Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
16 Dec, 2024
By Yuzo Yamaguchi, John Wu, and Cheska Lozano
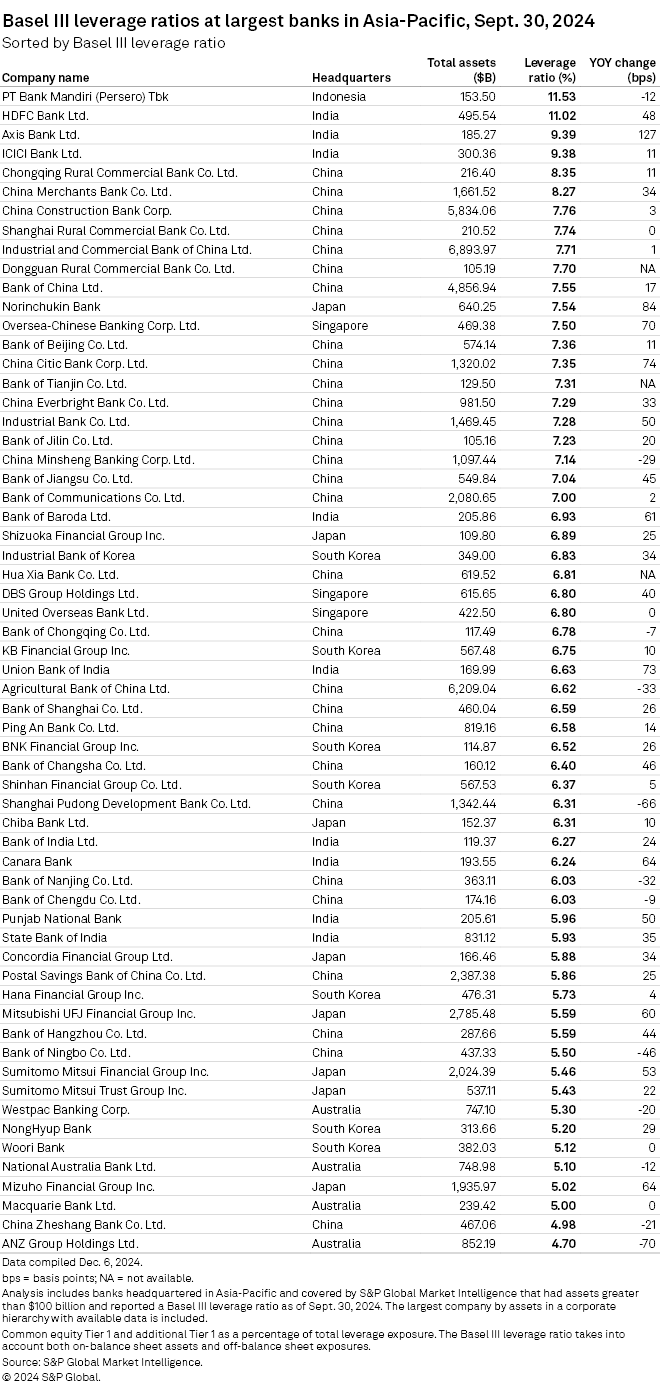
Major Indian banks are expected to sustain high leverage ratios as healthy profits and a rapidly growing economy will help them build buffers.
All nine Indian banks in S&P Global Market Intelligence's latest ranking of Asia-Pacific banks with more than $100 billion in assets by Basel III leverage ratios saw improvements in their ratios over the 12 months to September.
There is little possibility for Indian banks' leverage ratios to fall, said Makoto Saito, a senior analyst at NLI Research Institute. "The potential economic recovery is expected to increase cash demand and loans by banks, thereby supporting their profits," Saito said.
India's economic growth, which slowed to 5.4% year over year in the July–September quarter from 8.1% in the same period in 2023, is expected to recover as most economists expect the government and companies to step up spending in the coming months. The Asian Development Bank expects the economy to grow 6.5% in 2024 and accelerate to 7.0% in 2025. This outpaces the average growth of 4.7% in Southeast Asian countries during the same two-year period, according to estimates released by the Asian Development Bank on Dec. 11.
"Strong cash demand from companies is expected to increase bank loans, leading to an expansion of profits at banks," according to a report from SBI Okasan Asset Management. "A high level of capital ratios at banks would also contribute to higher profits."
The Basel III leverage ratio measures a bank's common equity Tier 1 and additional Tier 1 capital as a percentage of total leverage exposure. This measure considers both on-balance sheet assets and off-balance sheet exposures, indicating a bank's capital reserves and preparedness for financial crises.
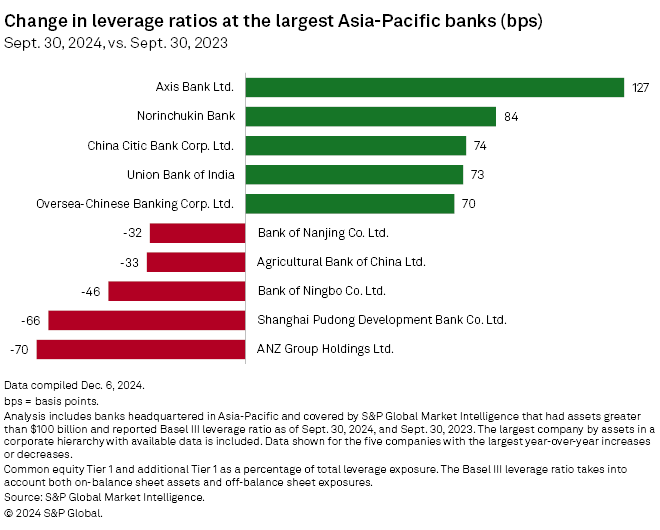
India's Axis Bank Ltd. was the biggest gainer in leverage ratio of 127 basis points to 9.39% in the 12 months through September, placing third among 60 Asia-Pacific banks in the sample. The lender posted a 19.3% year-over-year increase in net income to 74.01 billion rupees in the July–September quarter.
HDFC Bank Ltd., India's largest private-sector bank by assets, logged a 48-basis-point growth in leverage ratio to 11.02% as it reported net income of 178.26 billion rupees for the three months to September, up 6% year over year. ICICI Bank Ltd.'s ratio increased 11 basis points to 9.38%, with its net income climbing 18.8% year over year to 129.48 billion rupees.
Leverage ratios at major Chinese banks also rose, although this was more a reflection of slower asset growth amid a weaker economic outlook. Market intelligence data shows that more than half of the 28 Chinese banks improved their leverage ratios for the 12 months to September.
The ADB expects growth in the world's second-largest economy to slow to 4.5% in 2025 from 4.8% in 2024.
"The weaker GDP forecast suggests that capital spending could come under pressure, leading to tepid cash demand and lending," said Yusuke Miura, a senior economist at NLI Research Institute covering the Chinese economy.
China Citic Bank Corp. Ltd. posted the highest increase of 74 basis points to 7.35% in leverage ratio among the Chinese lenders, while seven other Chinese lenders ranked 5th to 11th in the ranking, with their ratios ranging between 7.55% and 8.35%. Among those Chinese lenders were Industrial and Commercial Bank of China Ltd., the country's biggest lender by assets, China Construction Bank Corp. and Bank of China Ltd.
Australia's ANZ Group Holdings Ltd. was at the bottom of the table with a ratio of 4.70%, down 70 basis points year over year.