Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
ECONOMICS COMMENTARY
Aug 02, 2021
South Korea Economic Rebound Threatened by New COVID Wave
GDP rebounds in first half of 2021
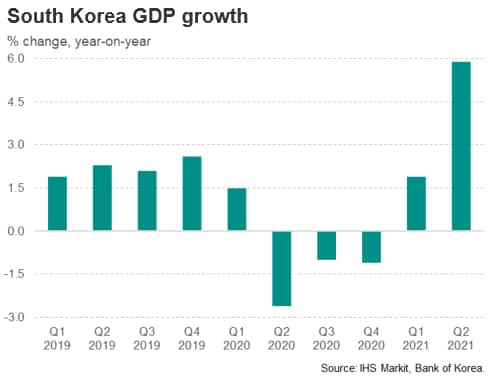
South Korea's GDP grew by 0.7% quarter-on-quarter (q/q) in the second quarter of 2021, following an increase of 1.7% q/q in the first quarter of 2021. GDP rose by 5.9% year-on-year (y/y) in the second quarter of 2021, compared with growth of 1.9% y/y in the first quarter of 2021.
Continued economic expansion in the second quarter of 2021 was underpinned by strong consumption expenditure growth. Private consumption expanded by 3.5% q/q, compared with growth of 1.2% q/q in the first quarter of 2021. Government consumption spending also strengthened, rising by 3.9% q/q in the second quarter of 2021, compared with growth of 1.6% q/q in the first quarter of 2021. Overall, final consumption expenditure rose by 3.6% q/q in the second quarter, strengthening compared with growth of 1.3% q/q in the first quarter.
Compared to a year ago, final consumption expenditure rose by 4.1% y/y in the second quarter, improving on the 1.5% y/y growth rate in the first quarter. In 2020, final consumption had been in a protracted slump, having recorded four consecutive quarters of negative year-on-year growth. The Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy released data showing that South Korea's overall retail sales saw year-on-year growth of 11.4 percent in June.
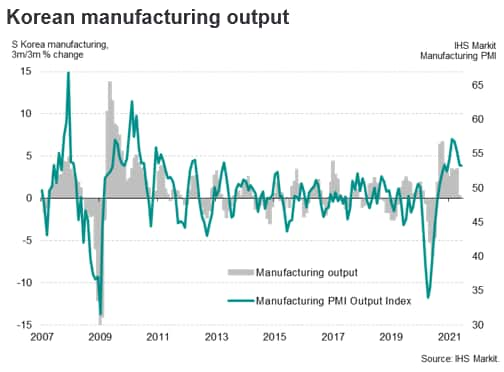
Manufacturing output grew by 13.7% y/y in the second quarter of 2021, reflecting increasing output of autos, electronic, optical and chemical products, with strengthening business conditions. Auto production rose by 11.5% y/y during the first six months of 2021.
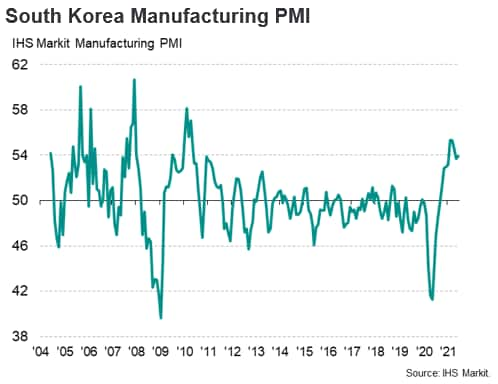
The seasonally adjusted IHS Markit South Korea Manufacturing Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI) edged up to 53.9 in June from 53.7 in May, indicating a further improvement in the health of the manufacturing sector and extending the current sequence of expansionary conditions to nine months.
A key driver for the rapid expansion in manufacturing output in the first half of 2021 has been the rebound in exports. Stronger economic growth in major economies such as the US, China, EU and UK linked to the rollout of vaccination programs during the first half of 2021 helped to boost South Korean new export orders from its key export markets. South Korean exports rose by 39.7% y/y in June 2021, buoyed by strong growth in exports of electronics and autos. South Korean auto exports rose by 50% y/y in value terms during the first six months of 2021. Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy data showed that Korea's exports in the first half of 2021 increased 26% y/y, hitting a record-high value of USD 303 billion.
In the latest IHS Markit South Korea Manufacturing PMI Survey, manufacturers pointed to a further acceleration in input cost inflation during June. Input price pressures intensified in the latest survey period and were the steepest on record as businesses widely reported sharp rises in the cost of raw materials amid acute shortages. At the same time, South Korean goods producers sought to pass these costs on to clients, resulting in the strongest rise in output prices since the survey began in April 2004.
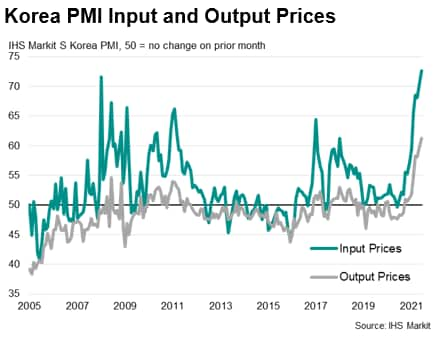
The Bank of Korea indicated in its Monetary Policy Decision in July 2021 that consumer price inflation will continue to run in the lower- to mid-2% range for some time. Core inflation is forecast to increase gradually to the mid-1% range. The Monetary Policy Board of the Bank of Korea has signalled that it will maintain an accommodative stance of monetary policy as there remain uncertainties posed by the COVID-19 virus. However, the Korean economy is expected by the BOK to continue its recovery and inflation to remain at a high level for some time. While maintaining accommodative monetary policy in the near-term, the Monetary Policy Board have indicated that they will continue to assess whether it is appropriate to adjust the degree of accommodation.
Electronics sector exports rebound
The electronics manufacturing industry is an important part of the manufacturing export sector for South Korea which is a major global exporter of electronics products to key markets such as the US, China and EU. As Vietnam is an important production hub for South Korean electronics multinationals such as Samsung and LG for a wide range of electronics products such as mobile phones, Vietnam is a key export market for South Korean electronics components.
The strong rebound in world consumer markets, notably in the US, China and Western Europe, are continuing to drive growth in demand for electronics. This is resulting in buoyant growth in household spending on electronics products as well as products that are intensive users of electronics, notably autos.
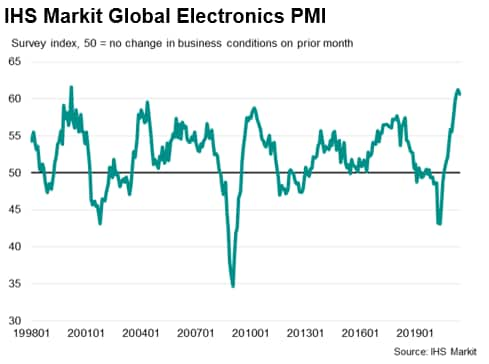
The headline seasonally adjusted IHS Markit Global Electronics PMI registered 60.7 in June, continuing to show strong operating conditions, albeit edging down from 61.2 in May. Sharp growth was once again seen across output and new orders, driving another strong rise in employment.
The IHS Markit Global Electronics PMI new orders index meanwhile showed the rate at which demand improved during June was strong, despite easing slightly from the 17-year high recorded in the previous month.
The South Korean Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy has released statistics showing that outbound shipments of Korea's information and communications technology (ICT) goods showed strong growth in the first half of 2021 and increased by 29% y/y in June. South Korean semiconductor exports rose by 34% y/y, with exports of memory chips up 31% while exports of system chips rose by 47% y/y. Exports of displays rose by 30% y/y. Exports of computers were up 9.4% y/y while exports of peripheral devices were 19.5% higher.
The strength of South Korean ICT exports in the first half of 2021 has been boosted by rapid growth in exports to the world's largest consumer markets. In June, electronics exports to the US were up 32% y/y, while exports to the EU were up 51% y/y. Electronics exports to China rose by 28% y/y.
ICT exports to Vietnam, which is a key manufacturing hub for South Korean electronics firms, also showed rapid growth of 25% y/y in June, reflecting large exports of intermediate electronics parts and components for final assembly in Vietnam. However, the severe escalation in the new COVID-19 wave in Vietnam during July poses a near-term risk to South Korean exports to Vietnam as well as to the South Korean manufacturing supply chain if Vietnamese industrial production suffers significant disruptions due to the escalating domestic pandemic.
Samsung Electronics stated on 29th July that in Vietnam, there were production disruptions to their operations in certain places due to lockdowns that affected their production. However, the firm managed to minimize the impact by shifting production to other countries in their global supply chain. Samsung Electronics has large-scale manufacturing production operations in Vietnam.
South Korean economic outlook
The near-term outlook for the South Korean economy is for GDP growth to recover to a pace of around 3.8% y/y in 2021, with continued firm expansion at a pace of around 3.0% in 2022. The economic recovery in the first half of 2021 has been driven by consumption growth and merchandise exports. The Bank of Korea has forecast GDP growth in 2021 at around 4%. The South Korean Ministry of Economy and Finance raised its GDP growth forecast for 2021 from 3.2% y/y to 4.2% y/y in June 2021.
However, despite the strong rebound of consumption during the first half of 2021, the escalating COVID-19 wave during July has created downside risks to the near-term outlook.
South Korea commenced its COVID-19 vaccination program in late February, with the government aiming to have 25% of the population vaccinated by June 2021. By July 27th, around 35% of the total population had received first dose vaccinations, with 13.6% of the population having received both doses. However, so long as a large share of the population remain unvaccinated against COVID-19, the economy faces continued vulnerability to an escalating wave of COVID-19 cases. The downside risks have intensified particularly due to the increased transmissibility of new strains of the COVID-19 virus that have impacted upon other countries worldwide, including a number of Asian nations.
An additional challenge is that the recovery of South Korean trade in services is expected to be delayed and protracted, as international travel restrictions in the Asia-Pacific region continuing to constrain any early recovery in exports of tourism and commercial aviation, which are an important component of total services exports.
Once vaccination rates reach a high share of the total population, this is expected to support normalization of domestic economic activity, based on the experience of North America and Western Europe.
Over the medium-term outlook, South Korean exports are expected to grow at a rapid pace, helped by the sustained strong growth of intra-regional trade within APAC, as China, India and ASEAN continue to be among the world's fastest-growing emerging markets. South Korea's strong competitive advantage in exporting key electronics products, notably semiconductors and displays, are expected to be an important positive factor underpinning export growth.
The rapid growth of South Korean exports is also expected to be strengthened by the regional trade liberalization architecture. This includes the large recent RCEP multilateral trade agreement and major bilateral FTAs. South Korea is also actively evaluating the possibility of applying to join the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) trade agreement and has begun unofficial bilateral talks with the CPTPP member nations to prepare for its potential formal membership application.
Rajiv Biswas, Asia Pacific Chief Economist, IHS Markit
Rajiv.biswas@ihsmarkit.com
© 2021, IHS Markit Inc. All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole
or in part without permission is prohibited.
Purchasing Managers' Index™ (PMI™) data are compiled by IHS Markit for more than 40 economies worldwide. The monthly data are derived from surveys of senior executives at private sector companies, and are available only via subscription. The PMI dataset features a headline number, which indicates the overall health of an economy, and sub-indices, which provide insights into other key economic drivers such as GDP, inflation, exports, capacity utilization, employment and inventories. The PMI data are used by financial and corporate professionals to better understand where economies and markets are headed, and to uncover opportunities.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fsouth-korea-economic-rebound-threatened-by-new-covid-wave-aug21.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fsouth-korea-economic-rebound-threatened-by-new-covid-wave-aug21.html&text=South+Korea+Economic+Rebound+Threatened+by+New+COVID+Wave+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fsouth-korea-economic-rebound-threatened-by-new-covid-wave-aug21.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=South Korea Economic Rebound Threatened by New COVID Wave | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fsouth-korea-economic-rebound-threatened-by-new-covid-wave-aug21.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=South+Korea+Economic+Rebound+Threatened+by+New+COVID+Wave+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fsouth-korea-economic-rebound-threatened-by-new-covid-wave-aug21.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}




