Introduction
Growth at a reasonable price (GARP) is a well-recognized investment strategy that combines elements of growth and value investing. While pure growth strategies often pursue high growth but expensive stocks, and pure value strategies may take years to deliver results, GARP aims to strike a balance. This approach focuses on companies that exhibit consistent earnings and sales growth, strong profitability, robust financial strength and reasonable valuations.
To address the needs of market participants, we have developed systematic versions of GARP by creating the S&P GARP Indices. In this paper, we introduce the S&P 500® GARP Index, S&P Midcap 400® GARP Index and S&P SmallCap 600® GARP Index, highlighting their construction methodology, risk/return profiles, fundamental characteristics and attribution analysis.
Constituent Selection
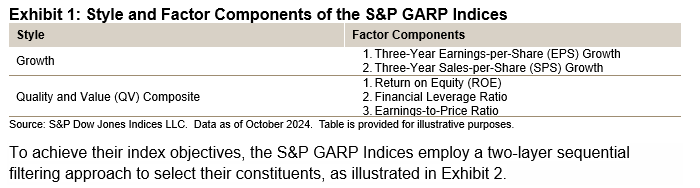
Exhibit 1 illustrates the relevant style and factor components associated with the GARP indices.
To achieve their index objectives, the S&P GARP Indices employ a two-layer sequential filtering approach to select their constituents, as illustrated in Exhibit 2.

In the first step, stocks are ranked by their growth z-scores, which are based on the average of their three-year EPS and SPS growth. The top 30% of these highest-ranked stocks remain eligible for inclusion.
In the second step, the remaining stocks are ranked by their QV composite z-scores, with the top half selected for inclusion. The QV score is calculated as the average of two quality factors (ROE and financial leverage ratio) and one value factor (earnings-to-price ratio).
Constituent Weighting
Once constituents are selected, they are weighted proportionally to their growth score, with a maximum weight of 5% for any single stock and a 40% limit on sector weight. This approach seeks to provide high growth exposure while limiting the concentration risk associated with mega-cap companies and enhancing sector diversification.