Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
BLOG
May 08, 2020
Daily Global Market Summary - 8 May 2020
A new record high US unemployment rate did little to stop the week's positive momentum in the global markets, as equities closed higher across the globe along with oil and IG/HY credit. Hopefully, the consumers who are still employed, and living in locations that are in the process of reopening, will help bring the global economy to that V-shaped recovery everyone is hoping for by increasing their spending with the same degree of unabated optimism as the equity markets.
Americas
- US equity markets closed higher on the day; Russell 2000 +3.6%, DJIA +1.9%, S&P +1.7%, and Nasdaq +1.6%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed lower at +5bps/0.69% yield.
- IHS Markit's CDX North America investment grade index closed -1bp/92bps and high yield -10bps/634bps.
- US nonfarm payroll employment declined by 20.5 million in
April, and the unemployment rate rose 10.3 percentage points to
14.7%. Both readings were unprecedented in their respective
histories. (IHS Markit Economists Ben Herzon and Michael Konidaris)
- Just as occurred in the March report, there was a large number of unemployed persons who were incorrectly counted as employed but absent from work. Had they been classified correctly, the April unemployment rate would have been roughly 20%.
- There was a historic drop in labor-force participation, as the participation rate plunged 2.5 percentage points to 60.2%. Prior to April, there had never been a decline larger than 0.7 percentage point. Had those who dropped out of the labor force been counted as in the labor force and unemployed, this would have boosted the unemployment rate by roughly 3 percentage points.
- Were it not for (a) and (b), then, the April unemployment rate would have been roughly 23%. As a point of reference, the peak unemployment rate during the Great Depression (of the 1930s) was about 25%.
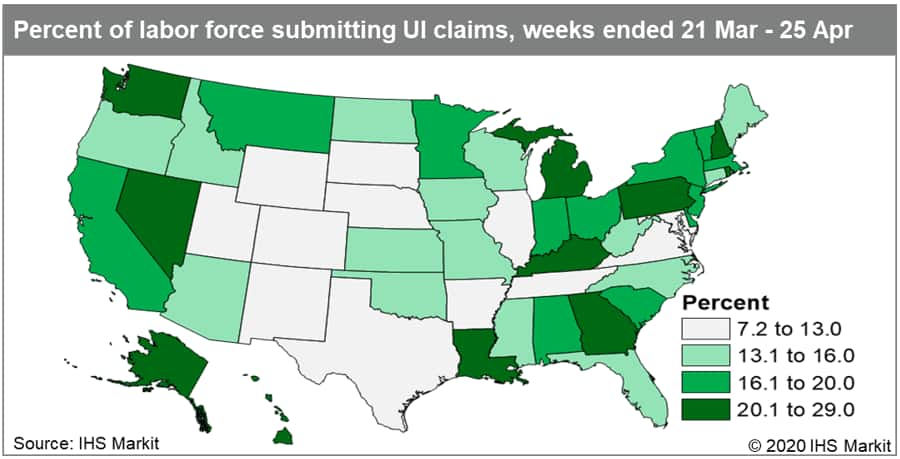
- Initial claims for unemployment insurance nationally measured
3,495,703 in the week ended 25 April, remaining near historically
high levels while steadily declining from the record high in the
week ended 28 March. During the initial spike in claims in
mid-March through the first half of April, states that instituted
early shutdown orders such as California, Pennsylvania, and New
York accounted for the largest shares of claims. In recent weeks,
however, Florida's claims have spiked considerably—the state
accounted for 3.3% of US initial claims between mid-March and early
April, which then swelled to 12.2% over the last two weeks of
April. (IHS Markit Economists Alex Minelli and Fran Hagarty)
- Outstanding nonmortgage consumer credit fell by $12 billion in March as the effects of COVID-19 ramped up over the course of the month. Revolving (mostly credit card) consumer credit plunged $28 billion (seasonally adjusted), the most on record and nearly double the runner-up, a decrease of $16 billion in November 2009. The ratio of nonmortgage consumer credit to disposable personal income was 25.5% in March, a 0.4-percentage-point step up from the prior month, as incomes fell but nonrevolving debt obligations remained stubbornly present as the crisis unfolded. (IHS Markit Economist David Deull)
- Crude oil closed +5.1%/$24.74 per barrel, which is +25% on the week.
- Noble Energy reported first quarter 2020 net loss of $3,963 million, compared with a net loss of $313 million a year ago. First quarter results included a $4.2 billion of impairments associated with Texas proved and unproved properties resulting from a decline in commodity prices and a $110 million of goodwill impairment related to Noble Midstream Partners Saddle Butte Pipeline system in the DJ Basin. Net loss including noncontrolling interest was $4,007 million. The company further slashed its 2020 capital budget to around $750 - 850 million in response the current macroeconomic and commodity environment, down about 53% from its original capital budget of $1.6 - 1.8 billion, announced in February 2020. The company cuts an additional $50 million in capex from its revised number announced on 15 March 2020. (IHS Markit's Upstream Companies and Transaction's Karan Bhagani)
- Nissan has issued a brief statement indicating that it will further suspend production in the United States, without providing any indication as to when it could resume. The statement simply reads, "Nissan is extending production downtime for most of its manufacturing facilities in the U.S. The company will continue to evaluate the status of the COVID-19 pandemic, current market demand and supplier readiness before setting a restart date." (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- Canada's job market was devastated once again with a 1,993,800 decline in net employment, which was weaker than IHS Markit expectations. The monthly decrease in full-time (down 1,472,000) positions was far greater than that in part-time (down 521,900) positions. The labor force participation rate declined 3.7 percentage points to 59.8% and the jobless rate climbed 5.2 percentage points to an eye-popping 13.0%. Most of the job cuts were in the private sector, with a sizable 1,874,000 decrease. Public-sector payrolls were down 76,800 and there were 43,100 fewer self-employed workers. The job losses over the past two months have been horrific and sharp. The recovery process will be long given the necessary multi-phased approach to reopen the economy while maintaining physical distancing. (IHS Markit Economist Arlene Kish)
- Canada's total housing starts declined 12.4% month on month (m/m) to 171,260 units in April, which was the lowest level since February 2019. Urban single-family starts plummeted 34.9% m/m while multifamily starts inched down 1.8% m/m. The decrease was mainly due to the halt in residential construction activity in Quebec (down 89.3% m/m) owing to the COVID-19 virus. Except Quebec, housing starts jumped 10.8% m/m to 166,415 units from 150,224 units in March. (IHS Markit Economist Chul-Woo Hong)
- Canadian automotive supplier Magna has released its first-quarter 2020 results, showing a sales decline of 18% year on year (y/y) to USD8.65 billion, compared with USD10.59 billion in the first quarter of 2019 (both ended 31 March). Adjusted EBIT declined 44% y/y in the first quarter to USD403 million on lower sales, reducing its margin to 4.7% from 6.8% in the first quarter of 2019 and 7.2% in the fourth quarter of 2019. Excluding the impact of foreign currency translation effects and divestitures net of acquisitions, Magna's consolidated sales declined 14% y/y, its power and vision sales dropped 5%, its seating sales fell 13%, its body exteriors and structures sales decreased 14%, and sales of complete vehicles shrank 29%. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
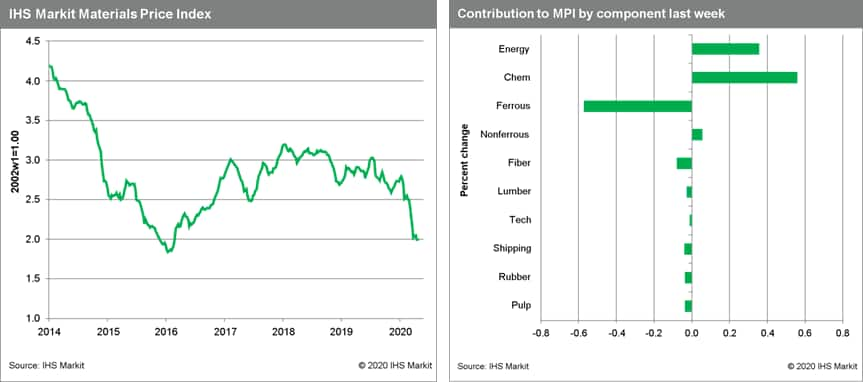
- Commodity prices, as measured by the IHS Markit Materials Price
Index (MPI), kept just above water last week, rising 0.2% as oil
prices rallied. he energy subindex led the MPI higher, rising 4.2%,
mainly due to a 35.2% jump in crude oil, which largely cancelled
out the previous week's 37.3% fall. West Texas Intermediate (WTI)
rallied from $3.30/barrel to $14.90/bbl on slowing inventory builds
in the US and falls in the US rig count. Thermal coal continued its
fall, due to weak global electricity generation. Having held up
through February, coal prices are now down 25% since late March.
Chemicals also rallied, increasing 3.9% on stronger ethylene and
propylene prices due to stabilizing feedstock costs. Ferrous prices
fell 1.3% on stronger iron ore deliveries into China. Even so,
ferrous prices are remaining stubbornly high due to weak
first-quarter shipments. Fiber, lumber, freight, pulp, DRAMs and
rubber all recorded small drops because of continuing concerns
about demand. (IHS Markit Pricing and Purchasing's Thomas
McCartin)
- Argentina's industrial production posted a 16.8% year-on-year (y/y) decrease in March, according to the country's National Institute of Statistics and Censuses (Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Censos: INDEC). The seasonally adjusted data show a 17.0% month-on-month (m/m) drop in March, a stark change in direction from the February figure; although the seasonally adjusted data provided by INDEC continue to be highly volatile, the March figure is unique. Construction activity collapsed in March, down by 32.3% m/m in seasonally adjusted terms and down by 46.8% y/y; construction permit data for March was not released because of the closure of public-sector offices during that time period as a result of the strict lockdown. The outlook for industrial production remains bleak. The country is working on a roadmap for a staggered quarantine exit, beginning on 10 May. (IHS Markit Economist Paula Diosquez-Rice)
- The central bank of Argentina (Banco Central de Argentina: BCRA) announced on 7 May the establishment of a credit guarantee line for micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs). These corporations will be able to access low-interest loans if they do not currently have bank loans in progress. Banks cannot deny access to these loans, which will be provided at a subsidized interest rate of 24% for companies with an 'MSME Certificate' from the Ministry of Productive Development. The program will provide funds of ARG22 billion (USD328 million). (IHS Markit Banking Risk's Gabrielle Ventura)
Europe/Middle East/ Africa
- Germany's Federal Statistical Office (FSO)'s external trade data for March (customs methodology, seasonally adjusted, nominal) are the first to reflect a significant impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. Exports suffered their largest monthly decline since the pan-German series started in August 1990, while imports slipped by less than half as much (for details, see table and charts below). Year-on-year rates (unadjusted) deteriorated from 0.3% to -7.9% for exports and from -2.8% to -4.5% for imports. These annual rates paint a misleadingly favorable picture as calendar effects were supportive in March; in seasonally and calendar adjusted terms, exports were 11.7% and imports 6.9% lower than a year ago. (IHS Markit Economist Timo Klein)
- Following a 17-year low of 2.3% in 2019, the Swiss unemployment rate has leapt higher to 3.3% within four months and is now increasingly likely to temporarily exceed the 4% level owing to the recession triggered by the COVID-19 virus pandemic. State Secretariat for Economic Affair's (SECO)'s data reveal that Switzerland's seasonally adjusted unemployment rate increased markedly in April, rising by 18,830 people or 13.5% month on month (m/m) to 153,818 people. This compares with just 105,000 in December 2019, the end-point of a downward trend that started in mid-2016 at roughly 150,000. In the forthcoming May forecast round, IHS Markit will predict that Switzerland's GDP will plunge by 6.5% in 2020 and that the average unemployment rate, which stood at 2.3% in 2019, will exceed 3.5% and stand above 4.0% at the end of the year. (IHS Markit Economist Timo Klein)
- During its session yesterday (7 May), the Czech National Bank (CNB) reduced the policy interest rate by a larger-than-expected 75 basis points, to 0.25%. That is down from 2.25% in February. Price pressures are projected to ease in the coming months as weaker domestic demand and falling fuel costs outweigh the inflationary impact of the depreciating koruna and rising food costs. As a result, inflation is projected to return to the upper limit of the 1-3% tolerance band over the next few months, hitting the 2% target by the end of 2021. GDP is projected to fall 8.0% in 2020 before recovering to +4.2% in 2021. The pre-pandemic level of GDP is not likely to be achieved by the end of next year, mainly due to a drop in fixed investment. (IHS Markit Economist Sharon Fisher)
- Brent crude closed +5.1%/$30.97 per barrel.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed mixed; Italy -9bps, Spain -3bps, France/UK flat, and Germany +1bp.
- European equity markets closed higher across region; Germany +1.4%, France/Italy +1.1%, and Spain +0.8%.
Asia-Pacific
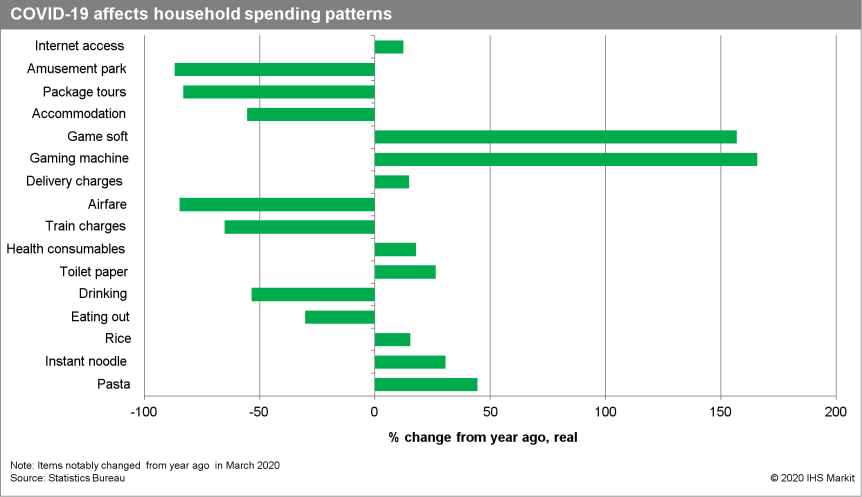
- Japan's nominal monthly cash earnings continued to rise, but
softened to 0.1% year on year (y/y) in March, while real monthly
cash earnings fell by 0.3% y/y. The softer increase for nominal
wages reflected a 0.3% y/y drop in special earnings and a 4.1% y/y
decline in non-scheduled cash earnings. Restriction measures for
COVID-19 also led to the sharp decline in monthly household
expenditures by 4.0% in March (see chart below for details):
- Japan has approved Gilead Sciences (US)' remdesivir as a treatment for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), according to Nikkei Asian Review, citing a press briefing by Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW). The MHLW has approved remdesivir for patients with severe COVID-19 symptoms. The approval comes three days after the US company filed for fast-track approval in Japan. (IHS Markit Life Science's Sophie Cairns)
- Teijin reports a 44% fall in net profit to ¥25.25 billion ($237.4 million) for the full fiscal year ended 31 March, on sales down 3.9% to ¥853.7 billion. Profit was impacted mainly by one-time expenses associated with the transfer of subsidiaries in films and an impairment related to a subsidiary in the polyester fibers and trading and retail business. Operating income declined by 6.3% to ¥56.2 billion. Operating income for the materials business unit stood at ¥17.2 billion, down by 9.3%, with sales falling 5.6% to ¥633.8 billion. In aramid, sales dropped for para-aramid fibers for automotive applications, such as friction materials and rubber reinforcements, due to the impact of a decrease in demand in automotive. However, product mix and pricing efforts contributed positively to profits. In carbon fibers, sales of carbon fibers "were soft for use in aircraft, mainly reflecting inventory adjustments in the supply chain." Sales volume of compound applications for automotive and electronics decreased because of a persistent decline in demand since the final stretch of the previous fiscal year.
- Preliminary data show that Hong Kong SAR's real GDP slumped 8.9% year on year (y/y) in the first quarter, worsening sharply from an already steep drop of 2.9% y/y in the second half of 2019. This marks the largest contraction in history, outpacing the steep declines of 8.3% y/y and 7.8% y/y seen at the bottom of the 1998 Asian financial crisis and the 2008-09 global financial crisis, respectively. In seasonally adjusted terms, the economy also plunged at a record speed of 5.3% from the preceding quarter, representing the fourth consecutive quarter of contraction in economic activity. The result for the first quarter was worse than IHS Markit's projection of a 7.8% y/y decline as the contraction in private consumption and exports turned out to be bigger than expected. (IHS Markit Economist Ling-Wei Chung)
- According to a notice posted on the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC) website on 6 May, asset investment companies (AICs) attached to banks will be given asset management companies (AMCs)' ability to manage securities obtained through debt-to-equity (DTE) schemes. The AICs can obtain funding from individuals (with annual income of at least CNY600,000 [USD84,600]), family trusts (with at least CNY5 million of assets), and insurance and pension funds to invest in the securities. In the past few years, banks have conducted DTE swaps to absorb bad loans and artificially lower the non-performing loan (NPL) ratio in the banking sector. We assess this to be a risk-positive development as banks have more channels to offload the securities obtained through DTE. (IHS Markit Banking Risk's Angus Lam)
- The China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM) on 7 May released the estimates of its April sales prior to its monthly briefing. According to a statement posted by the association on its WeChat social media account, it expects new vehicle sales to reach 2 million units in April, up by 39.8% from March and up by 0.9% from April 2019. In the first four months of 2020, new vehicle sales in China are expected to reach around 5.67 million units, down by 32.1% year on year (y/y). The estimates are based on April's sales reports released by major automotive groups in the country. IHS Markit expects more details to be released by the CAAM in the coming week. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Abby Chun Tu)
- The municipal government of Shanghai unveiled its "new infrastructure" investment plan on 7 May. A total of CNY270 billion (USD38 billion) will be invested in 48 projects to upgrade networks, innovative infrastructure, integrated platforms, and smart terminals in three years (2020-22), aiming to lay solid foundations for modern industry development and the city's digital transformation. Different from traditional infrastructure investment projects, private investment will play the leading role in the new investment plan, accounting for over 75% of the overall investment package, according to an official from the local development and reform commission. The expansion of 5G network and construction of data centers will be the key focus of this investment plan. Planned investment in these two fields are set to go beyond CNY50 billion in 2020. (IHS Markit Economist Lei Yi)
- South Korean automakers posted a 48.4% year-on-year (y/y) plunge in combined global sales to 341,944 units in April, according to data released by the five major domestic manufacturers and reported by the Yonhap News Agency, as compiled by IHS Markit. The five automakers reported a 6.5% y/y increase in combined domestic market sales last month to 145,141 units, while their combined overseas sales nosedived 62.6% y/y to 196,803 units. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
- Mobile carrier LG Uplus will launch a 5G-based autonomous
shuttle service in the South Korean city of Siheung in the second
half of this year, reports Aju Business Daily. The service will
enable commuters to travel from a subway station to their homes in
a suburban new town in the city. The demonstration is part of a
government-led pilot project launched by the Ministry of Land,
Infrastructure and Transport in partnership with Seoul National
University and AUTOMOS, a domestic autonomous vehicle technology
provider. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)Vietnam
on 7 May allowed non-essential businesses such as cinemas and
fitness facilities to resume operations, taking further steps to
ease lockdown restrictions following the reopening of schools and
public transport on 23 April. As of 7 May, Vietnam, a country with
95 million people, had 288 confirmed cases of COVID-19, with no
fatalities. (IHS Markit Economist Anton Alifandi)
- The number of imported cases is likely to increase in the coming weeks as the government is arranging chartered flights to repatriate Vietnamese nationals from overseas, including from high-risk regions such as North America and Europe.
- The government has earmarked VND700 trillion (USD30 billion) in public investment this year, more than twice it spent in 2019. Most notably, the eight projects of the 654km-long eastern section of the North-South Expressway, running from Nam Dinh to Vinh Long province, was swiftly converted last month into state investment projects from public-private partnership schemes that have been progressing slowly because of a poor legal framework.
- The reopening of high-traffic secondary border crossings with China in northern provinces such as Lang Son and Quang Ninh on 7 May is likely to accelerate the recovery of Vietnam's agriculture and manufacturing sectors.
- The recovery of Vietnam's tourism industry is likely to be slow and led initially by domestic tourism.
10. The Philippines' real GDP fell by 0.2% year on year (y/y), marking the first contraction since the fourth quarter of 1998 during the Asian financial crisis. In seasonally adjusted terms, the economy contracted at a record speed of 5.1%, compared with a 1.8% gain in the fourth quarter of 2019. Gross investment spending plunged by 18.3% y/y in the first quarter as the pandemic and virus-controlling measures dragged down business confidence and severely impacted economic activities. Fixed investment contracted by 4.3% y/y in the first quarter, driven by a 7.7% y/y drop in business spending on durable equipment, which marked the fourth straight quarter of contraction. (IHS Markit Economist Ling-Wei Chung)
11. APAC equity markets closed higher across the region; Nikkei +2.6%, Hong Kong +1.0%, South Korea +0.9%, Shanghai Composite +0.8%, India +0.65, and Australia +0.5%.
Complimentary Access to Price Viewer
In light of current events, IHS Markit is offering complimentary access for qualified market participants to our historical cross asset coverage of global fixed income pricing and liquidity data, as well as OTC Derivatives data via the Price Viewer web-based data portal.
We use screenshots from the Price Viewer very frequently in this report and corporations use the credit default swap and bond price/yield data to identify potential risks to their supply chains. Request complimentary access here or contact sales@ihsmarkit.com.
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-08-may.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-08-may.html&text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+8+May+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-08-may.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Daily Global Market Summary - 8 May 2020 | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-08-may.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+8+May+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-08-may.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}




