Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
BLOG
May 19, 2020
Global Daily Market Summary - 19 May 2020
Global equity markets closed mixed today, with most APAC markets higher on the day and both Europe and the US lower. US equity markets were toggling between slightly positive/negative for most of the day until mid-afternoon NY time when a news article critical of yesterday's preliminary positive phase 1 vaccine trial results appeared to rapidly change the tone of the market, which led to a sharp increase in volatility, sell-off in both equities and US IG/HY credit indices, as well as a modest rally in US government bonds.
Americas
- US equity markets were slightly higher on the day until suddenly switching course at around 2:50pm ET, which coincided with the release of a STAT news article that raised questions about yesterday's preliminary Moderna vaccine trial results. Following that news, the markets closed lower on the day; Russell 2000 -2.0%, DJIA -1.6%, S&P 500 -1.1%, and Nasdaq -0.5%.
- 10yr US govt bonds were higher for most of the day, but rallied an additional 3bps after the STAT article, to close the day at -4bps/0.69% yield.
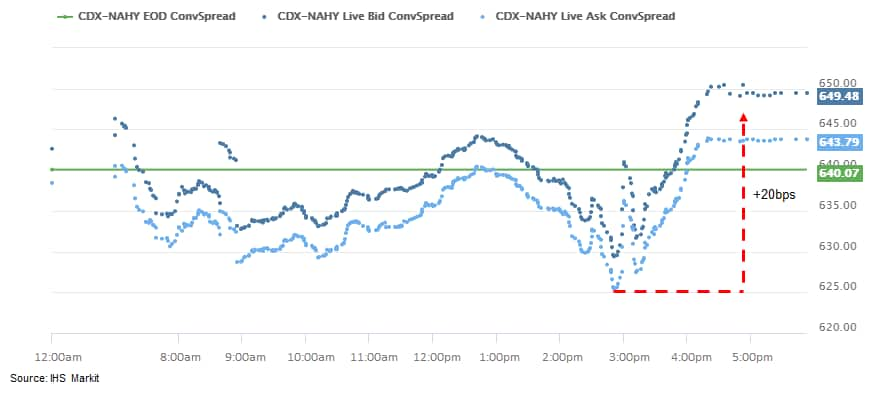
- CDX-NAIG closed unchanged/90bps and CDX-NAHY +6bps/647bps; both
indices began to widen at 2:50pm ET (CDX-NAHY below):
- According to the article published today by health and medicine
periodical STAT news, some vaccine experts say Moderna didn't share
enough critical data to properly assess their COVID-19 vaccine in
Phase I trials. Some experts suggest that the early readout should
be taken lightly for the below reasons:
- The National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) has partnered with Moderna on this vaccine. NIAID did not put out a press release yesterday and declined to provide comment on Moderna's announcement.
- Yesterday's statement indicated that eight volunteers developed neutralizing antibodies, but the results did not indicate those eight people's age ranges (younger people may have a better response) and the results for the other 37 trial participants were not available yet (albeit testing for neutralizing antibodies is more time-consuming than other antibody tests)
- The report of neutralizing antibodies in subjects who were vaccinated comes from blood drawn two weeks after they received their second dose of vaccine, which is potentially too early to determine if the antibodies are in fact durable.
- Crude oil closed +0.4%/$31.96 per barrel.
- The global economy is in the midst of the worst downturn since
the 1930s. China's real GDP plunged a record annual rate of 33.8%
quarter on quarter (q/q) in the first quarter of 2020. On a
comparable basis, IHS Markit estimates that US real GDP will
plummet a record 36.5% or more in the second quarter. Modest
recoveries are expected in subsequent quarters. A combination of
factors will make the post-crisis recovery unusually slow: (IHS
Markit Economists Sara Johnson and Nariman Behravesh)
- A tidal wave of bankruptcies among small and large industries will make restarting the manufacturing sector more challenging than in typical recoveries.
- Moreover, the damage to the finances of households and businesses will substantially delay any return to old spending levels.
- Last, but by no means least, the fear of crowds will postpone any return to "normal" in the travel and leisure industries. Even massive stimulus will only offset a small part of plunging growth (roughly 0.4 percentage point in 2020 for the US economy).
- Crucially, any resurgence in the number of infections will only worsen these trends. The recent flare up of cases and re-imposition of restrictions in South Korea and parts of China are worrisome.
- US housing starts tumbled 30.2% (+/- 11.0%, statistically
significant) in April from March to an 891,000-unit seasonally
adjusted annual rate (SAAR). The 385,000 (SAAR) one-month drop in
units was the largest since April 1984; the 676,000-unit (SAAR)
two-month drop is unprecedented. The data's starting point is
January 1947. (IHS Markit Economist Patrick Newport)
- Single-family starts plummeted 25.4% (+/- 9.6%, statistically significant); multifamily starts nose-dived 40.5%. Single-family starts in the Northeast set a record low.
- Housing permits fell 20.8% (+/- 0.9%, statistically significant) to a 1.074 million rate; single-family permits plunged 24.3% (+/- 1.6%, statistically significant); multifamily permits fell 14.2% to a 405,000 rate. Single-family and total permits were down in all four regions.
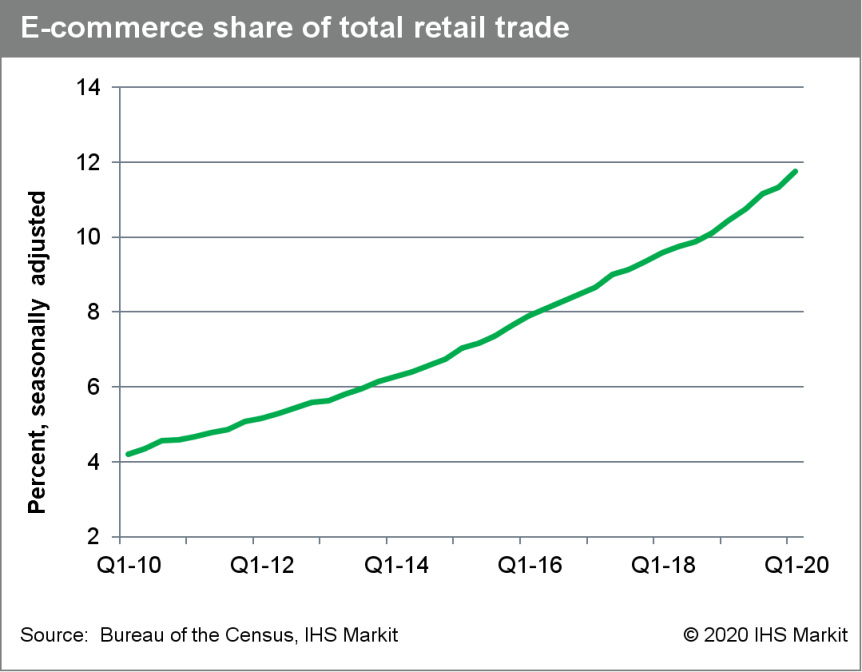
- US e-commerce retail sales growth cooled in the first quarter
of 2020 as the entire retail segment took a bath amid business
closures and reduced consumer spending owing to COVID-19. Total
retail trade and food services declined 2.2% in the first quarter.
Still, e-commerce retail sales managed quarterly growth of 2.4%, a
slight increase from the previous quarter's mark of 2.2%. Growth
was a solid 14.8% on a y/y basis, but down from 16.6% in the fourth
quarter of 2019. (IHS Markit Economists David Deull and James
Bohnaker)
- Brick-and-mortar retail sales have been ravaged by COVID-19 and associated "nonessential" business closures. This has been a boon to e-commerce retail, at least temporarily, as consumers observe social distancing policies.
- Consumers have turned to online delivery for in-demand "essential" items such as groceries, toilet paper, and cleaning supplies, and to a lesser extent, discretionary goods such as clothing, electronics, and furniture.
- The e-commerce industry for food and beverages has taken off in particular, with estimated growth of 81% y/y in the first quarter of 2020.
- COVID-19 will continue to suppress retail sales at physical
locations and encourage online shopping, both temporarily and
permanently. High numbers of retail store closings in the past few
years have thinned out the retailers unable to compete in the
online segment, and COVID-19 will only accelerate that trend.
- The Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago published a report on 17
May entitled 'Impacts of the Fed Corporate Credit Facilities
through the Lenses of ETFs and CDX'. In their study, they used the
liquid and efficient bond ETF prices and CDX spreads to quantify
the effects of the announcements of the Primary and Secondary
Market Corporate Credit Facilities on the underlying corporate
bonds. They found that those announcements triggered:
- Large and positive jumps in the prices of directly-eligible ETFs as well as ETFs holding eligible bonds and their close substitutes
- A discrete drop in the perceived credit risk of eligible bonds especially following the April 9th announcement
- A roaring back of investment-grade issuance and a pick-up in high-yield issuance.
- US authorities are struggling to get information about how cell-cultured meat companies intend to scale up to commercial production. According to a new report from the Government Accountability Office (GAO), the US FDA and USDA also need more insight into what final products such businesses intend to sell to consumers. The GAO stated: "General information about the process of making cell-cultured meat is available, but specific information about the technology being used and the eventual commercial production methods as well as the final products is not yet known." Other questions remain about many key parts of producing cell-cultured meat including tissue collection, notably how often producers will need to collect biopsy samples from live animals and if regulators will ensure that biopsies are collected from healthy animals. (IHS Markit Agribusiness' J. R. Pegg)
- Argentine media on 18 May reported the details of restructuring
counterproposals that private creditors had offered the government
days earlier on its USD66-billion debt under foreign legislation.
Three groups of bondholders presented separate counterproposals:
these groups respectively included Greylock, Gramercy and Fintech;
BlackRock, Fidelity, Ashmore and T.Rowe Price; and Monarch and BHK
Capital. (IHS Markit Country Risk's Carla Selman)
- The three offers each include a one-year grace period (compared to the three years proposed by the government), and a net present value of 58-60% of nominal value, with exit yields of 10% (with coupons rising to over 5%).
- These proposals were submitted after bondholders rejected the government's initial 17 April offer, consisting of a 62% reduction in interest payments and a 5.4% write-off on capital, depending on the bond.
- The government has extended its deadline for agreement until 31 May (from 8 May initially). A 30-day grace period to pay USD500 million of unpaid interest to private creditors expires on 22 May.
- If this remains unresolved, Argentina will default.
- The extended deadline and renewed negotiations with bondholders signal the government's willingness to avoid default. Local media report that Finance Minister Martín Guzmán has been instructed by President Alberto Fernández and vice-president Cristina Fernández de Kirchner to settle with bondholders.
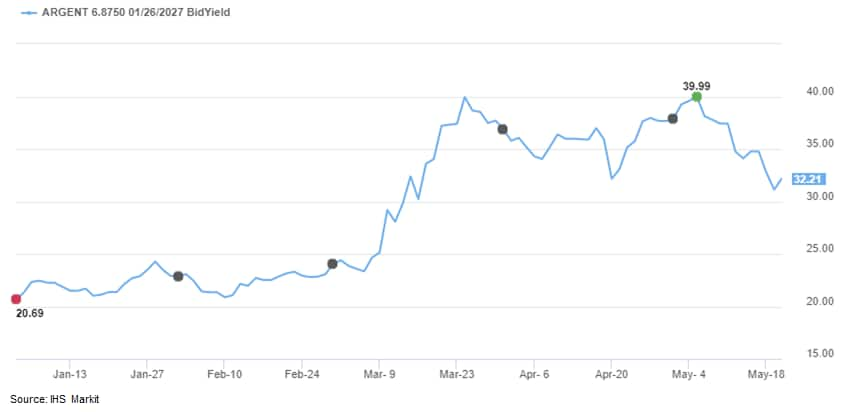
- IHS Markit bond price data in Price Viewer indicates that the
Argentine Republic 6.875% 1/2027 US dollar denominated issue closed
at a 31.98 price / 32.2% yield today:
- Preliminary data released by the Central Bank of Chile (Banco
Central de Chile: BCC) indicate that the economy only just managed
positive growth, averaging 0.4% year on year during the first
quarter of 2020. This follows a significant decline caused by
social unrest during the end of 2019 that caused significant
infrastructure damage and deteriorated domestic demand. (IHS Markit
Economist Ellie Vorhaben)
- On a quarterly basis, Chile's economy grew by 3%, but this is a testament to the sharp decline observed during the fourth quarter of 2019, not to the strength of the Chilean economy.
- Construction expanded at a positive 5.3% with support from all sectors, including mining, housing, and non-residential buildings.
- The mining sector grew by 5.1% despite weak copper prices that declined by around 4% compared with the fourth quarter in 2019, partly because of the leap year's additional working day and the weak comparison from 2019 in which weather and maintenance disruption led to very weak copper production.
- Industrial production expanded by 1.1%, supported by food production as well as chemical, pharmaceutical, and cleaning supply production because of increased demand during the pandemic.
- IHS Markit forecasts significant declines for the rest of the year for a 2020 average of -5.1%.
- Volvo owned performance electric car brand Polestar has announced its first US retail partners and plans for expansion in the United States in 2021. Polestar issued a statement on 18 May announcing the retail partners for its first locations, which are in New York City and Los Angeles and two locations in the San Francisco Bay area. The first retail partners include Manhattan Motorcars, Galpin Motors, and Price-Simms Automotive Group, which plan to open Polestar sales in the second half of 2020. In addition, the company plans to expand to Boston, Denver, Texas, Washington DC, and Florida in 2021. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
Europe/Middle East/ Africa
- Most European equity markets closed lower except for Germany +0.2%; Spain -2.5%, Italy -2.1%, France -0.9%, and UK -0.8%.
- Most 10yr European govt bonds closed higher except for Germany +1bp; Spain -8bps, Italy -3bps, UK -1bp, and France flat.
- European CDS indices closed higher on the day, with iTraxx-Europe investment grade index closing -2bps/82bps and iTraxx-Xover high yield index -10bps/490bps.
- Brent crude closed -0.7%/$34.55 per barrel.
- German Chancellor Angela Merkel and French President Emmanuel
Macron on 18 May proposed the creation of a temporary
EUR500-billion fund within the European Union's Multiannual
Financial Framework (MFF) 2021-27 to support recovery from the
COVID-19 virus pandemic in member states. (IHS Markit Sovereign
Risk's Dijedon Imeri, Jan Gerhard, Petya Barzilska, and Bibianna
Norek)
- The fund would be raised by the European Commission borrowing directly from the capital markets and would be used to boost EU spending, distributed among the countries worst-affected by the COVID-19 virus pandemic.
- Crucially, these funds would take the form of grants rather than loans and thus would not generate an increase in the public debt of recipient EU member states (MSs).
- In response, Austrian Chancellor Sebastian Kurz tweeted that he and his counterparts in Sweden, Denmark, and the Netherlands are still opposed to the two main pillars of the Franco-German proposal: increasing the European Commission's borrowing capacity and distributing the funds as grants.
- Federal Statistics Office (FSO) data show that total German
employment in the first quarter of 2020 was at 45.036 million, down
from the previous quarter's all-time high of 45.503 million for
seasonal reasons but still up by 147,000 from year-ago levels. (IHS
Markit Economist Timo Klein)
- Annual employment growth thus has declined from 0.6% to 0.3% y/y and compares to a 1.0% average during 2010-18.
- The absolute increase of 147,000 in the first quarter is almost as high as the aggregate employment setback of -199,000 (-0.5%) during March-July 2009, the recession triggered by the global financial market crisis.
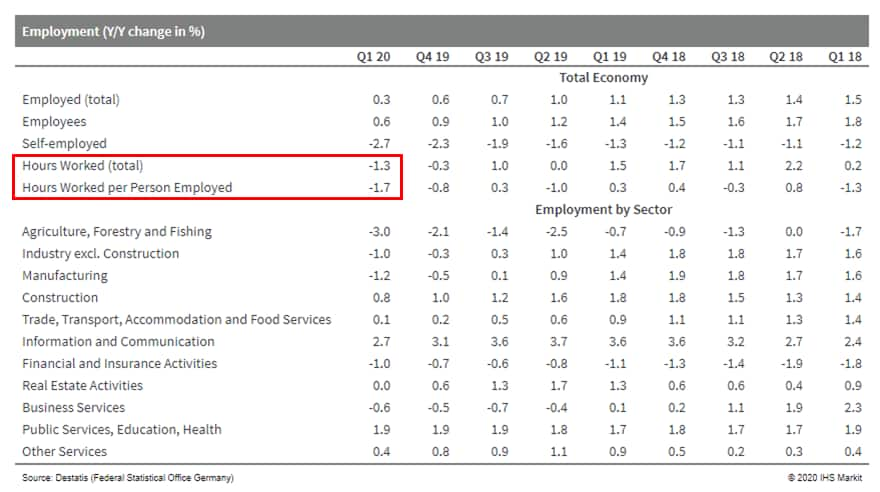
- The breakdown by sector (see table below for details) shows that year-on-year (y/y) declines were already found in agriculture, industry, and two areas of the service sector (banking/insurance and business services). By contrast, employment growth held up quite well in the information and communication sector, among public services/education/health, and in construction.
- Unlike the limited impact on employment, the emerging COVID-19
virus crisis has already been reflected in a sharp decrease in
hours worked, both in the aggregate and per employee. This mirrors
the rapid expansion of short-time work applications in March,
rather than of redundancies.
- The Volkswagen (VW) Group's European production network is gradually returning to normal with the company's Slovakian facility announcing a move back to a two-shift production system. While it is positive news that VW Slovakia aims to return to a two-shift system next week, it remains to be seen how long this will continue for, given the extremely weak demand across Europe. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
- According to detailed data released by the Albanian Institute
of Statistics (INSTAT), real GDP growth fell 0.2% year on year
(y/y) in the fourth quarter of 2019. In quarter-on-quarter (q/q)
terms, GDP fell 2.0% in October-December 2019. In 2019, real GDP
growth averaged 2.2% compared with 2018. (IHS Markit Economist
Dragana Ignjatovic)
- Domestic demand was the key driver of the weak fourth quarter performance, with the fall in fixed investment (-12% y/y) offsetting the gains from household (+1.6% y/y) and government (+2.6% y/y) spending. Investment has been falling since the second quarter, with the pace of decline gaining speed throughout the year, reflecting the completion of several large infrastructure projects in the country.
- Positively, export growth remained buoyant in the fourth quarter, rising by nearly 10% y/y while imports fell by 0.8% y/y. Exports still only account for around 60% of imports, but 2019 marks the fifth consecutive year where exports have outpaced imports.
- Albanian inflation is projected to stay below the 3% target in 2020-21, as the slump in global commodity prices, particularly oil, filters through to the domestic economy. Falling wage growth from the likely rise in unemployment will also serve to weaken inflationary expectations. However, food prices are likely to put upward pressure on inflation for as long as COVID-19-related disruption to imports and the agricultural sector persists.
- The United Arab Emirates' First Abu Dhabi Bank (FAB) has terminated talks to acquire the Egyptian subsidiary of Lebanon's Bank Audi, Reuters reports. According to reports, the talks were terminated because of the current market conditions associated with the spread of the COVID-19 virus. The acquisition discussion began in January and Bank Audi was likely looking to use funds from the sale of its Egyptian subsidiary to shore up its domestic operations as risks in the Lebanese banking sector continue to escalate. (IHS Markit Banking Risk's Gabrielle Ventura)
Asia-Pacific
- APAC equity markets closed higher across the region; South Korea +2.3%, Hong Kong +1.0%, Australia +1.8%, Japan +1.5%, China +0.8%, and India +0.6%.
- Borealis says it will not proceed with the development of a multibillion-dollar integrated ethane cracker and polyethylene (PE) project in Kazakhstan. "The decision to discontinue this project is based on a thorough assessment of all aspects of the prospective venture and impacted by the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic as well as the increased uncertainty of future market assumptions," Borealis states. The company signed a joint development agreement in March 2018 with United Chemical Co. (UCC; Astana, Kazakhstan) to develop the world-scale petrochemical project at Atyrau, Kazakhstan. UCC earlier put the estimated total investment figure for the petchem project at $6.8 billion.
- Mitsubishi posted a JPY25.8-billion loss during the full fiscal
year (FY) 2019/20. Operating income declined sharply by 89% year on
year (y/y) to JPY12.8 billion, and net revenue was down 10% y/y to
JPY2.27 trillion. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tarik Arora)
- Mitsubishi sold 1.127 million vehicles during this period, a 9% y/y decline.
- ASEAN volumes reached 290,000 units (down 9% y/y).
- Europe reached 215,000 units (down 9% y/y)
- North American declined 8% y/y to 160,000 units.
- Domestic market volumes declined 10% y/y to 95,000 units
- Australia and New Zealand declined 14% y/y to 88,000 units.
- China's public fiscal revenue dropped by 15.0% year on year
(y/y) in April, up from a 26.1% y/y contraction in March, according
to release by the Ministry of Finance (MOF) on 18 May. (IHS Markit
Economist Yating Xu)
- Tax revenue declined by 17% y/y with broad improvement across tax items. Domestic value-added tax contracted at a slower pace, domestic consumption tax rose to expansion from contraction in the past three months, the decline in corporate income tax and individual income tax narrowed, land and real estate related tax growth accelerated. Meanwhile, value-added tax and consumption tax of imports increased at a faster rate, in contrast to a sharp drop in April commodity imports. Also, non-tax revenue increased to expansion.
- Public fiscal spending rose 7.5% y/y, up from a 9.4% y/y contraction in March as local governments' spending increasing by 11.1% y/y, while the growth of central government's spending declined by 7.1% y/y. Spending on social security jumped by 29 percentage point to a 24% y/y growth, spending on urban and rural community affairs as well as agriculture, forestry and water improved to expansion for the first time since the start of 2020. However, spending on transportation recorded deeper contraction.
- Revenue of government fund declined by 1.3% y/y in April from 0.8% y/y increase in the previous month, as the growth of land sales revenue slowed.
- The fiscal revenue through April declined by 14.5% with continuous contraction across all sub-tax items except individual income tax and stamp tax, as well as vehicle tax improving from contraction to expansion in April. Fiscal spending fell by 2.7% y/y with decline in all sub-spending items except larger spending in social security, health and debt payment.
- For first quarter 2020, Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine
Engineering Co (DSME) posted a revenue of USD1.7 billion (KRW2.0
trillion), 10% lower compared with that of USD1.8 billion (KRW2.1
trillion) a year ago. (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's
Jessica Goh)
- Despite lower revenue, profits increased in terms of both net and operating profit. Net profit for the quarter increased 18% year on year (y/y) to USD205 million (KRW242.5 billion) while operating profit increased 33% y/y to USD236 million (KRW279.0 billion). Higher value works from LNGCs and change orders in the offshore segment drive the increase.
- DSME secured new orders worth USD380 million during the first quarter of 2020, achieving 5.3% of its 2020 new order target of USD7.2 billion. Backlog as at end March 2020 stood at USD21.5 billion, 3% higher than its 2019 year-end backlog of USD20.9 billion.
- DSME expects the shipbuilding market to slow down due to the COVID-19 pandemic. LNGC new orders will slow down in this year due to falling LNG price and weakened global economy.
- A fire at a catalyst plant operated by LG Chem at Seosan, South Korea, has killed one worker and injured two others, according to company and fire officials. The incident occurred at the catalyst plant at about 2:25pm local time on Tuesday. The facility was immediately shut down and the fire was extinguished just over an hour later, according to a Reuters report quoting a fire department official. LG Chem says it is looking into the exact cause of the fire, but that it is likely to have been caused by a spontaneous ignition of powder, reported as alkyl aluminum. LG Chem is currently dealing with the aftermath of a styrene gas leak on 7 May at a polystyrene facility near Visakhapatnam, India, operated by its subsidiary LG Polymers India (Mumbai), which killed 12 people and caused sickness in up to 1,000 local residents. It is investigating the cause of that incident.
- Pony.ai has received permission to test its autonomous vehicles (AVs) carrying passengers in Beijing (China), reports Caixin Global. The startup's fleet will drive on specified public roads in the city's Haidian district and Yizhuang town. The vehicles will have a safety driver behind the wheel to take control in case of an emergency. This comes nearly five months after Beijing city allowed autonomous car road tests to transport qualified passengers as well as goods for delivery. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Kia Motors India has resumed single-shift operations at its Ammavaru Palli plant in Andhra Pradesh (India), reports The Hindu BusinessLine. The automaker began operations on 8 May after receiving all necessary permissions from the Andhra Pradesh state government and the Anantapur Municipal Corporation. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Isha Sharma)
- IHS Market has downgraded Indonesia's short-term risk rating by
one notch to a numerical score of 15 (A+ on the generic scale) and
shifted the outlook to Negative from Stable; we have also lowered
the outlook for the medium term to Stable but left the rating
unchanged (40, BBB- on the Generic scale). (IHS Markit Economist
Bree Neff)
- The decision to undertake the one-notch downgrade to Indonesia's short-term risk rating and shifting the outlook to Negative stems from the extraordinary shock from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) virus pandemic to global demand for Indonesia's commodities and tourism exports, plus remittances inflows, and foreign direct investment (FDI), which will put pressure on the country's near-term liquidity and solvency measures.
- In addition, the Indonesian rupiah remains vulnerable to sudden and disruptive capital outflows resulting from shifts in investor sentiment. This is due to extreme dependence on foreign capital; 32.7% of tradeable rupiah-denominated government bonds were held by non-residents in March 2020, although this is down sharply from 38.0% in December 2019. This makes near-term foreign debt servicing a risk to monitor especially in light of Indonesia's systemically high debt servicing costs.
- Despite the heightened near-term risk, Indonesia's near-term solvency and liquidity ratios remain generally favorable, and the country's sovereign default risks remain limited in the next 12 months. For the sovereign's short-term rating, a downgrade could arise if interest rates rise too sharply and remain elevated because of heightened risk aversion, or if a dramatic, sustained collapse in export earnings or capital outflows arises. An upgrade is unlikely until the pandemic has run its course.
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fglobal-daily-market-summary-19-may-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fglobal-daily-market-summary-19-may-2020.html&text=Global+Daily+Market+Summary+-+19+May+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fglobal-daily-market-summary-19-may-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Global Daily Market Summary - 19 May 2020 | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fglobal-daily-market-summary-19-may-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Global+Daily+Market+Summary+-+19+May+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fglobal-daily-market-summary-19-may-2020.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}




