Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Language
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
Events
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
Events
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
S&P Dow Jones Indices — 29 Apr, 2021
By Qing Li
This article is reprinted from the Indexology blog of S&P Dow Jones Indice.
Dividend strategies appeal to investors for various reasons. High-dividend-yield strategies can offer generous income, while dividend growth strategies tend to emphasize the quality of dividends. The Dow Jones International Dividend 100 Index, launched in March 2021, seeks to provide global exposure to both high dividend yield and dividend growth.
Here we review the methodology of this index’s construction. The Dow Jones International Dividend 100 Index is comprised of non-U.S. large- and mid-cap companies that exhibit consistent dividend payout history, strong fundamentals, and relatively low volatility. Exhibit 1 outlines the key process of the index construction, which involves multi-layered screens to incorporate various factors.
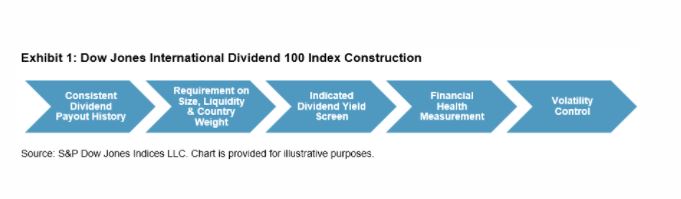
The initial universe consists of the large- and mid-cap issues1 from the Dow Jones Global ex-U.S. Index. Additional parameters (see Exhibit 2) are applied to form a selection universe.

After this screening, only the securities whose indicated dividend yields ranked among the top half of those considered are qualified for further financial health evaluation. The subsequent measurement is a composite score combining cash flow-to-debt, return on equity (ROE), indicated dividend yield, and the five-year dividend growth rate.
Cash flow-to-debt indicates the efficiency level of a company in producing cash to cover its debt. As a profitability ratio, ROE signifies how well a company is using its shareholders’ capital, and a company with higher ROE is more capable of cash generation. The use of indicated dividend yield reflects expected income2 rather than realized income that an investor will receive. While indicated dividend yield represents cash income, dividend growth rate helps determine if a company can sustain its long-term dividend distribution. We define the dividend growth rate as the percentage rate of growth of a company’s annualized dividend per share over the past five years. Analyzing these fundamentals can help investors gauge a company’s financial health.
The composite score is calculated as the average rank of the four fundamental-based factors. A high composite score means a company is financially healthy. Based on the composite score, the top 400 securities are selected for volatility screen, where volatility is calculated as the three-year price volatility in USD. The initial portfolio is formed with the top 100 ranked stocks whose volatilities are less than or equal to the median volatility of the 400 top-scoring stocks.
The index is float-market-cap weighted, with various weight constraints to reduce concentration risk. During the annual March rebalancing and quarterly updates, the weightings are evaluated to ensure that a security only represents a maximum 4% of the index, each of the Global Industry Classification Standard (GICS®) sectors are capped at 15%, and the emerging market exposure is limited at 15%. In addition, the index is subject to a daily weight cap check when the sum of the stocks whose weights are greater than 4.7% exceeds 2%.
To reduce turnover, buffer rules3 that favor the existing index members are applied in multiple layers during the selection process, including buffer zones on size, country weight, indicated dividend yield, volatility, and count.
The Dow Jones International Dividend 100 Index adds a multi-level process to the rule-based framework. In our next blog, we will analyze how this index has performed.
1 REITs are excluded. For China, only the shares that trade in developed markets are eligible.
2 Using Trailing Dividend Yield Versus Indicated Dividend Yield
3 Please refer to the Dow Jones Dividend Indices Methodology for details.
The posts on this blog are opinions, not advice. Please read our Disclaimers.