodologies
SPICE
Your Gateway to Index Data
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Language
The S&P Carbon Efficient Indices are designed to reduce exposure to high-carbon companies in a systematic way, while maintaining a risk/return profile similar to that of their benchmarks.
The indices do this by adjusting constituents’ weights according to their relative carbon-to-revenue footprint. These carbon weight adjustments are calculated using the S&P Carbon Global Standard, a proprietary carbon classification system.
How the Proposed Consultation on GICS Structure Changes May Affect the S&P Carbon Efficient Indices

This paper aims to estimate how the proposed GICS structure changes in the consultation may potentially affect the S&P Global Ex-Japan LargeMidCap Carbon Efficient Index and the S&P/JPX Carbon Efficient Index, in terms of GICS sector and GICS industry group index weight, carbon decile weight distribution, index carbon intensity reduction, and index portfolio turnover.
Institutional investors, including Japan’s GPIF, are increasingly integrating ESG into their strategies. S&P DJI's Andrew Innes is joined by S&P Global Trucost’s Neil McIndoe to talk about how the innovative S&P Carbon Efficient Indices are being used as institutional portfolio building blocks.
Indices
Featured Indices
-
Constituent Selection
Constituent Selection
Starting with a market-cap index as the universe, companies are screened for liquidity and to remove companies certified as “High Non-Disclosing Carbon Emitters.” Remaining companies are included in the index.
-
Weighting
Weighting
Constituent companies are weighted based on an approach that accounts for whether they sufficiently disclose their carbon emissions, whether they are integrating the Taskforce on Climate Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), their carbon-to-revenue footprint ranking relative to industry peers, and whether their industry is classified as high-, low-, or mid-impact.
-
Ongoing Maintenance
Ongoing Maintenance
The indices are rebalanced annually. Companies may be removed between rebalancings based on controversies monitoring.
Carbon-to-Revenue Footprint Assessment
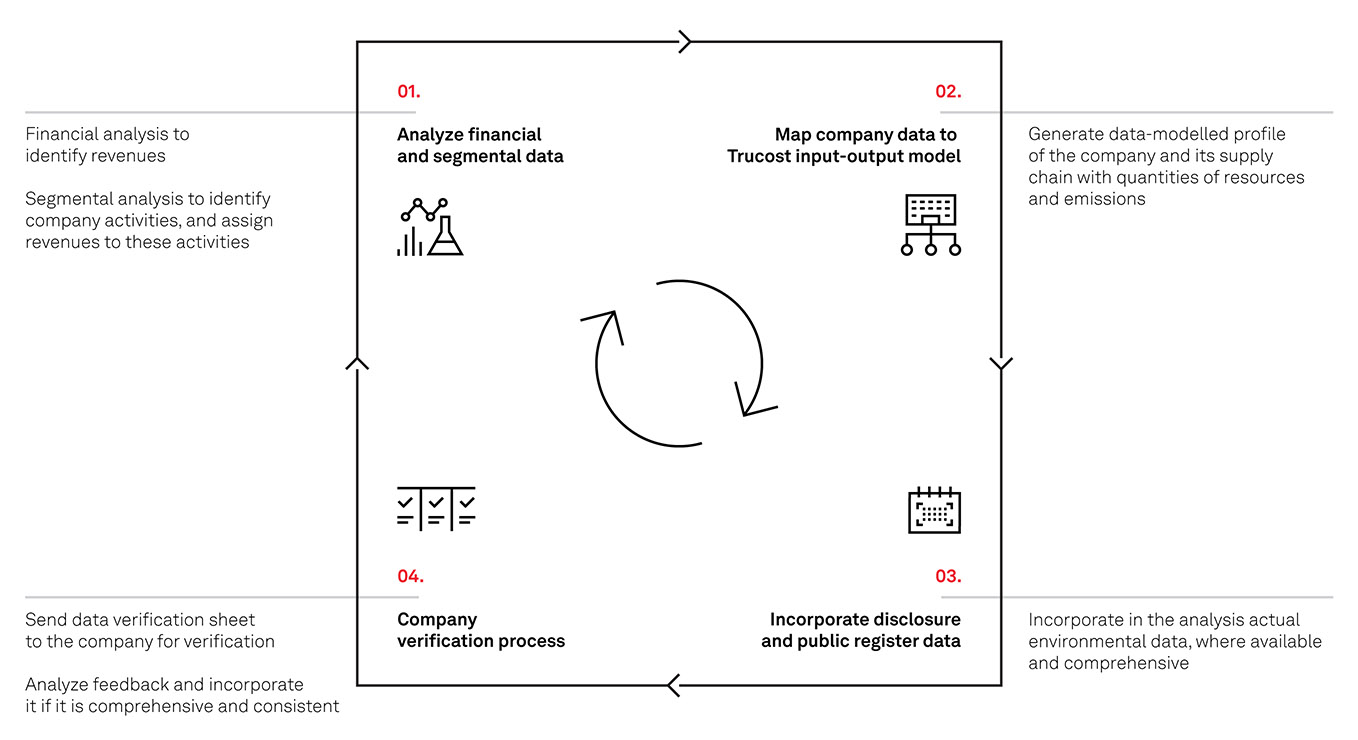
Fundamental to the construction of the S&P Carbon Efficient Indices are companies’ carbon-to revenue footprints, which are calculated by S&P Global Trucost, an ESG analytics specialist. Footprints are assessed for each company in S&P Global Trucost’s coverage universe as follows:

Companies within S&P Global Trucost’s coverage universe that do not have a recent disclosed annual carbon footprint are assigned one based on an estimate using S&P Global Trucost’s proprietary Input-Output model.
Direct and First-Tier Indirect Greenhouse Gas Emissions
To calculate the annual greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions (direct and first-tier indirect) used as inputs for each company’s carbon-to-revenue footprint assessment, S&P Global Trucost measures:
- The tons of carbon dioxide equivalents (CO2e) that a company directly emits
- The tons of carbon dioxide equivalents emitted by the first tier of its supply chain, encompassing purchased energy and emissions from direct suppliers to the company.
This gives a more complete view of the degree to which each company is carbon-exposed.
S&P Carbon Global Standard
The S&P Carbon Global Standard is a proprietary carbon classification system that uses companies’ carbon-to-revenue footprint data to create a framework for weighting constituents and calculating index values.
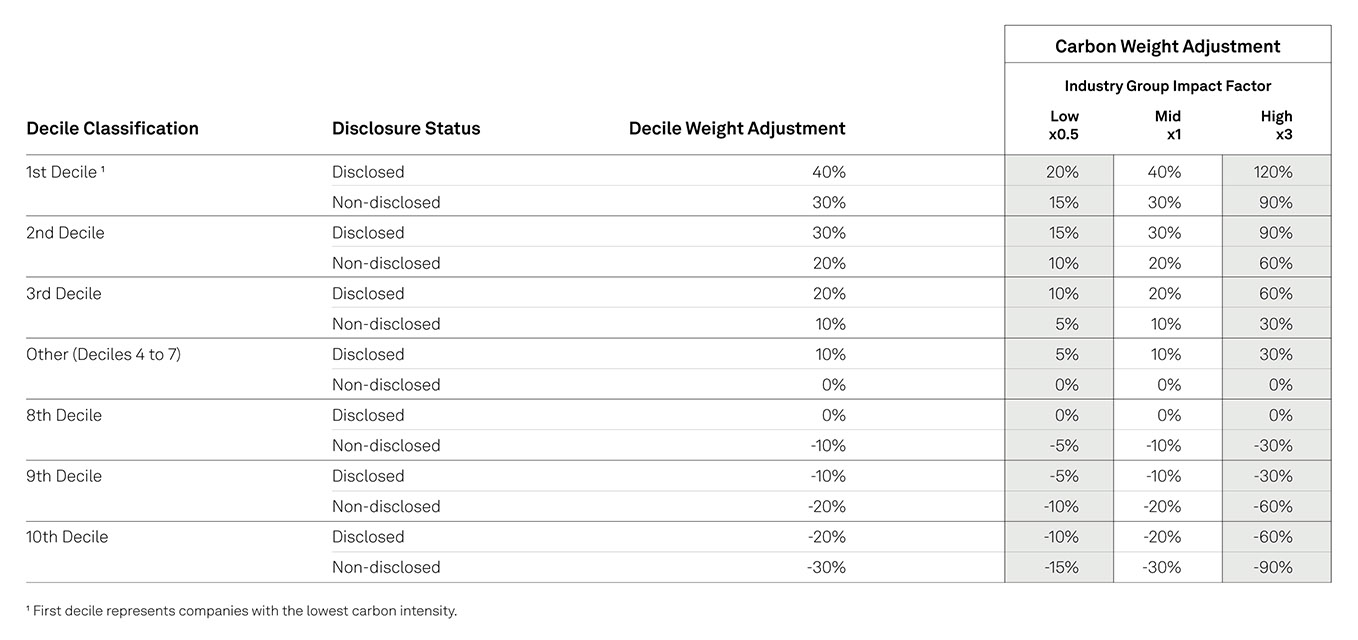
Decile Classification
Decile thresholds are determined for each GICS® industry group based on the carbon-to-revenue footprints of companies in the S&P Global LargeMidCap, a global benchmark. Using these thresholds, every company is then classified, independently of its index membership, into its S&P Carbon Global Standard decile.
Industry Group Classification
Each industry group is identified as high-, mid- or low-impact. This classification is based on the range of carbon-to-revenue footprints across the companies within that industry group in the S&P Global LargeMidCap. The range for each industry group is calculated as the spread between its first and last decile threshold.
Disclosure Status
Companies are divided into those that have been identified by Trucost as having sufficiently disclosed their carbon emissions and those that have not. Disclosure status is achieved when Trucost identifies companies as having full or partial disclosure in its largest carbon emissions category (between scope 1 and 2).
TCFD Framework Status
Companies with a Disclosure Status of “Disclosed” are additionally divided into those that have been identified by S&P Global as having integrated the Taskforce on Climate Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) framework in their public reporting. Companies identified by S&P Global as having integrated the TCFD framework receive an additional increase in their Decile Weight Adjustment.
Carbon Weight Adjustments
Each S&P Carbon Efficient Index seeks to maintain the respective industry group weights of its underlying index. It does this while adjusting constituent weights within each industry group to reduce overall exposure to carbon emissions per unit of revenue, as follows:
- A constituent’s weight within its industry group is calculated by dividing the constituent float-adjusted market cap by the industry group float-adjusted market cap.
- The weight is multiplied by 1 plus a Carbon Weight Adjustment factor that accounts for the company’s Decile Weight Adjustment, its Industry Group Impact Factor, and its Disclosure Status. This has the effect of a) overweighting companies that have lower carbon-to-revenue footprints and sufficiently disclose their carbon footprints, and b) underweighting companies that have higher carbon-to-revenue footprints and do not sufficiently disclose their carbon footprints—while also accounting for the impact of the company’s industry on overall carbon emissions.
- The weight is multiplied by a factor to account for the weight of the company’s industry in the underlying index to determine the company’s weight in the index. This step helps to ensure that the Carbon Efficient index maintains an industry group makeup similar to that of its underlying index.
- Within each industry group, constituent weights are adjusted so they sum to 100% by proportionately reducing or increasing the weights of stocks by decile, starting with the bottom or top deciles.
Controversies Monitoring
Index constituent companies are monitored by RepRisk, a leading provider of business intelligence on environmental, social, and governance risks. RepRisk analyzes companies for a range of issues including economic crime and corruption, fraud, illegal commercial practices, human rights issues, labor disputes, workplace safety, catastrophic accidents, and environmental disasters.* Using this data, each company is assigned a daily RepRisk Index (RRI) indicator.
If RepRisk reports that a company has met or exceeded an RRI indicator of 75, the company will be removed from the index. It will be considered for reinstatement only when it satisfies all the eligibility criteria and its RRI score has remained below 75 on all days since the previous year’s rebalancing date.
About S&P Global Trucost
S&P Global Trucost is a leader in carbon and environmental data and risk analysis. S&P Global Trucost assesses risks relating to climate change, natural resource constraints, and broader environmental, social, and governance factors.
S&P Global Trucost sheds light on the environmental performance of 14,000 companies, representing 99% of global market capitalization, through a four-step research process. For more details, read S&P Global Trucost’s methodology.