Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
BLOG
Sep 08, 2020
Daily Global Market Summary - 8 September 2020
Most APAC equity markets closed higher, while European markets closed lower after being down for most of the trading session and US markets closed lower after another significant bout of selling in US tech companies. US/European benchmark government bonds and the US dollar closed higher on the weakness in equities and iTraxx and CDX closed wider across IG/high yield. Gold closed modestly higher, while oil closed sharply lower again on concerns over waning demand, US supply increases, and US election uncertainty going into the fall.
Americas
- US equity markets closed sharply lower due to a selloff in the tech sector; Nasdaq -4.1%, S&P 500 -2.8%, DJIA -2.3%, and Russell 2000 -2.0%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed -4bps/0.68% yield and 30yr bonds closed -5bps/1.42% yield.
- CDX-NAIG closed +2bps/68bps and CDX-NAHY +18bps/384bps.
- DXY US dollar index closed +0.9%/93.52
- Gold closed +0.5%/$1,943 per ounce.
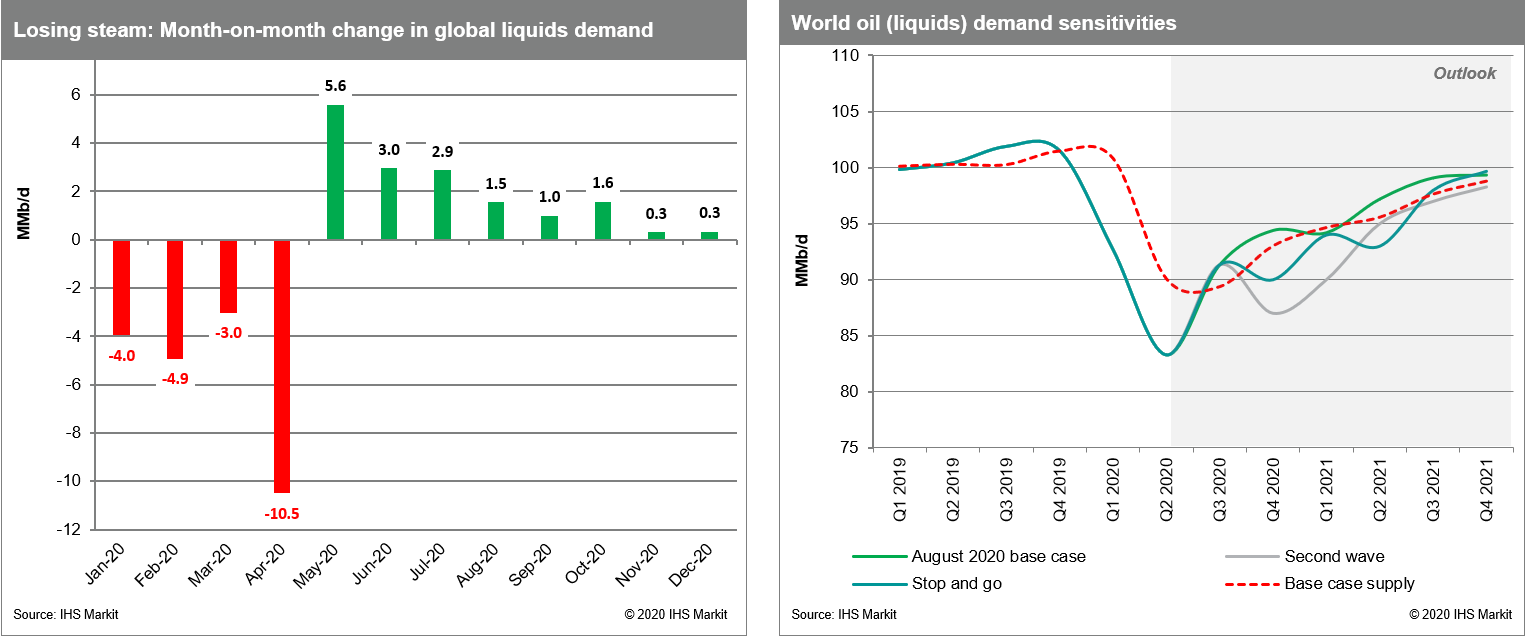
- Crude oil closed -7.6%/$36.76 per barrel, which is its lowest close since 12 June. Crude oil is now -15.3% from this quarter's highest close on 26 August.
- After a thunderous spring, and in the midst of a raging
pandemic, the stability in oil markets over the past two-plus
months has been remarkable, thanks in part to OPEC+ supply cuts and
recovering demand. Or at least that was the case through early last
week. Crude prices have plummeted by more than 12% since the
beginning of September, and by more than 5% in early trading this
week after the Labor Day holiday. In oil markets, optimism that
physical market indicators would continue to strengthen, which we
cautioned against through the summer, has waned. Oil prices have
also been dragged lower by a broader market sell off as macro
sentiment has soured. If bearish sentiment takes hold further and
prices do not retrace recent losses, this will mark the first real
test of the re-invigorated OPEC+ apparatus since the group managed
to rein in builds early in the summer. While markets appear to have
relatively high confidence in the prospective market tightening
once demand returns to 100+ MMb/d, be it in 2Q2021, 2H2021 or early
2022, the near term and especially the next three to four months
remain exceedingly uncertain. This naturally starts with demand and
containment measures, but also involves the US election, Chinese
buying, US supply trajectory post-shut ins return and OPEC+
proactiveness. Each of these factors has sufficiently large
physical implications to materially alter the market until the
post-COVID-19 era. (IHS Markit Energy Advisory's Roger Diwan, Karim
Fawaz, Justin Jacobs, Edward Moe, and Sean Karst)
- Outstanding US nonmortgage consumer credit increased by $12
billion to $4.14 trillion in July after an $11 billion increase in
June that followed a $96 billion plunge between March and May. (IHS
Markit Economist David Deull)
- The 12-month change in outstanding consumer credit edged down 0.2 percentage point to 0.7%, the lowest in nearly a decade, as spending has fallen and incomes have been supplemented by federal stimulus.
- Revolving (mostly credit-card) consumer credit edged down $0.3 billion (seasonally adjusted) in its fifth consecutive decline. The 12-month growth rate of this category was -8.3%.
- July was the last month during which the $600 expanded unemployment insurance benefit, passed as part of the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act, was issued. Going forward, consumers are likely to rely more on credit cards to finance daily purchases.
- Nonrevolving credit increased $12.5 billion, and its 12-month growth rate was unchanged at a brisk 3.9%. This category includes student and auto loans, and the growth of these types of obligations has remained stubbornly steady.
- The ratio of nonmortgage consumer credit to disposable personal income was 23.1% in July, unchanged from June.
- As consumers have pulled back on spending because of COVID-19, they have taken the opportunity to pay down credit card debts but have not made much of a dent in auto and student loans, which continue to grow at a brisk pace. With fiscal support waning and unemployment still elevated, a renewed increase in consumer debt is possible.
- General Motors Co. closed higher after the auto maker said it would help electric-truck startup Nikola develop and manufacture new models, the latest example of investor infatuation with electric vehicles. In exchange for its services, GM said it would receive an 11% stake in Nikola Corp., a would-be rival in the market for electrified pickups. (WSJ)
- Tesla Inc. shares closed lower on Tuesday after the electric-vehicle maker missed out on being included in the S&P 500 Index, taking investors who had invested in anticipation of its entry to the benchmark by surprise. Tesla shares fell as much as 20% on Tuesday, the biggest one-day loss since early February. Declines started premarket and worsened on the General Motors/Nikola announcement. (Bloomberg)
- Westlake Chemical says "some" of the production units at its facility in Lake Charles, Louisiana, will not restart until the end of September because of ongoing power outages resulting from Hurricane Laura, which struck on 27 August. "The local utility, Entergy Louisiana, has reported extensive damage to the electricity transmission system in the Lake Charles area, and that restoration of service will take a number of weeks," says a statement issued this morning by Westlake. "Given Entergy's latest guidance on the restoration of power to the Lake Charles area, barring other unforeseen circumstances, we currently expect production at some of our units to restart by the end of September and full production to resume in early October." The same statement was issued by Westlake Chemical Partners, which produces ethylene for Westlake. Westlake Chemical previously declared force majeure on ethylene dichloride (EDC), vinyl chloride monomer (VCM), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and styrene monomer (SM) owing to hurricane-related disruptions at the facility, which Westlake shut down in advance of the storm. Other companies with production assets in the Lake Charles area include Sasol, Lotte Chemical, and LyondellBasell.
- The US pistachio sales halved year-on-year to 13,840 (short) tons this June, bringing seasonal shipments to 251,500 tons, one quarter less. Chinese consumption did not recover, and imports fell by 90% this June to 690 tons and seasonal (September-July) by 36% to 36,648 tons. Key European importers such as Germany, Spain, France and the Netherlands cut also imports in June, although seasonal German and Spanish sales remained strong. Germany increased by 1,200 tons to 26,586 tons and Spain did that by 800 tons to 10,481 tons between September 2019 and July 2020. US pistachio exports have been relying on Chinese appetite for them, despite the trade war between the US and China. However, halted Chinese imports as a result of Covid-19 restrictions and buoyant Iranian pistachio sales in an on-year are hitting US sales and not favoring price recovery despite California crop being in an 'off-year'. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Jose Gutierrez)
- Ike Robotics has reached agreements to develop automated trucks for Ryder, DHL, and NFI. The three logistics operators will collectively procure 1,000 trucks equipped with Ike's technology through an annual software subscription model. Customers will buy trucks deployed with Ike's automation system from its OEM manufacturing partners. Automated trucks will be owned and operated by fleets and "Powered by Ike". The company has said, "We are proud to announce our first customers, who have collectively reserved the first 1,000 trucks Ike will power with our automation technology. The fleets we are working with are among the largest and most sophisticated in the world. The agreements we have signed are an entirely new kind of collaboration for our industry, and will ensure that we build a safe, reliable, commercially valuable product - together." Ike is a US-based autonomous truck start-up that sources its localization, perception, prediction, and planning software from autonomous delivery company Nuro. Last year, the company secured USD52 million in a Series A funding round led by Bain Capital Ventures. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Mexico's light-vehicle sales continued to decline in August on
the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, although the situation has
improved since April. Mexico's light-vehicle production and exports
also continued to decline in August. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's
Stephanie Brinley)
- After light-vehicle sales showed the steepest plunge this year in May, falling 59% year on year (y/y), the sales decline in each month since has become progressively smaller.
- The May decline was largely on the Mexican government closing non-essential business in the country from 31 March to 30 May.
- In August, light-vehicle sales dropped 28.7% y/y to 77,092 units, compared with 108,058 units in August 2019, according to data from the National Institute of Statistics and Geography (Instituto Nacional de Estadistica y Geografia: Inegi).
- Mexican light-vehicle sales in 2019 and 2018 were soft as well, with the seasonally adjusted annual rate (SAAR) falling to 1.3 million units in December 2019. The market was not in a robust period prior to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Nissan maintains its lead on the Mexican market. In August 2020, Nissan sold 16,540 units, declining 26.4% (Infiniti sold 54 units, down 46.0% from August 2019 and down 5 units from July 2020).
- Nissan was followed by GM at 12,115 units (down 27.6%).
- VW held third place with 7,355 units sold (down 36.9%).
- Audi is reported separately from VW, and saw a small 2.4% y/y decline, to 920 units.
- In fourth, Toyota sold 6,532 units in August 2020 (down 28.3%).
- BAIC and JAC had been making stronger efforts to join the Mexico market, and JAC saw sales of 370 units in August. BAIC sales, however, dropped to 141 units from 293 units in August 2019.
- IHS Markit's August forecast revision sees the country's full-year light-vehicle sales falling 28.8% to 940,847 units. IHS Markit also sees production in Mexico slipping to 2.96 million units.
- In a press release, ExxonMobil Corporation announced two more oil discoveries at the Yellowtail-2 and Redtail-1 wells on the Stabroek Block offshore Guyana, bringing the total numbers of discoveries on the Stabroek Block to 18. Redtail-1 is the ninth discovery in southeast area of the block, which encountered 232 feet (70 meters) of oil-bearing sandstone reservoir in 6,164 feet (1,878 meters) of water, the company said. The well is located approximately 1.5 miles (2.5 kilometers) northwest of the Yellowtail discovery. Yellowtail-2 encountered 69 feet (21 meters) of oil-bearing reservoirs. In December 2019, ExxonMobil and partners started oil production from Liza Phase 1, with a production capacity of 120,000 b/d of oil. Liza Phase 2 is expected to start up in 2022. In January 2020, ExxonMobil increased its estimated recoverable resources for the Stabroek Block from 6 billion boe to 8 billion boe. Stabroek Block is expected to produce more than 750,000 b/d of oil by 2025. ExxonMobil (45% interest) is the operator of Starbroek Block, with partners Hess (30%), and CNOOC Limited (25%). (IHS Markit Upstream Companies and Transactions' Karan Bhagani)
- Brazilian iron ore shipments have jumped to a 12-month high on strong Chinese appetite. As per IHS Markit's Commodities at Sea, Brazil iron ore and pellet shipments during August 2020 are calculated at 36.4 metric tons(mt) (30-day pace of 35.2mt) vs 27.8mt (on the 30-Day basis) a month before. The strong monthly PACE is due to strong loadings from all the terminals - but loadings from Itaqui (19.1mt on the 30-Day basis), Port Sudeste (2.9mt), and GIT (3.3mt) witnessed a significant uptick. Out of a total of 36.4mt around 28.5mt (78% share) is destined to China versus share of 64% averaged in 2019. For the said month, from the shipping side, on Valemaxes a total of 9.7mt of iron ore cargoes was loaded which is quite a strong number. In terms of other vessel segments, on VLOC, Newcastlemax and Capesize shipments were calculated at 6.8mt, 6.9mt, and 9.9mt, respectively. The surge in loadings on Valemaxes prevented massive demand for the Capesize vessel segment during the month. The demand for iron ore cargoes is quite strong from China as the government is exercising fiscal stimulus to increase infrastructure spending in the country. From the monetary front People's Bank of China (PBOC) due to a stronger-than-expected rebound in economic activity in the second quarter is expected to keep policy stable in the near term. (IHS Markit Maritime & Trade's Rahul Kapoor and Pranay Shukla)
- Pablo Di Si, the president of Volkswagen (VW) in Latin America, announced a negotiation of a 35% reduction in its workforce in Brazil, reports Automotive Business. This was due to a retraction in production in Brazil, as well as an increase in plant idleness to over 65%. According to the source, a 35% reduction equals about 5,000 people, and the reduction will affect both operational as well as administrative employees in São Bernardo do Campo, Taubaté, and São Carlos plants in São Paulo (SP), and São José dos Pinhais plant in Paraná (PR). Pablo Di Si said, "It won't be overnight, we won't surprise anyone, but we have an urgent need to adapt our production to demand in the coming months. It is not an easy negotiation, but we have to make this reduction of personnel, because it is not sustainable to work with only 45% of the capacity." He added that, "Now we are in a survival negotiation, we are not going to discuss any new product or investment. We still have some time until the middle of 2021 to define a new cycle. Of course, we have an idea of what we're going to do, but I prefer to wait longer to be sure of the market's behavior in the coming months." IHS Markit's latest recovery tracker estimates Brazil's production was at about 34% of the pre-COVID-19 crisis forecast output in June and about 59% in July. Production should improve in the third quarter and IHS Markit forecasts that, in October, Brazil's production will be at about 91% of the pre-COVID-19 forecast level. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tarun Thakur)
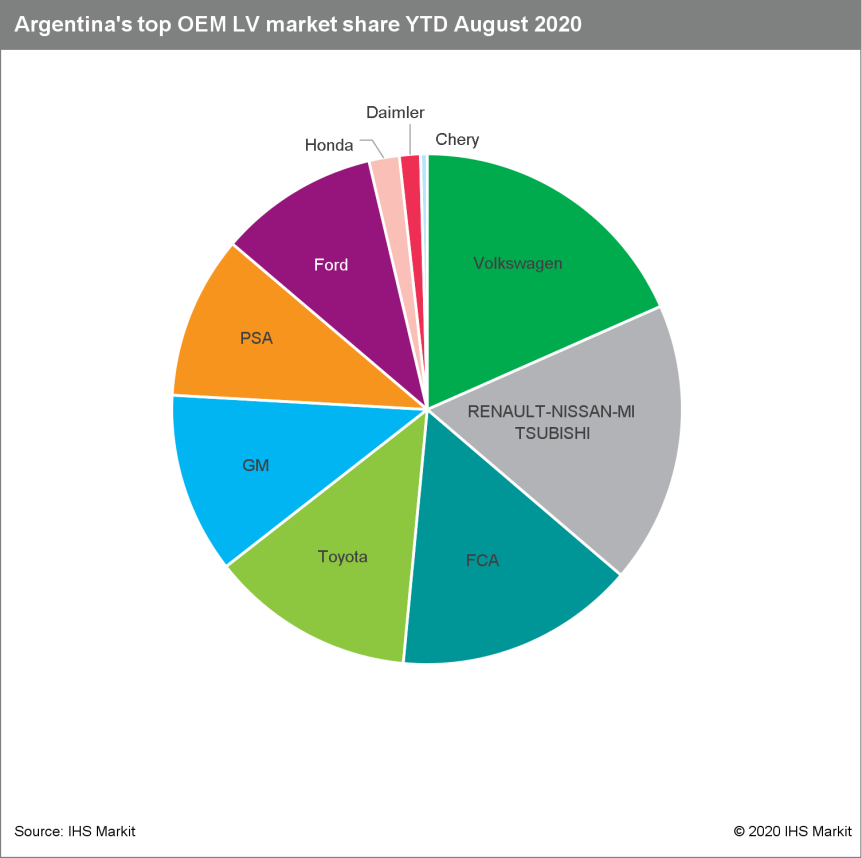
- Argentina's light commercial vehicle (LCV) registrations
decreased 21.9% % y/y in August, and passenger car sales were down
37.9% y/y. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tarun Thakur)
- Argentina's light-vehicle market is still driven by passenger-car sales, which accounted for 63.6% of total light-vehicle registrations in August. However, this share was down from 68.7% in August 2019.
- Sport utility vehicle (SUV) sales declined 36% y/y in August, although SUVs' market share continues to increase. In August 2020, SUVs held a market share of 20.2%, compared with 21.2% in August 2019.
- Argentina's light-vehicle sales dropped 43.5% in 2019. IHS
Markit projects a sharp 35.3% decline in Argentina's light-vehicle
sales in 2020, followed by a 1.8% increase in 2021, which may be
characterized as a step towards stability, since the projection for
2022 is 13.6% growth.
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- European equity markets closed lower across the region; Italy/Spain -1.8%, France -1.6%, Germany -1.0%, and UK -0.1%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed higher across the region; UK -6bps, Germany/France/Spain -3bps, and Italy -1bp.
- iTraxx-Europe closed +1bp/54bps and iTraxx-Xover +5bps/329bps.
- Brent crude closed -5.3%/$39.78 per barrel, which is its first time closing below $40 per barrel since 15 June.
- Rising German hourly labor costs continue to reflect the
reduction in hours worked because of the COVID-19-virus pandemic
rather than any increase in wages. (IHS Markit Economist Timo
Klein)
- Federal Statistics Office (FSO) data gleaned from a quarterly earnings survey show that labor costs per hour - in the producing sectors (manufacturing, construction, mining, and energy/water) and the entire service sector - have revealed a second strong quarterly increase in a row.
- Labor costs increased by 1.9% quarter on quarter (q/q) in the second quarter after a 2.3% q/q in the first quarter of 2020 (seasonally and calendar adjusted).
- This development is because of the lockdown imposed by authorities between mid-March and late April to contain the pandemic. First, employees were either urged by their employers to take annual leave as orders and production plunged or had to do so to take care of children who could no longer attend kindergarten or school. Second, a higher number of people than usual will have been on sick leave. In both cases, this boosts hourly labor costs via the depressing impact on the aggregate number of hours worked.
- The huge concurrent spike in short-time work does not affect the labor cost statistic directly as employers' payrolls also decline in accordance with the reduced number of hours worked. Employees' net pay fell by far less because the public-sector subsidy provided for short-time workers partially replaces the lost income, but these payments do not represent labor costs for the firm.
- The year-on-year (y/y) increase in labor costs advanced to 5.1% in the second quarter, which is the highest annual pace ever measured in the 25-year history of this series (since 1996) and compares with a long-run average of 2.1%.
- The latest labor cost data have been impacted quite significantly by the fallout of the pandemic. Since early 2018, there has been little slippage of Germany's relative cost competitiveness versus the European average (unlike during 2011-17), but this should prove temporary. Once the short-term volatility related to the reduction and subsequent rebound in hours worked reduces, a renewed deterioration is likely given that the German economy will probably emerge in better condition than many of its European neighbors (not least because of its massive fiscal support). Such a cost disadvantage should go together with better productivity developments, however, so the net effect on relative economic growth cannot be determined a priori.
- Germany's Federal Statistical Office (FSO) external trade data
for July (customs methodology, seasonally adjusted, nominal) reveal
a further increase in exports by 4.7% month on month (m/m), adding
to the cumulative rebound of 25% during May-June. Imports only
increased by 1.1% m/m, following a May-June rebound of 10.6%.
However, since exports had declined much more sharply than imports
during March-April, July's year-on-year (y/y) rates (unadjusted)
are now almost equal at roughly -11%. (IHS Markit Economist Timo
Klein)
- As German export levels have been exceeding import levels for decades, the seasonally adjusted trade surplus at EUR18.0 billion in July almost returned to the 2019 monthly average of EUR18.8 billion - up from the near-20-year low of EUR3.1 billion in April.
- The regional breakdown in July reveals limited divergence
between the EU and non-EU aggregates but larger differences between
eurozone and non-eurozone aggregates and between individual
countries.
- Exports to China already recovered to year-ago levels in July, whereas exports to the United States were down by 17% y/y and those to the United Kingdom by 12.6%.
- Exports to EU countries outside the eurozone also outperformed (only -7.0% y/y), which presumably reflects deliveries to Eastern Europe for the most part.
- On the import side, the disparity between eurozone and non-eurozone European countries was even larger than for exports, again mirroring greater economic resilience to knock-on effects of the pandemic in Eastern Europe compared with major eurozone economies such as France, Italy, and Spain. With respect to these countries, Germany's import capacity seemingly outstrips their export capacity so far. This also applies to the UK, as German imports from the country at -24.8% y/y were much weaker than the average. This probably reflects the COVID-19-virus situation in the UK and foreshadowing effects of Brexit as German supply chains are diverted away from the UK.
- Although the unadjusted trade surplus increased from EUR15.5 billion in June to EUR19.2 billion in July, the current-account surplus slipped marginally in July compared with June owing to the offsetting deterioration in the balances for services and secondary income (i.e., transfers). The picture differs with respect to the y/y comparison, however, as the trade surplus shrunk from EUR21.3 billion in July 2019 to EUR19.2 billion in July 2020, whereas the current-account surplus increased slightly from EUR19.4 billion to EUR20.0 billion.
- Germany's chemical industry association VCI (Frankfurt) says it expects the country's production of chemicals and pharmaceuticals to fall by 3% in 2020 compared with the prior year, with annual sales to decline by 6%. A return to pre-COVID-19 levels is not expected before the end of 2021 at the earliest, it says. The forecast of a 3% decline in annual production is a downward revision of VCI's previous expectation, issued in March, for a decrease of 1.5%. Initial signs of a recovery are, however, now being seen, says Christian Kullmann, VCI president and chairman of Evonik Industries. "If another shutdown can be avoided, demand for chemicals and pharmaceuticals is expected to stabilize in the second half of the year," he says. Production by Germany's chemical and pharmaceutical industry fell by 2.5% YOY in the first six months of this year, and sales shrank by 6.1% year on year (YOY) to €96 billion ($113 billion). Excluding pharmaceuticals, chemicals output fell by 3.6% YOY in the first half of the year. After a positive start to 2020, production in the second quarter fell by 5.8% compared with the prior-year quarter, with average plant capacity utilization falling to 77.5%, according to VCI. All product areas in the chemicals and pharmaceuticals sector faced weak demand domestically and internationally, with production of specialty chemicals falling by 3.9% YOY in the first six months of the year, VCI says. Polymers production declined by 8% YOY owing to the slump in demand from the automotive industry and plastics processors, it says. Production of pharmaceuticals recorded only a slight fall of 0.3% over the same period, and the decline in soaps and detergents output was 0.7%. "For one in four companies, the lack of orders continues to have a major impact on business activities," VCI says. The chemical and pharmaceutical sector "bottomed out" in the second quarter, with a survey of VCI's members showing that disruptions to operations are decreasing, it says. Overcoming the COVID-19 crisis "will take some time," it adds. About 49% of its member companies expect the industry to return to pre-pandemic levels by the end of next year. About 20% of those surveyed anticipate that it will take a further year, with 13% expecting only to be able to compensate for the decline at a later date or not at all, VCI notes.
- Italy's recovery stalled in July when retail sales in volume
terms decreased by 2.2% month on month (m/m) after gains of 10.2%
m/m in June and 24.2% m/m in May. (IHS Markit Economist Raj
Badiani)
- Retail sales in July therefore remained 4.9% below their level in February 2020, the last pre-COVID-19 month.
- A breakdown by type of goods reveals that spending on non-food items retreated by 3.2% m/m in July after posting very large gains in both June and May.
- In annual terms, retail sales shrank for the fifth consecutive month as they fell by 7.2% in July. The largest year-on-year (y/y) drops occurred for electric household appliances and audio-video (14.9%), clothing (27.9%) and shoes, leather goods, and travel items (17.3%).
- Despite disappointing retail sales in July, reviving overall consumer spending will help growth to revive from mid-2020. GDP is likely to expand by 6.1% quarter on quarter q/q) and by 2.6% q/q in the third and fourth quarters respectively. This was preceded by the economy shrinking 17.6% q/q in the first half of this year compared with end-2019.
- France's merchandise trade deficit stood at EUR6.994 billion
(USD8.269 billion) in July, down from a record EUR8.057 billion in
June. The deficit totaled EUR40.1 billion during the first seven
months of 2020, up from EUR31.1 billion during the same period of
2019. (IHS Markit Economist Diego Iscaro)
- Merchandise exports rose by 9.6% month on month (m/m) in July, following increases of 16.7% m/m in May and 17.0% m/m in June. Merchandise exports were still 22% below their level in February.
- On a m/m basis, exports of transport materials were the main driver of growth, rising by 33%. However, they had been by far the worst performers in March-April and exports of transport material in July were half their February's level.
- The geographical breakdown shows exports to the United States being particularly strong (+26.0% m/m) in July, while exports to Germany (+4.1% m/m) and Italy (+9.7% m/m) were also robust. Exports to China rose by 8.4% m/m in July.
- Meanwhile, merchandise imports rose by 5.1% m/m in July, following a rise of 15.2% m/m in June. They remained 17.4% below their pre-pandemic level.
- Component suppliers for battery-electric vehicles (BEVs) are said to be interested in Nissan's facilities in Barcelona (Spain), which are planned for closure. Sources told La Vanguardia that Schneider Electric is interested in occupying the facilities through its InnoEnergy subsidiary. The report adds that discussions have taken place between the company and Spain's Ministry of Industry regarding an investment of up to EUR3.5 billion (USD4.1 billion), which would not only retain the automaker's current workforce, but would also create 3,000 direct jobs. The publication also sites a report by Spain's TV3 that suggests that LG Chem may also be interested in occupying certain locations. However, the initial-phase discussions suggest that the investment would be smaller and would save between 1,500 and 2,000 jobs. The Spanish government's unions and workers have been hoping for other companies to take over Nissan's manufacturing facilities in Barcelona following the confirmation of their eventual closure in late May. After being on strike for three months, workers managed to gain a delay for the site, which is now planned for closure at the end of 2021 instead of the initially planned end-2020. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
- The Finnish passenger car market recorded a steeper fall during
August. According to the latest data published by the country's
Automotive Information Centre (Autoalan Tiedotuskeskus: AuT),
registrations during the month fell 15.1% year on year (y/y) to
8,485 units. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
- Registrations for the year to date (YTD) are now down 18.3% y/y at 64,976 units.
- The light commercial vehicle (LCV) market retreated by 35.8% y/y to 1,038 units in August, while in the YTD it is now down by 23.2% y/y at 8,058 units.
- Registrations in the medium and heavy commercial vehicle (MHCV) category also dipped by 6.1% y/y to 232 units last month, and its YTD registrations are now down 22.6% y/y at 2,197 units.
- Swedish passenger car registrations recorded a further decline
in August, according to data published by trade association
Bilindustrieföreningen (BIL Sweden). (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's
Ian Fletcher)
- Sales decreased by 13.4% year on year (y/y) to 25,522 units. During the month, Volkswagen (VW) was the biggest selling brand with 3,736 units, albeit posting a decline of 15.2% y/y.
- It was followed by Volvo, which recorded a drop of 17.3% y/y to 3,424 units, while Kia ended the month in third with 2,819 units registered, an improvement of 25% y/y.
- The Swedish passenger car market has now fallen by 21.3% y/y to 173,925 units in the year to date (YTD). In the commercial vehicle categories, registrations of light commercial vehicles (LCVs) with a gross vehicle weight (GVW) of less than 3.5 tons dropped by 51.3% y/y to 2,881 units in August, while in the YTD, they are now down by 45.7% y/y at 16,996 units.
- Sales of heavy commercial vehicles (HCVs) with a GVW of more than 16 tons recorded a further improvement in August, with a gain of 12.1% y/y to 325 units last month. Nevertheless, in the YTD, sales of HCVs of more than 16 tons are down by 31.1% y/y at 3,116 units.
- The Russian light-vehicle market has returned to declining
sales in August, with a fall of 0.5% year on year (y/y) to 137,517
units, following an increase of 6.7% y/y in July. (IHS Markit
AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
- According to data compiled by the Association of European Businesses (AEB), this left the cumulative sales tally during the first eight months of the year down by 16.9% y/y at 880,198 units.
- This year-to-date (YTD) decrease follows the accelerated declines witnessed in the second quarter as a result of the Russian government's COVID-19 pandemic-related lockdown and the impact on business confidence and activity.
- Russia's leading automotive brand, AvtoVAZ's Lada, posted a 5% y/y sales decline to 28,621 units during last month. The brand slightly lagged the market average in the first eight months of the year, with an 18% y/y fall in registrations to 192,397 units.
- The Granta again retained its position as the market's best-selling car during last month, but its volumes declined to 10,550 units, in comparison to 11,132 units in August 2019. It also remained the best-selling car in the YTD with sales of 71,922 units, in comparison to 85,766 units in the first two-thirds of 2019. The Lada Vesta was the second best-selling car in Russia again in August and in the YTD.
- Second-placed Kia managed to outperform the market significantly with a creditable sales increase of 7% y/y to 19,818 units during last month.
Asia-Pacific
- Most APAC equity markets closed higher except for India -0.1%; Australia +1.1%, Japan +0.8%, Mainland China/South Korea +0.7%, and Hong Kong +0.1%.
- China's merchandise exports rose 9.5% year on year (y/y) in
August in terms of USD, accelerating from 7.2% y/y in July and the
third consecution month of expansion, according to the General
Administration of Customs (GAC). (IHS Markit Economist Yating Xu)
- Merchandise imports declined by 2.1% y/y in terms of USD, down from a 1.4% y/y contraction in the previous month.
- Recovery of global demand and relatively weaker supply were main drivers to China's export growth. Exports of machinery increased by 11.9% y/y, while high-tech products exports slowed. Meanwhile, overseas demand of clothes and home appliance increased notably and furniture exports maintained double-digits growth. Exports of pandemic prevention supplies maintained strong growth, but the momentum continued to slow and its contribution to headline export growth declined from 2.7 percentage points in July to 2.4 percentage points in August.
- By country, business recovery in the US led its purchase to rise by 20.0% y/y and exports to ASEAN and EU slowed but remained in double-digit growth and exports to Japan contracted slowly.
- Commodity price decline, supply-chain disruption and slowing domestic recovery combined drove down imports in August. Prices of imported crude oil, iron ore, and soybean declined 33.0% y/y, 10.1% y/y and 2.6% y/y respectively.
- The volume of soybean imports increased by 1.3% y/y, down 15.5 percentage points from the previous month and integrated circuit imports slowed as well.
- Strong recovery in exports and decline in imports led trade surplus amount to USD58.9 billion in August, up 70.0% from a year ago, compared to a 41.6% y/y increase in July.
- China's foreign change reserves (forex reserves) expanded to
USD3.16 trillion at the end of August, the fifth consecutive month
of growth, according to the State Administration of Foreign
Exchange (SAFE) on 7 September. The year-to-date forex reserves
have risen by USD56.7 billion from the end of last year. (IHS
Markit Economist Yating Xu)
- SAFE attributed the sustained growth in forex reserves to China's strong economic resilience and pricing of foreign assets. Under the monetary easing policies adopted by the US, non-dollar currencies have appreciated against the US dollar, which raised financial asset prices and the total value of forex reserves.
- Increasing settlement of exchange and overseas purchase of domestic RMB dominated assets, with stronger RMB, as well as August's trade surplus contributed to the increase in forex reserves.
- Although the COVID-19 pandemic is yet to be controlled globally and there are still many uncertainties in the financial markets, China's sustained economic recovery and constrained stimulus policy may continue to support a strong RMB and help to stabilize forex reserves over the near term.
- The ongoing opening up of financial markets will help to attract capital inflow and increase forex reserves in the long run.
- Fading infection fears domestically bode well for a sustained
recovery in Mainland China's services sector, which is essential
for stabilizing income prospects and reviving consumer demand.
Still, remaining pandemic-related restrictions would continue to
weigh on the economy's full return to normalcy. (IHS Markit
Economist Lei Yi)
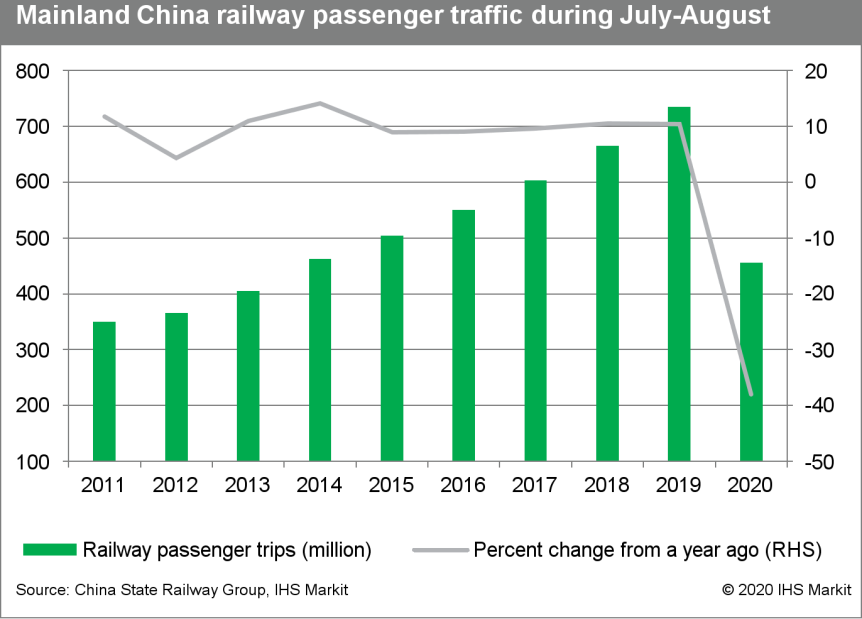
- According to the State Railway Group, railway passenger trips in mainland China totaled 456 million through the July-August summer holiday, a level last seen back in summer 2014. By month, railway passenger trips reached 207 million in July and 249 million in August.
- While summer passenger traffic level still represents year-on-year contraction of 38%, improvement has been notable compared with the first half of this year, during which railway passenger trips have recorded year-on-year decline of 54%.
- With the pandemic situation in mainland China largely brought
under control, recovery in transportation is set to continue
towards the year end, helping services sector to regain growth
momentum. Given services' essential role in job creation, this
would also support stabilizing employment and income prospects,
which in turn boosts private consumption. As of 7 September,
mainland China has reported zero domestically transmitted cases for
23 consecutive days.
- Nongfu Spring was officially listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange (8 September), with a market capitalization of HKD445.3 billion (USD57.4 billion), at the highest price of HKD39.84 per share. The IPO price was set at HKD21.5/share, initially intended to raise HKD8.149 billion. Bottled water contributed 61.9% of its total revenue in January-May 2020. Chinese media widely reported and discussed Nongfu's high gross profit margins in 2017-2019. Bottled water fetched 60.2%, RTD tea 59.7%, functional beverages 50.9% and juice 34.7%. Nongfu owns 10 water sources around the country, including Xinjiang Tianshan, Guangdong Wanlu Lake and Heilongjiang Daxinganling. Each water source is drawn with a radius of 500 kilometers, which covers a vast geographical area. This gives Nongfu an overwhelming competitive advantage in production costs such as distribution and warehousing. Proximity to water sources and consumers counts for bottled water margins. The company has 4,280 resellers, covering millions of retail outlets in tier three and below cities. Its huge economies of scale also give it the negotiation power in procurement of raw material such as PET. The company also produces juices, RTD coffee, plant-based yogurt and sparkling water and some agricultural products such as rice, fresh oranges and apples. In 2018, Nongfu acquired New Zealand's Otakiri Springs bottled water brand. Its brands are hardly known beyond China. Meanwhile, Nestle and Danone both have decided to focus on developing their high-end international brands and have sold their local Chinese bottled water brands. IHS Markit will publish a special report about China's bottled water market in the next couple of weeks. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Hope Lee)
- Ford is making steady progress on steering its Chinese business
back to growth after its sales in the world's largest auto market
plummeted to a five-year low in 2019. The sales report for August
released by Changan Ford, Ford's passenger-vehicle joint venture in
China, indicated sales of Ford-branded vehicles reached 16,623
units, up 10.2% month on month. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Abby
Chun Tu)
- The automaker said that sales volumes of Ford models in China during August were still slightly lower than during last August; however, specific sales figures from last August were not given.
- If locally produced Lincoln vehicles are included, Changan Ford said its sales rose by 37% year on year (y/y) to 20,229 units in August on the back of rising demand for the new-generation Explorer and Ford Escape.
- Ford's steady performance in August has again ignited hopes that its sales decline in China will bottom out in 2020 and the automaker will regain some momentum under the leadership of Chen Anning, Ford China's CEO.
- According to Changan's recent sales reports, Changan Ford posted sales growth for five straight months in August. Thanks to the continues sales rebound, Changan Ford has seen its sales rise 29% y/y in the first eight months of 2020 to around 140,000 units.
- A separate company statement released by Lincoln says the brand's sales increased 65% to 6,100 units in China in August, a new monthly record since Lincoln's official brand launch in the Chinese market in 2012.
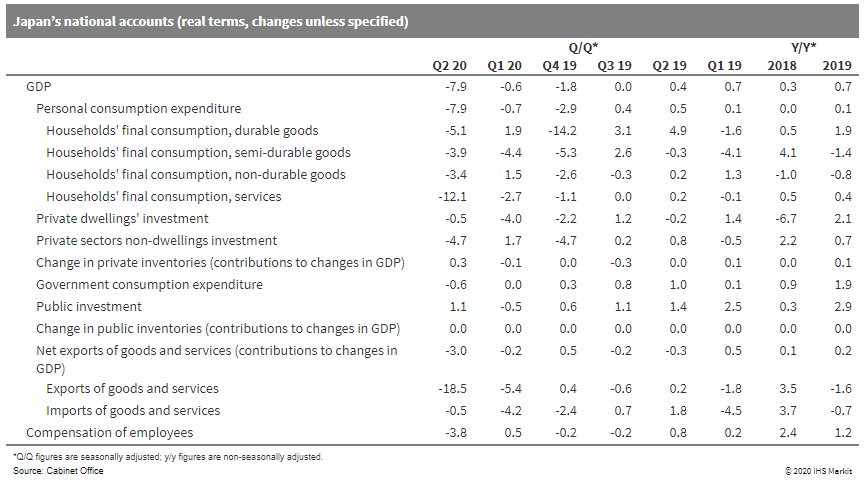
- Japan's real GDP growth for the second quarter of 2020 was
revised down to a 7.9% quarter-on-quarter (q/q) drop (or down 28.1%
q/q annualized) from a 7.8% q/q decrease (or 27.8% q/q annualized).
(IHS Markit Economist Harumi Taguchi)
- The major reason for the downward revision was weaker private capex, which fell from a 1.6% q/q decline to a 4.7% q/q drop as. Private residential investment and public demand were also revised down slightly, and this was partially offset by upward revisions to consumer spending and changes in private inventories.
- The decline for capex largely reflected the fourth straight quarter of contractions for investment in machinery and equipment (down 5.0% q/q) and a 16.2% q/q drop in investment in transport equipment. The steep fall of investment in transport equipment partially reflected the temporary closure of some auto plants because of containment measures and disruptions in the supply chain. A sizeable decrease in production and containment measures increased inventories of raw materials and distribution stocks. The softer decline in consumer spending largely reflected a milder fall for spending in services, which was not fully available with the first preliminary release.
- According to the Ministry of Finance, the current-account surplus fell by 27.4% from a year earlier to JPY1.5 trillion (USD13.8 billion) on a non-seasonally adjusted basis and by 8.1% month on month (m/m) to JPY964.0 billion on a seasonally adjusted basis. However, the trade balance turned to a surplus of JPY137.3 billion on a non-seasonally adjusted basis (or JPY55.7 billion on a seasonally adjusted basis). While the narrower current-account surplus was due largely to a decline in income from direct investment, reflecting sluggish business conditions under the COVID-19 virus pandemic, the softer contraction of exports (due to easing containment measures abroad) in conjunction with weaker imports suggests that a solid rebound in net exports could contribute to a return to positive growth of real GDP in the third quarter.
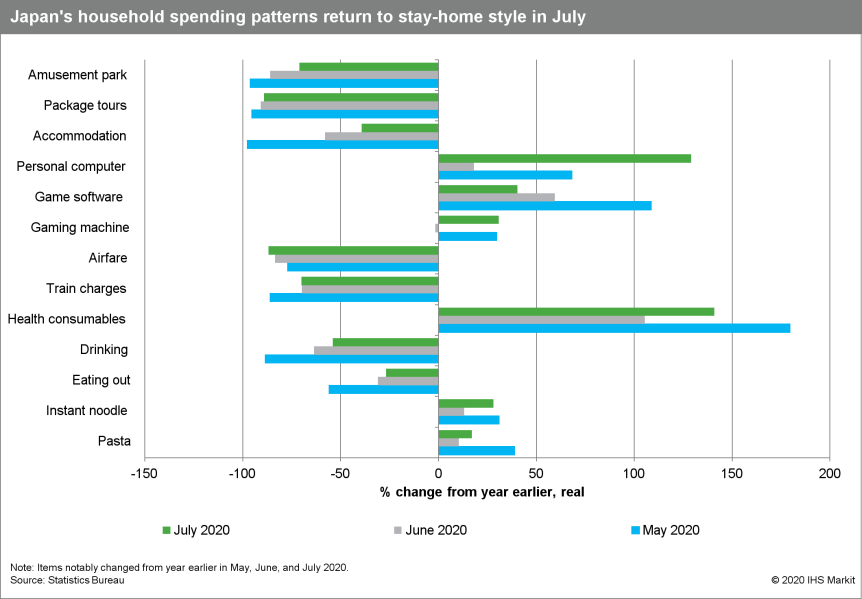
- Monthly real household expenditure for July suggests easing
momentum of the upside from the resumption of economic activities,
with a decline of 6.5% m/m in July following a 13.0% m/m rise in
the previous month. The y/y contraction widened to 7.6%. An uptrend
in new confirmed COVID-19 cases made consumers cautious about
crowds and travel, which led consumer's pending patterns to shift
back to stay-home/work-form-home styles. Spending in clothing and
footwear and furniture and household utensils declined sharply, and
spending in travel, leisure, and drinking/eating-out remained
sluggish.
- The Japanese government has guaranteed JPY104 billion (USD978 million) of a loan from the Development Bank of Japan (DBJ) to Nissan Motor, reports Reuters, citing an unnamed source with knowledge of the matter. According to the report, this means that the Japanese government is now a guarantor of over 40% of the JPY713-billion loan to the automaker. The report states that the automaker has previously secured loans of JPY120 billion from Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group and JPY50 billion from Sumitomo Mitsui Financial Group. However, these loans are not guaranteed by the Japanese government. The need for the government guarantee indicates that the financial institutions are quite cautious about lending money to automakers. In July, Nissan was reported to have received JPY832.6 billion in financing from its creditors since April to improve its cash position and help to offset declining sales due to the COVID-19 virus pandemic. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Nitin Budhiraja)
- The Japan Automobile Importers' Association (JAIA) has reported
that imported vehicle sales in the country declined by 13.1% year
on year (y/y) during August to 21,648 units. This figure includes
sales of foreign brands' imported vehicles, which fell by 15.4% y/y
to 18,183 units, and Japanese brands' imported vehicles, which
increased 0.9% y/y to 3,465 units. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's
Nitin Budhiraja)
- Mercedes-Benz continued to lead the imported market with a 18.4% share, its sales declining by 7.2% y/y to 3,983 units in August.
- Volkswagen (VW) followed in the rankings with sales of 3,014 units, down 6.7% y/y, and a market share of 13.9%.
- BMW took third place with a market share of 11.3% and sales of 2,464 units, down 32.6% y/y.
- Among the Japanese brands, Nissan sold 1,512 imported units last month, compared with 505 units in the same month last year, followed in the rankings by Toyota with 1,096 units, down 29.2% y/y.
- In the year to date (YTD), sales of imported vehicles in Japan are down 20.9% y/y to 180,315 units.
- Imported vehicle sales in Japan declined for an 11th consecutive month in August. However, the decline slowed in August, compared with the fall in July, as the government began to ease the COVID-19 virus outbreak-induced restrictions.
- Hyundai Motor Group and SK Innovation have agreed to cooperate in the development of a sustainable ecosystem for electric vehicle (EV) batteries, including battery sales solutions, battery management services, and battery reuse and recycling, according to a Hyundai press release. Under the partnership, Hyundai and SK innovation aim to strengthen the stability of the battery supply chain and create a virtuous cycle of resources from recycling to production; reduce carbon emissions; encourage optimal design that connects EVs and battery reuse; and create synergies by maximizing added value through the optimal design of batteries. Hyundai and SK Innovation are carrying out a process to collect and verify the Kia Niro EV's battery pack, while working together to reuse batteries for other purposes and extract economically valuable metals such as lithium, nickel, and cobalt. Furthermore, Hyundai Motor Group and SK Innovation plan to synergize their respective affiliates' business infrastructures and capabilities spanning diverse industries, thereby strengthening their battery competitiveness and expanding the growth of related sectors. The latest development follows Hyundai Motor Group Executive Vice-Chairperson Chung Euisun's meeting with SK Group Chairman Chey Tae-won in July, when they discussed possible co-operation on next-generation EV battery technologies, power management chips, and the "battery-as-a-service (BaaS)" platform. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
- Singapore-based energy utility company SP Group has announced a strategic investment in electric vehicle (EV)-charging company The Mobility House AG (TMH) (operating from Munich, Zurich, and Belmont), to explore smart charging and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) feasibility in Singapore, according to a TMH press release. "V2G is the basis for the energy world of the future - and thanks to our intelligent software, our partners will be able to access it and make use of all the opportunities it holds. With SP on board, it gives me great pleasure to see all those years of hard work at The Mobility House pay off and that we will now be able to cover a global market," said TMH CEO and founder Thomas Raffeiner. Significance: SP Group will leverage TMH's expertise and technology in Europe and the United States to expand Singapore's electric mobility capabilities. TMH's collaboration with SP will expand its presence in Asia. Together, the two companies aim to accelerate the goal of a zero-emission future on a global scale and realize the commercial integration of EVs into the energy market. TMH offers V2G and vehicle-to-home (V2H) platforms for integrating EV batteries into power grids using intelligent charging, energy, and storage solutions. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-8-september-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-8-september-2020.html&text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+8+September+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-8-september-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Daily Global Market Summary - 8 September 2020 | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-8-september-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+8+September+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-8-september-2020.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}




