Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
BLOG
Sep 11, 2020
Daily Global Market Summary - 11 September 2020
Global equity markets closed mixed across each region, with the US markets having a particularly volatile day. European credit indices were wider across IG and high yield, while European benchmark government bonds were higher across the region. Brent crude closed lower, while WTI was slightly higher. US government bonds and the US dollar were close to unchanged on the day, as both rallied on the open of the US equity markets after being lower overnight.
Americas
- US equity indexes closed mixed after a rollercoaster ride of a trading session; Russell 2000 -0.7%, Nasdaq -0.6%, S&P 500 +0.1%, and DJIA +0.5%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed -1bp/0.67% yield and 30yr bonds flat/1.42% yield.
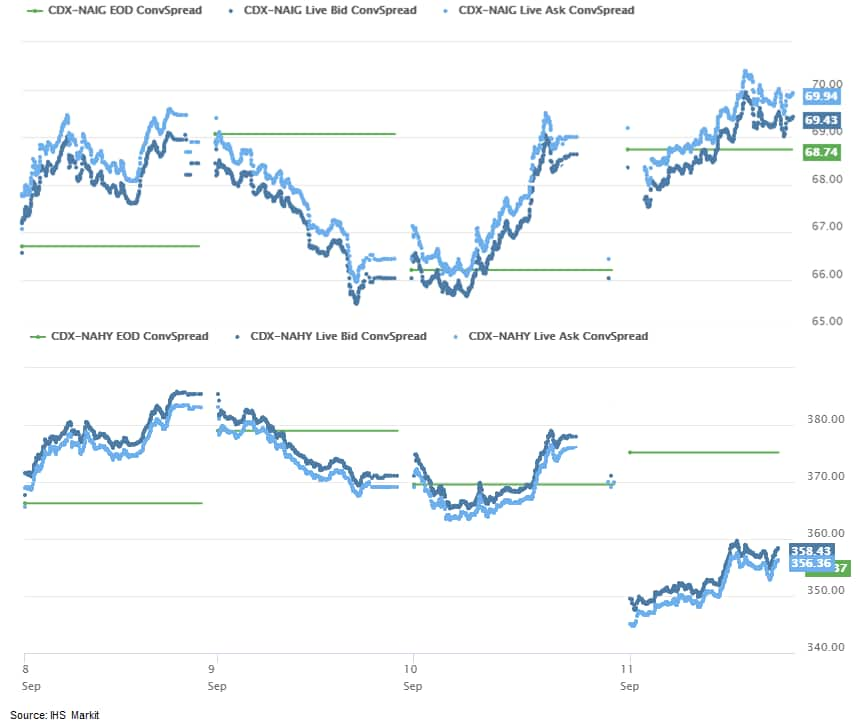
- CDX-NAIG closed +1bp/70bps and CDX-NAHY -20bps/355bps (series
34.9 now OTR), which is +3bps and -11bps week-over-week,
respectively.
- DXY US dollar index closed -0.1%/93.26.
- Gold closed -0.8%/$1,948 per ounce.
- Crude oil closed +0.1%/$37.33 per barrel.
- The US consumer price index (CPI) rose 0.4% in August following
0.6% increases during each of the prior two months. During August,
the CPI for energy rose 0.9% while the food index rose just 0.1%.
The core CPI, which excludes the direct effects of movements in
food and energy prices, rose 0.4%. (IHS Markit Economists Ken
Matheny and Juan Turcios)
- Price declines in sectors that experienced plummeting demand due to COVID-19 have been partially reversed over the last three months. The core CPI rose 1.2% over the last three months (not annualized) following a 0.6% decline over the February-to-April period. The three-month change in the overall CPI rebounded from -1.3% as of May to 1.5% as of August.
- Despite recent monthly increases, core and headline inflation remains subdued and below pre-COVID rates. Twelve-month increases for core and headline CPI were low in August at 1.7% and 1.3%, respectively, well below pre-pandemic rates of 2.4% and 2.3%, respectively.
- A sharp increase in the index for used cars and trucks (5.4%) accounted for approximately 40% of the increase in the core CPI in August. Other categories within the core CPI posting large swings included apparel (0.6%), airline fares (1.2%), and lodging away from home (0.9%). Rent of primary residence and owners' equivalent rent each rose just 0.1%. Increases in these two components have slowed since last winter.
- Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) data collection efforts continued to be hampered by the COVID‑19 pandemic. Despite extra efforts, the percentage of prices not available for the CPI was above historical norms in August.
- Flint Hills Resources (Wichita, Kansas) has agreed to sell its expandable polystyrene (EPS) business in Peru, Illinois, to private equity fund Balmoral Funds (Los Angeles, California). The companies signed a definitive agreement for the fund to purchase and operate the EPS business through a management buyout led by industry veteran Brad Crocker, who will serve as CEO, they say. The transaction, for an undisclosed amount, is expected to close before the end of the year. The EPS production facility at Peru is one of North America's leading EPS resin producers, according to Balmoral. Flint Hills acquired the EPS plant as part of its $350-million purchase of Huntsman's US polymers business in 2007. The acquisition by Balmoral "gives us the opportunity to invest further in the business and expand on its substantial growth potential," says EPS plant manager Chris Eager. Balmoral "typically invests in companies that have revenues [of] $30-500 million and require equity investments of $10-60 million," it says.
- US commercial vehicle and engine manufacturer Navistar has
posted a net loss of USD37 million on USD1.7 billion in revenue in
the third quarter of financial year (FY) 2019/20. Separately, the
company has confirmed receiving a revised bid to acquire the
company from Volkswagen (VW)'s Traton trucking division. (IHS
Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- In the third quarter (ended 31 July 2020) of FY 2019/20, Navistar's revenues decreased 45% year on year (y/y), which the company said was largely as a result of economic restrictions related to efforts to contain the spread of the COVID-19 virus. However,
- Third-quarter FY 2019/20 revenues were also in comparison to year-earlier revenues that came at the peak of the prior industry cycle. The medium- and heavy-duty truck manufacturer also said that in its core business (class 6 to 8 trucks and buses in the United States and Canada), revenues were down 53% y/y.
- Navistar also stated that its efforts to conserve cash and reduce costs were having a positive effect, and the company closed the quarter with USD1.6 billion in manufacturing cash, cash equivalents, and marketable securities.
- Navistar chief financial officer Walter Borst said that the company's focus on temporary cash conservation actions was shifting to sustainable cost savings. Navistar is targeting selling, general, and administrative expenses in the range of 7% to 9% of sales revenues.
- Although Navistar reported a loss in the third quarter of FY 2019/20, the cause was largely external shocks to the automotive industry, and Navistar showed financial discipline in those areas that it could control. The company's EBITDA remained positive in the quarter, although they dropped from USD281 million in third quarter FY 2018/19 to USD73 million in third quarter FY 2019/20.
- The Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (Instituto
Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística: IBGE) has reported that
industrial production jumped 8.5% month on month in July.
Plummeting values in March and April have been almost compensated
by strong growth in May, June, and July, such that industrial
production was down only 3.1% year on year (y/y) in July. (IHS
Markit Economist Rafael Amiel)
- According to the IBGE, retail sales have performed even better as by July they had jumped 29.3% from their April trough. This indicator has fully recovered and it is now 5% above its pre-COVID-19 virus pandemic levels.
- Another data release by the IBGE earlier this week showed that inflation amounted to 0.24% in August and annual inflation was 2.44%. Meanwhile, core inflation amounted to 0.9% at the end of the 12-month period ended August 2020. The core price index excludes items with high price volatility such as energy and agricultural prices.
- Inflation in August was driven by higher energy prices, mainly gasoline (petrol), and electricity. In addition, (controlled) tariffs for internet services were allowed to go up 8.5%.
- The Argentine grower and processor Ledesma has reported sales of ARS28.9 billion (USD3.7 billion) and net profits reached ARS735.9 million in the 2019-20 marketing year (June-May) despite Covid-19, after suffering losses in two previous years. The company's fruit crop reached 105,620 tons, and it sold 34,760 tons in the fresh market and processed 67,190 tons to produce juices and purées. In addition, it produced 472 tons of essential oils, mainly citrus-based. It exported 95% of its production. Its fresh orange exports totaled 28,420 pallets, mainly Valencias. On the other hand, the company only exported 477 pallets of fresh lemons. Ledesma expects to process 3.8 million tons of sugar cane to produce sugar (77%) and alcohol (23%). Bioethanol may take 90% of the sugar output. Its soya, wheat, maize and oat crops reached 59,973 tons (12% less year-on-year), 33,739 tons (35.9% less), 45,143 tons (60.5% more) and 179 tons (three and a half times more). Finally, its meat production totaled 4,838 tons (23% more), mainly beef. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Jose Gutierrez)
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- European equity markets closed mixed; Spain -0.8%, Germany -0.1%, Italy flat, France +0.2%, and UK +0.5%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed higher across the region; Germany/UK/France -5bps, Spain -4bps, and Italy -3bps.
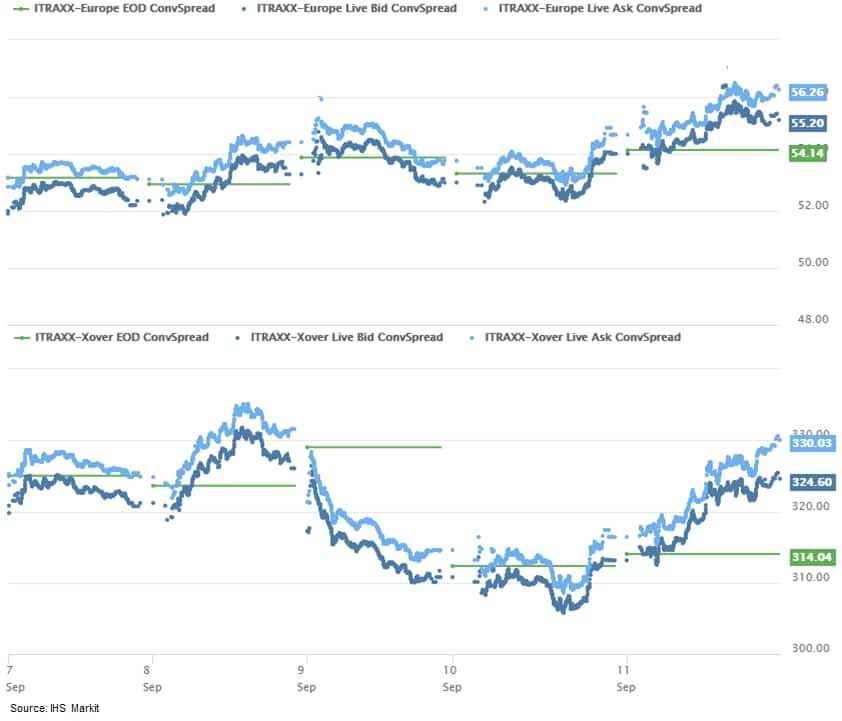
- iTraxx-Europe closed +2bps/56bps and iTraxx-Xover
+13bps/327bps, which is +3bps and +2bps week-over-week,
respectively.
- Brent crude closed -0.6%/$39.83 per barrel.
- Chemicals production in the EU suffered a steeper fall in
percentage terms in the first half of 2020 than the worldwide
decline in chemicals output, plunging by 5.2% year on year (YOY)
compared to a global decrease of 3.4% YOY, according to European
chemical industry association Cefic's latest quarterly report.
- Producer prices in the EU27 countries were 4.8% lower to end-June than in the first half of 2019, with total combined domestic and export chemical sales for the first five months of the year falling by 7.9% YOY to €202.2 billion ($239.6 billion), it says.
- Weak domestic demand in Europe and the deterioration of the business environment due to the impact of COVID-19 negatively impacted sales, it says. Chemical production capacity utilization in the EU27 area in the first half of the year was about 9% below the 2019 equivalent figure.
- Cefic says that chemicals production in France and Italy has been "most impacted" by the COVID-19 crisis compared to other countries. Chemicals output in France and Italy fell by at least 12% in first-half 2020 compared to the previous year, followed by Spain and Portugal with a YOY drop of more than 6.5%.
- Belgium and the Netherlands registered a decrease of about 6% in chemicals production over the same period, with Germany reporting a drop of 3.6%, while Poland saw output decline by 1.7%. The UK reported a YOY drop of 6.2% in chemicals output, Cefic adds.
- Some of the EU's chemical sectors providing for essential supply chains during the pandemic did post growth over the period, with soaps and detergents reporting production growth of 2.9% for the first six months of 2020 compared to last year, it notes.
- EU27 chemical exports outside the EU27 area in the first five months of 2020 fell by €2.7 billion, or 3.7%, compared to the prior-year period to €72.4 billion, according to the report.
- EU27 chemical exports of petrochemicals to the US rose by €2.3 billion, or 8.8%. This was countered, however, by a significant decrease of EU27 exports to the US in specialty chemicals and consumer chemicals over the same period.
- EU27 chemical exports to China totaled €6.3 billion, up 1.2% YOY. Data for April and May showed two consecutive declines in EU27 chemical exports outside of the area, with "no clear sign of recovery" for exports being seen, according to Cefic.
- Chemical imports into the EU27 countries from outside the area declined by 1.4% YOY, or €800 million, to €56.2 billion in the first five months of 2020.
- A fall in imports of polymers, down €2.1 billion, and consumer chemicals, down €400 million, contributed most to the decrease in total imports, it says. There was, however, a "significant increase" of imports into the EU27 area of specialty chemicals and petchems over the same five-month period, it adds.
- EU27 chemical imports from China increased by 0.6% YOY to €6.5 billion.
- The United Kingdom's Office for National Statistics (ONS)
reports that the economy grew by 6.6% month on month (m/m) in July
and was preceded by m/m gains of 2.4% m/m in May and 8.7% in June.
(IHS Markit Economist Raj Badiani)
- Meanwhile, in annual terms, the economy in July was 11.7% smaller compared with a year earlier.
- Nevertheless, the UK's monthly GDP was still 11.7% below its pre-pandemic level seen in February.
- The further easing of the COVID-19-virus lockdown measures occurred in early July, with hair salons, pubs, and restaurants allowed to reopen. Indeed, accommodation and food services rose by 140.8% m/m in July but remained 60.1% below their pre-COVID-19-virus February level. Some children returned to school in July, resulting in education services output rising by 21.1% m/m.
- Industrial production rose by 5.2% m/m in July, led by improving manufacturing activity. The manufacturing sector saw all 13 sub-sectors recover further lost ground from the large falls across March and April. However, despite the continued recovery in July, production output was still 7.0% lower than the level in February, with manufacturing 8.7% lower.
- The economy contracted by 7.6% in the three months to July compared with the three months to April. The chart above shows that the main sectors reported lower rates of contraction in May-July.
- The rise in GDP in July points to a record GDP gain in the third quarter of 2020, spelling the end of the recession during the first half of the year. A COVID-19-virus lockdown-exit strategy will deliver an immediate resumption of growth, estimated at 11.5% quarter on quarter (q/q) and 2.6% q/q in the third and fourth quarters of 2020, respectively, in the August forecast update.
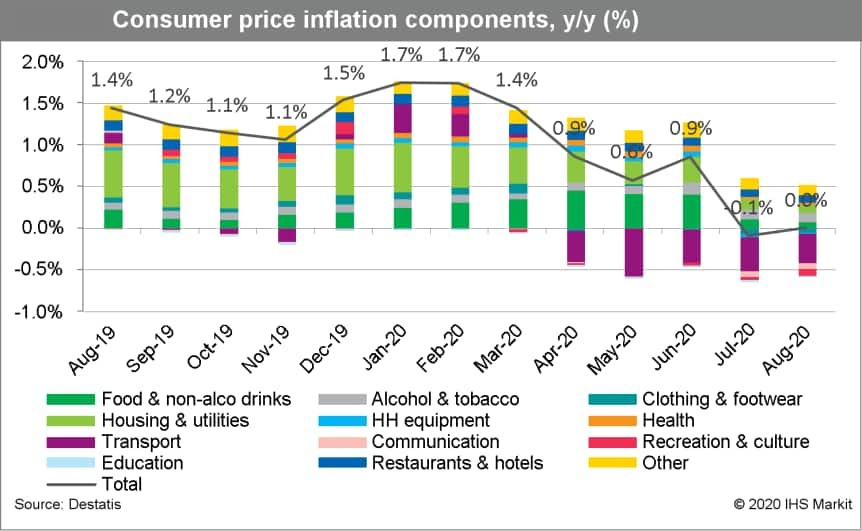
- Germany's final August data based on national methodology from
the Federal Statistical Office (FSO) showed a month-on-month (m/m)
decline by 0.1% and a slight increase of the annual inflation rate
from July's -0.1% to 0.0%, confirming the 'flash' data released on
31 August. (IHS Markit Economist Timo Klein)
- The European Union-harmonized consumer price index (CPI) measure declined by 0.2% m/m, leading to a marginal dip of its annual rate from 0.0% to -0.1%.
- Germany's harmonized inflation nonetheless moved above the eurozone average (-0.2%) again, and the spread between the two actually switched from -0.4 percentage point in July to 0.1 percentage point in August. This demonstrates that Germany's VAT cut was largely to blame for the inflation drop in July, whereas underlying trends played more of a role elsewhere in the eurozone.
- At 0.7% year on year (y/y), the CPI excluding food and energy as a measure of core inflation remained steady compared with July, but this is about half the annual pace measured on average between mid-2019 and mid-2020. The component breakdown reveals that energy had a modest dampening impact in m/m terms in August (-0.5%), but base effects pushed up its annual rate from -6.7% to -6.3%. The prices of food and recreation and culture (which includes package tours) had the largest dampening impact on August's inflation, whereas clothing and footwear and household equipment and furniture were the components exerting the most upward pressure.
- Unlike for July, the FSO did not attempt to quantify possible effects from the VAT cut on measured inflation, other than stating that this factor remains an important dampening influence on the y/y comparison throughout the second half of 2020.
- The split between goods and services shows that inflation in the former has become slightly less deflationary (the y/y rate edged up from July's -1.4% to -1.3% in August), whereas service-sector inflation has moderated from 1.2% to 1.0%.
- Average underlying inflation, which had been at around 1.2%
during 2016-17 before firming to the 1.5% area during the last two
years, will now remain below 1% throughout the second half of 2020,
and will rebound to the 1.5% area in early 2021.
- The working group on Germany's tax revenue estimates for the
whole public sector, comprising Ministry of Finance officials from
federal and Länder authorities meeting twice a year to provide the
basis for budgetary planning, has reduced its projections further
for 2021-24, compared with those published in May. (IHS Markit
Economist Timo Klein)
- The projection for 2020 has stayed broadly unchanged at EUR717.7 billion, but this steady overall figure hides the fact that various fiscal support measures passed during June-August are expected to lead to tax revenue losses of EUR25.5 billion that are estimated to be exactly offset by revenue improvements related to less pessimistic growth assumptions.
- Estimates for 2024 reflect revenue losses from legislative changes that are either exacerbated by a worsened GDP growth assumption (2021) or are only partially offset (2022-24).
- The underlying assumption for nominal GDP growth in 2020 was lifted from -4.7% (May's projection) to -4.0%, whereas the growth assumption for 2021 was reduced from 6.8% to 6.0%. The assumptions for 2022-24 were raised from 2.8% to 3.0%.
- Wage growth assumptions are even more important for tax revenue estimates. For 2020, the projection has improved slightly from -1.5% to -1.2%, and was curtailed from 4.1% to 3.2% for 2021, while the assumptions for 2022-24 were left at 2.8%.
- Corporate and asset income is much more sensitive to both the economic cycle and changes in legislation. Thus, the projection for 2020, which had been at a catastrophic -21.1% in May, was lifted substantially to -8.3%. This mirrors foremost the various fiscal support measures (short-time work subsidies, grants, and loans) that have prevented an early surge of company insolvencies and the tax revenue losses that this would have entailed. The flip side of this is that the projection for 2021 has been drastically reduced from 22.8% to 3.5%. Projections for 2022-24 were lowered slightly from 3.8% to 3.6%.
- The government projects that overall public-sector tax revenues will decline from EUR799.3 billion in 2019 (then up by 3.0% year on year [y/y]) to EUR717.7 billion in 2020 (-10.2% y/y) before rebounding by 7.7% to EUR772.9 billion in 2021 and 4.9% to EUR810.5 billion in 2022. Revenue growth in 2023-24 is projected at an average of 4.4%.
- The Volkswagen (VW) Group introduced a sustainability rating for direct suppliers one year ago, and a comprehensive system developed by RCS Global now also tracks adherence to sustainability criteria at sub-suppliers, refineries, smelters, mines, and recyclers. New guidelines for improvements issued to suppliers make an active contribution to achieving improvements when risks and shortcomings are identified. Serious audit violations may even lead to the disqualification of suppliers from the supply chain. That applies, for example, to small-scale mining operators when child labor cannot be ruled out. The approach builds on the Due Diligence Guidance of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Under the co-operation with RCS Global it has already been possible to identify 134 sub-suppliers and 18 mines in the VW Group's battery supply chains and they will be monitored and removed from the company's list of suppliers if any violations of the code are discovered. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
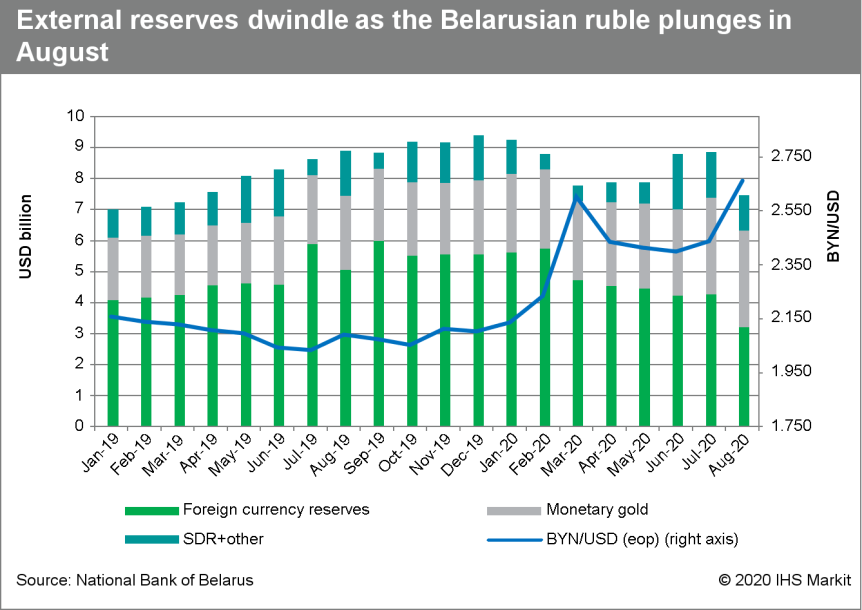
- Total external reserves (including gold and other external
assets) at the National Bank of Belarus (NBB) fell by some 16%
during August to USD7.5 billion, while foreign currency reserves
declined by nearly 25%, to USD3.2 billion. (IHS Markit Economists
Alex Kokcharov and Venla Sipilä)
- In cumulative terms, total external reserves contracted during the first eight months of the year by around 21%, while foreign currency reserves ended August some 42% lower than at the beginning of the year.
- The value of total reserves fell despite the increase in the price of gold counteracting the impact of the decline in foreign currency reserves on total external assets. In value terms, the NBB's gold reserves increased by 30% during January-August.
- Reserves were drained by the central bank engaging in foreign currency interventions to stem the depreciation of the Belarusian ruble. Confidence in the domestic currency has been damaged by social unrest on an unprecedented scale following the contested 9 August presidential elections, which has been increasing demand for foreign exchange.
- As reported by CEEMarketWatch, the NBB used around USD352 million for external debt service during August.
- The ruble's value against the US dollar weakened by 8.4% during
August alone, ending the month at a record low of BYN1.00:USD2.663.
In cumulative terms, the Belarusian currency depreciated by 21%
during the January-August period.
Asia-Pacific
- Most APAC equity markets closed higher except for Australia -0.8%; Mainland China +0.8%, Hong Kong +0.8%, Japan +0.7%, and India/South Korea flat.
- According to the Business Outlook Survey for the third quarter
of 2020, Japan's current Business Survey Index (BSI) for large
enterprises rose by 49.6 points to 2.0, suggesting improving
business conditions following three quarters of decline. (IHS
Markit Economist Harumi Taguchi)
- Despite a V-shaped recovery in line with the resumption of business activity, the seasonally adjusted reference series of the BSI remains below zero (up 42.5 points to -1.1), reflecting persistent sluggish business conditions for large manufacturing enterprises (up 42.5 to -5.1).
- The future-conditions BSI suggests all enterprises anticipate a gradual improvement of business conditions. However, the outlooks remain gloomy, as the BSI for large enterprises shows easing upward momentum, while the BSI for small and medium-sized enterprises for the next two quarters is holding at zero. The weak outlooks are largely attributed to outlooks of sluggish domestic business conditions.
- The outlook for sales of all industries in fiscal year (FY) 2020/21 (ending 31 March) was revised down to a 6.8% year on year (y/y) drop, from a 5.2% y/y drop, because of outlooks for a weak recovery.
- Ordinary profit outlooks were revised up slightly to a 23.2% y/y drop, from a 23.5% y/y decline, largely reflecting upward revisions in the information and communication, and wholesale and retail sales sectors.
- Labor demand remains resilient, as a broad range of enterprises (particularly non-manufacturing industries) faced labor shortages.
- Fixed investment plans for FY 2020/21 were revised down from a 4.4 % y/y drop to a 6.8% y/y drop.
- Toyota Research Institute-Advanced Development (TRI-AD) has announced that it will set up Woven Capital, a USD800-million global growth-stage investment fund, to add to its ability to achieve its vision of 'Mobility to Love, Safety to Live'. This will be part of the new Woven Planet Holdings, which will begin operations in January 2021. The investment fund will assist the holding company by investing in startup companies in the Toyota AI Ventures that are focused on developing innovative technologies and business models in areas such as autonomous mobility, automation, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, data and analytics, connectivity, and smart cities. Woven Capital will also invest in other venture capital funds to broaden and accelerate its global coverage. TRI-AD was established in March 2018 as a joint venture (JV) between Toyota Motor Corporation, Denso, and Aisin to provide software for autonomous vehicles (AVs). TRI-AD is helping Toyota achieve its goal of introducing a Level 2 AV commercially in 2020. In July, TRI-AD announced that it will expand and improve its operations by forming Woven Planet Holdings and two new operating companies: Woven CORE and Woven Alpha. The new holding company will involve a capital of JPY20 billion (USD188 million), while Woven CORE will involve JPY50 million and Woven Alpha JPY100 million. Woven Planet Holdings will act as a decision-maker for the entire group and provide corporate shared services to the operating companies. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Nitin Budhiraja)
- Zhejiang expanded its list of major investment projects to
include another 147 projects worth of CNY549.6 billion (USD78.5
billion) in total, of which CNY46.4 billion worth of investment
should be completed in 2020, according to the local development and
reform commission on 8 September. (IHS Markit Economist Lei Yi)
- Newly added projects cover sectors including agriculture, water resource management, transportation, energy, industry, urban development, and modern services.
- After this adjustment, Zhejiang now has 817 major projects arranged for 2020, with a total investment value of CNY3.6 trillion; CNY461.4 billion worth of investment is set to be completed within 2020.
- The adjustment in investment plan is expected, as Zhejiang had completed 76.2% (CNY316 billion) of the pre-adjustment investment target though the end of July. In 2019, Zhejiang expanded the major project list in November, after completing the original full-year investment target of CNY390 billion in the first 10 months.
- The Chinese new vehicle market experienced sales gain for the
fifth straight month in August. New vehicle sales on a wholesale
basis increased by 11.6% year on year (y/y) to 2.19 million units
in China during the month, while production rose by 6.3% y/y to
2.12 million units, according to preliminary data from the China
Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM). (IHS Markit
AutoIntelligence's Abby Chun Tu)
- Thanks to a rebound in new vehicle demand that began in April, vehicle sales and production volumes in the year to date (YTD) are narrowing the gap each month with the equivalent period of last year.
- In the YTD for August, China's new vehicle sales were down 9.7% y/y at 14.55 million units, while production volumes contracted by 9.6% y/y to 14.43 million units.
- The passenger vehicle (PV) sales increased of 6.0% y/y to 1.76 million units in August, while PV production fell by 0.1% y/y to 1.69 million units.
- The CAAM definition of passenger vehicles includes sedans, sport utility vehicles (SUVs), multi-purpose vehicles (MPVs), and minivans.
- In the YTD, sales of PVs were down 15.4% y/y at 11.29 million units, while production of PVs fell 15.5% y/y to 11.18 million units.
- Commercial vehicle sales (including medium and heavy vehicles) continued to rally in August, although the pace of growth slowed compared with growth in July. Sales volumes of commercial vehicles surged 41.6% y/y to 431,000 units during August, contributing to the strong rebound in new vehicle sales.
- Driven by surging market demand, commercial vehicle production increased 42.8% y/y to 425,000 units in August.
- In the YTD, sales of commercial vehicles have risen by 17.3% y/y at 3.263 million units, while production of commercial vehicles increased by 19.3% y/y to 3.256 million units.
- Sales of new energy vehicles (NEVs), which include battery electric vehicles (BEVs), plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), and fuel-cell vehicles (FCVs) , increased 25.8% y/y to 109,000 units in August, while NEV production rose by 17.7% y/y to 106,000 units.
- The continued rebound in China's auto market has been aided by policy measures aimed at boosting sales. The incentives include city-level auto-purchase incentives in the form of subsidies and preferential policies in top-tier cities to ease controls on new vehicle registrations.
- IHS Markit's forecast on Greater China's light-vehicle production has been adjusted upwards in our August update. The forecast on light-vehicle production volumes in the region has been increased by 400,000 units and 73,000 units for 2020 and 2021 respectively, compared with our July forecast.
- Baidu has opened the "Apollo Go Robotaxi" service for the public in the Chinese city of Beijing, reports Xinhua News Agency. The company has deployed 40 robotaxis that run in a trial area with a total length of 700 kilometres (km). The route has 100 pick-up and drop-off locations covering major residential and business areas in the city's Yizhuang, Haidian, and Shunyi districts. Users can hail a robotaxi ride after registering on Baidu Maps or the Apollo website. Zhenyu Li, corporate vice-president of Baidu and general manager of Intelligent Driving Group, said, "Baidu Apollo will continue pushing for the commercial application of autonomous driving. With our technology and platform advantages, we will contribute more to the development of autonomous driving and smart transportation in Beijing and support the city to become a world-leading AI [artificial intelligence] innovation hub." Baidu is the first company to deploy robotaxis that are picking up passengers in Beijing. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Tesla's Model Y production in China is likely to begin ahead of schedule, as early as November, reports InsideEVs. The report mentioned that work is progressing rapidly on the second phase (Phase 2) of the Shanghai Gigafactory, at which the Model Y will be produced, and that the main structure of the plant has been completed. Tesla is said to have proceeded with "interior decoration" and "electromechanical works", with the former set to be completed by October and the latter by November. Several reports surfaced recently centering on the progress of the Shanghai Gigafactory's Phase 2. Information from these reports is still largely aligned with previous estimates given by Tesla regarding the Phase 2 progress. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Abby Chun Tu)
- Hyundai has kicked off a "global advocacy program" to explain its efforts in hydrogen fuel-cell technology and has expanded the availability of the Nexo fuel-cell electric vehicle (FCEV) in the United States. The new campaign is called Hydrogen to You (H2U) and it has the goal of raising awareness of Hyundai's leadership in hydrogen fuel-cell technology, featuring the Nexo FCEV. The H2U campaign is focused on Germany and the automaker has selected several Berlin-based brand ambassadors. Hyundai said in its statement on the new campaign, "The campaign challenges the ambassadors to reflect on the industries they work in and demonstrate how hydrogen fuel cell mobility fosters a sustainable lifestyle and positively impacts their everyday life, fostering a healthy environment and improving the economy and society for a better future." The H2U ambassadors include a DJ, a model, a scientist and "YouTuber", a photographer, a journalist, a tech influencer, and a car-tuning expert. Separately, Hyundai announced on 10 September that it has expanded the availability of the Nexo FCEV in the US by including a dealership in northern California in its network distributing the model. The availability of the Nexo in the US and Canada has been centered on California, as the state has more hydrogen refueling infrastructure than other regions. The expansion announced on 10 September includes the Nexo being available in Sacramento, California. In California, the Nexo is available for lease only, for a fee of USD379 per month for the Blue model and USD449 per month for the Limited model, and for a 36-month term. Sales of FCEVs are hampered by the availability of hydrogen refuelling, but Hyundai has been more involved in researching and deploying the technology than most automakers; the Nexo is the follow-up to the Tucson-based FCEV. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- Coal imports into India increase for the second consecutive month. As per the latest update from the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, steel production along with electricity generation in July 2020 surged 7% m-o-m. The rebound in steel production is triggered by the resumption of infrastructure activities by the government. However, cement production declined 8% m-o-m. Domestic coal production from India's largest miner CIL during August 2020 stood at 37.2 metric tons (mt) (down 1% m-o-m and up 7% y-o-y). The offtake for the said period stood at 44.3mt (up 2% m-o-m and 10% y-o-y). Despite the recovery in demand, CIL is still having high stockpiles calculated at close to 62mt (down 10% m-o-m but up 158% y-o-y). In the first eight months of the year, CIL production totaled at 409mt, up 1.1% y-o-y. For the same period, CIL dispatches are calculated at 373mt, down 8% y-o-y. Anticipating a rebound in demand from the power plants as well as industries the imported coal arrivals in the country have started recovering. As per IHS Markit's Commodities at Sea, total coal arrivals into India during August 2020 is calculated at 16.8mt, with thermal and metallurgical coal arrivals at 13.1mt (up 20% m-o-m, but still down 6% y-o-y) and 3.6mt (up 16% m-o-m and down 27% y-o-y), resp. Total coal arrivals were 19% higher versus the previous month but still 11% lower on an annual basis. In the first eight months of the year, total imported coal arrivals in the country were calculated at 140.8mt, down 15% y-o-y. Thermal and metallurgical arrivals during the first eight months of this year were calculated at 104mt (down 17% y-o-y) and 36.7mt (down 5% y-o-y), respectively. (IHS Markit Maritime & Trade's Rahul Kapoor and Pranay Shukla)
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-11-september-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-11-september-2020.html&text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+11+September+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-11-september-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Daily Global Market Summary - 11 September 2020 | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-11-september-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+11+September+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-11-september-2020.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}




