Welcome to the second edition of the S&P Global Sustainability Quarterly, featuring research authored by a cross-section of representatives from across S&P Global. We publish at a pivotal time for the sustainability world — hard on the heels of the U.N. Climate Change Conference in Sharm el-Sheikh, Egypt, known as COP27. The second part of the U.N.'s Convention on Biological Diversity, known as COP15, is underway in Montreal. As we head into 2023, it is increasingly clear that these two topics — nature and climate — are inextricably linked.
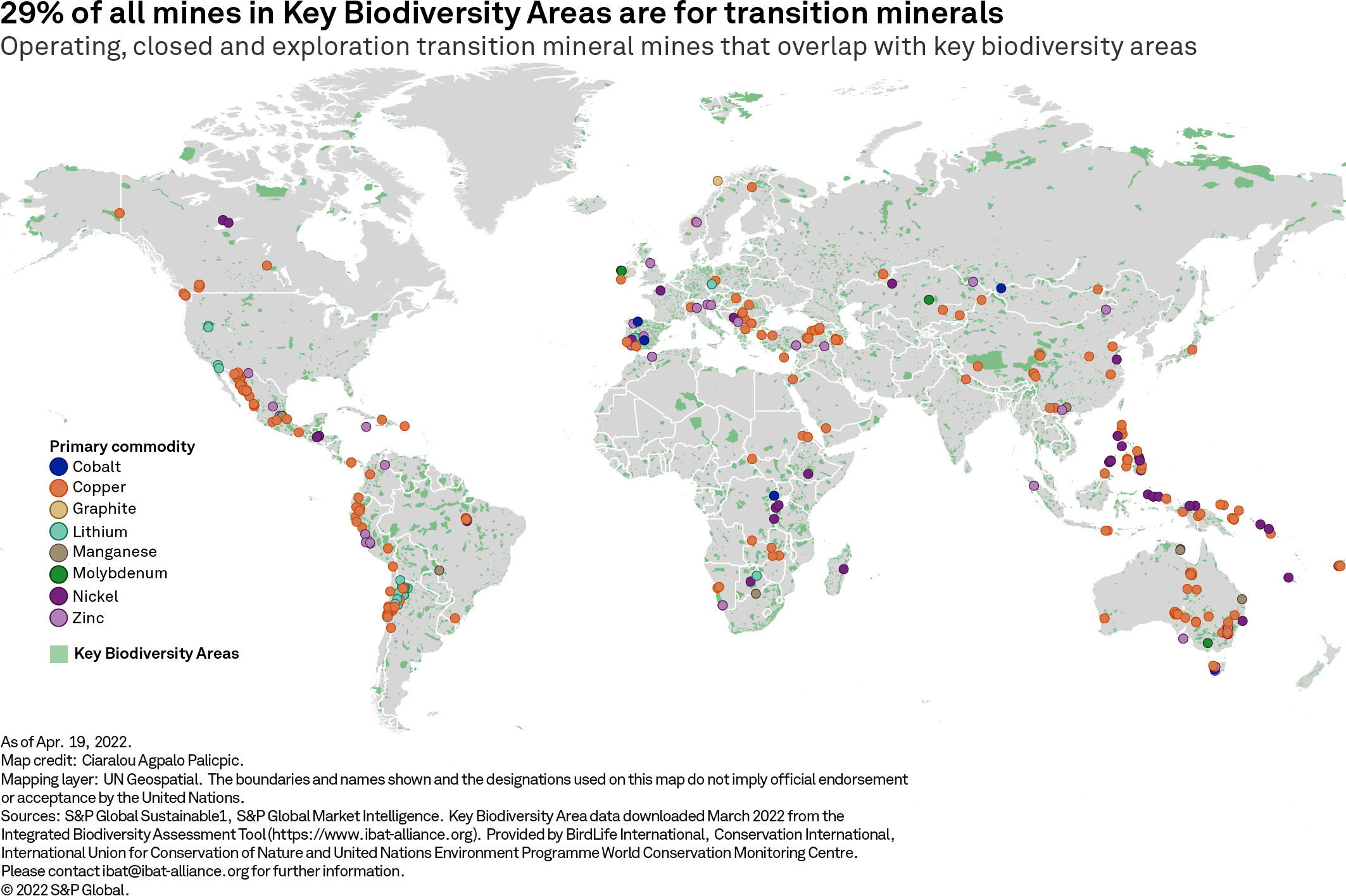
For example, mining exploration around the world is picking up as companies seek new deposits of elements like lithium and copper to support the energy transition. But research by S&P Global Sustainable1 finds that many existing mines and exploration sites overlap with some of the world’s most important areas for biodiversity. Enabling the energy transition while managing the potential negative impacts on biodiversity is a complex challenge. It is also increasingly urgent, given that trillions of dollars of economic activity rely on nature.
While the challenges of climate change and nature loss are ubiquitous, their impact differs across geographies. Developing countries disproportionately face increasing costs and disruption from the physical impacts of climate change. Read on for a special report from S&P Global’s Economics & Country Risk team exploring the impact of water issues and extreme weather events in Latin America. The research finds that water scarcity in Latin America is likely to intensify supply chain and operational disruptions, regulatory risks, and economics losses for businesses over the next decade.
The challenges also differ by sector. During COP27, we saw commitments from public and private sector alike, including ambitious carbon reduction initiatives from one sector that is a major contributor to global CO2 emissions: cement. The EU is leading the way on decarbonizing the cement industry, and in the pages that follow, S&P Global Ratings analyzes the steps some European players are taking to decarbonize their operations and update their strategies to meet changing customer demands. The research also looks at the potential financial and operational implications for companies in light of the EU's goal to hasten emissions reduction and the challenges the industry faces, given the current nascent stage of decarbonization technology.
In the banking sector, there has been an increasing number of regulatory initiatives across the globe to accelerate the assessment of exposure to and management of climate risks, notably through stress tests. Research from S&P Global Ratings explores the approaches of regulators and prudential authorities and aims to identify the key challenges that remain.
With the acceleration of global ambition to tackle climate change, market participants increasingly need to better understand the greenhouse gas competitiveness, or the relative greenhouse gas intensity, between different sources of crude oil globally. A newly developed proprietary model helps do just that by modeling greenhouse gas emissions down to individual assets and the sources of emissions. Research by S&P Global Commodity Insights applies this model to the North Sea — one of the most significant oil- and gas-producing regions globally.
There is no one-size-fits-all solution to climate and nature challenges. In the research that follows, we seek to understand the sustainability challenges different parts of the world and the economy face — and the solutions to help address these challenges.
Biodiversity
Rocks and hard places: the complicated nexus of energy transition minerals and biodiversity
Minerals such as copper, lithium and cobalt are key to ramping up low-carbon technologies like electric vehicles and solar panel manufacturing. But the process of extracting them — from exploring potential sites to closing depleted mines — poses significant threats to the ecosystems and species that often coincide with potential mineral deposits. A new analysis by S&P Global Sustainable1 finds there is overlap between existing mines and exploration sites and some of the world’s most important areas for biodiversity.
Listen: Platts Future Energy —
How ESG shapes the development of battery supply chains
Despite serving multiple purposes in the energy transition, batteries have their own footprint, and downstream players want to have that addressed. With automakers in the driving seat, ESG requirements have been spreading out through battery supply chains, although there remains a lack of standardized guidelines.
In this episode of the Platts Future Energy podcast, metals editors Henrique Ribeiro and Leah Chen discuss the main ESG challenges faced by the battery industry and what steps are being taken to mitigate the risks.
Keep up with the latest ESG developments affecting business, trade, and capital investment by subscribing to the free newsletters.
SUBSCRIBE TO THE NEWSLETTERSWater Scarcity
Water in Latin America: Operational challenges
Access to water is likely to become increasingly strategic and disruptive in Latin America over the coming decade. Climate scenario projections for the coming decades forecast that water stress and drought frequency will increase in many parts of Latin America, particularly in southern Argentina, northern Mexico and the Antofagasta region in northern Chile. Water scarcity is likely to be an ongoing constraint to the region’s contribution to meeting global energy transition targets, affecting lithium extraction and green hydrogen.
Listen: Climate modeling in focus as we count down to COP27
The U.N. climate conference known as COP27 kicks off next week. Adaptation to a changing climate will be an important part of the talks.
In this episode of the ESG Insider podcast, we look at how companies and investors are using climate modeling to measure and manage the future financial impacts of climate hazards such as wildfires, drought and flooding. According to a new S&P Global Sustainable1 dataset, 92% of S&P Global 1200 companies will have at least one asset highly exposed to physical hazards by the 2050s under a business-as-usual high-emissions scenario.
Decarbonization
Decarbonizing cement: How EU cement-makers are reducing emissions while building business resilience
European cement manufacturers have committed to reducing carbon emissions by 30% by 2030, which we view as achievable. However, if more stringent regulations are enacted to mandate emissions reduction, we believe that it will be challenging for the industry to achieve net-zero by 2050 without putting profitability under pressure.
Listen: Why collaboration is critical to cutting supply chain emissions
The UN climate conference known as COP27 is underway, and today (Nov. 11) is Decarbonization Day. In this episode of the ESG Insider podcast, we explore how companies are setting decarbonization targets in their operations and across their supply chains.
Climate Risk & Resilience
Bank regulation and disclosure to foster climate-related risk analysis
Climate-related risks are being considered in stress testing, prudential frameworks and disclosure standards to raise banks’ awareness of and preparedness for such risks. Still, banks face many obstacles to the effective assessment and management of those risks.
Listen: As COP27 approaches, central banks signaling need for action on climate
Climate Week NYC is ending, and the United Nations Climate Conference known as COP27 is fast approaching. As the urgency to address climate change intensifies, financial regulators and supervisors are taking an increasing interest in climate change and the impact it is having on the financial system and the economy at large.
To get a better understanding of this landscape, we’re looking at some of the recent actions central banks have taken on climate in this episode of the ESG Insider podcast.
Subscribe to ESG Insider, a podcast from S&P Global Sustainable1 that takes you inside the environmental, social and governance issues shaping the business world through in-depth analysis and interviews with sustainability leaders.
ESG podcastsMeasuring Emissions
Greenhouse gas intensity of the North Sea
An examination of the U.K. and Norwegian North Sea, using a new and comprehensive approach to upstream oil and gas production emissions, finds that the average greenhouse gas intensity of production in 2021 was 12 kilograms of carbon dioxide equivalent per barrel of oil equivalent. Productivity, electrification and the extent of gas flaring all contribute to different levels of emissions for production operated by the U.K. and by Norway.
Listen: What a new EU energy plan means for renewables investment
The European Commission in May proposed its ‘REPowerEU’ plan to wean the EU off supplies of Russian fossil fuels and accelerate its transition to a low-carbon economy. In this episode of the ESG Insider podcast, we talk with experts about the plan and what it means for investment in renewables.
Around the globe, countries are facing growing exposure to the physical impacts of climate change. The inaugural S&P Global Sustainability Quarterly is a roadmap to understanding this evolving climate landscape.
READ MORE






