Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Language
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
S&P Global — 26 Sep, 2022 — Global
By S&P Global
Start every business day with our analyses of the most pressing developments affecting markets today, alongside a curated selection of our latest and most important insights on the global economy.
Semiconductor Industry Confronts Softening Demand, Geopolitics
The semiconductor industry could serve as the poster child for global trade. Chips designed by U.S. West Coast technology companies are developed in Taiwan and then manufactured in vast quantities in mainland China, Malaysia or South Korea. But the same factors that have dragged on global trade over the past few years — geopolitical tensions, pandemic restrictions and economic slowdown — are threatening an industry that has built its success on a widely distributed supply chain.
For two years, shortages of semiconductors caused by COVID-19 lockdowns and restrictions have obstructed the consumer technology and auto industries. Now, just as those supply concerns show signs of easing, chipmakers are confronting weaker consumer demand, excessive stockpiling by manufacturers and changes to U.S. regulatory and trade policies.
The electronics industry was one of the few bright spots in a world bedeviled by the COVID-19 pandemic. In the past two years, consumer electronics for remote working and home entertainment drove up the prices of semiconductors. However, the August 2022 S&P Global Electronics Purchasing Managers’ Index survey signaled a softening in demand. The slowing economies of the U.S., EU and China are weakening appetites and limiting new electronics orders. Luckily for the electronics industry, a backlog for key electronics products such as semiconductors will likely keep earnings strong through the end of the year.
Geopolitical tensions and the experience of pandemic-driven shortages have led many countries to look toward “near-sourcing,” or the moving of business operations close to where end products are sold, for semiconductors. Establishing domestic electronics production capacity for critical electronics components has become a national priority for the U.S., EU and China. In the U.S. and EU, recent legislation was passed to reduce the reliance on Asian semiconductor production. The U.S.’ CHIPS and Science Act sets aside $50 billion to increase the domestic production of semiconductors.
The Biden administration has been introducing measures aimed at curtailing China's access to cutting-edge chips out of a concern that they could be used in Chinese military equipment. The Biden administration is also expected to block U.S. companies from exporting chipmaking equipment to Chinese factories that produce advanced semiconductors.
With Chinese suppliers under threat of sanction, the U.S. semiconductor industry has been looking to alternative partners to strengthen semiconductor supply chain resiliency. Malaysia, which is also a key supplier of components for global semiconductor production, recently signed a memorandum of cooperation with the U.S. Commerce Department aimed at increased collaboration on semiconductor manufacture.
While the global supply chain for semiconductors may be undergoing upheaval, the outlook for electronics demand looks healthy. The rollout of 5G technology over the next five years will likely drive sales of 5G mobile phones, which require new semiconductors. Industrial automation and the build-out of the internet of things could also propel demand in industrial electronics.
Today is Monday, September 26, 2022, and here is today’s essential intelligence.
Written by Nathan Hunt.
Eurozone Downturn Deepens In September As Price Pressures Intensify
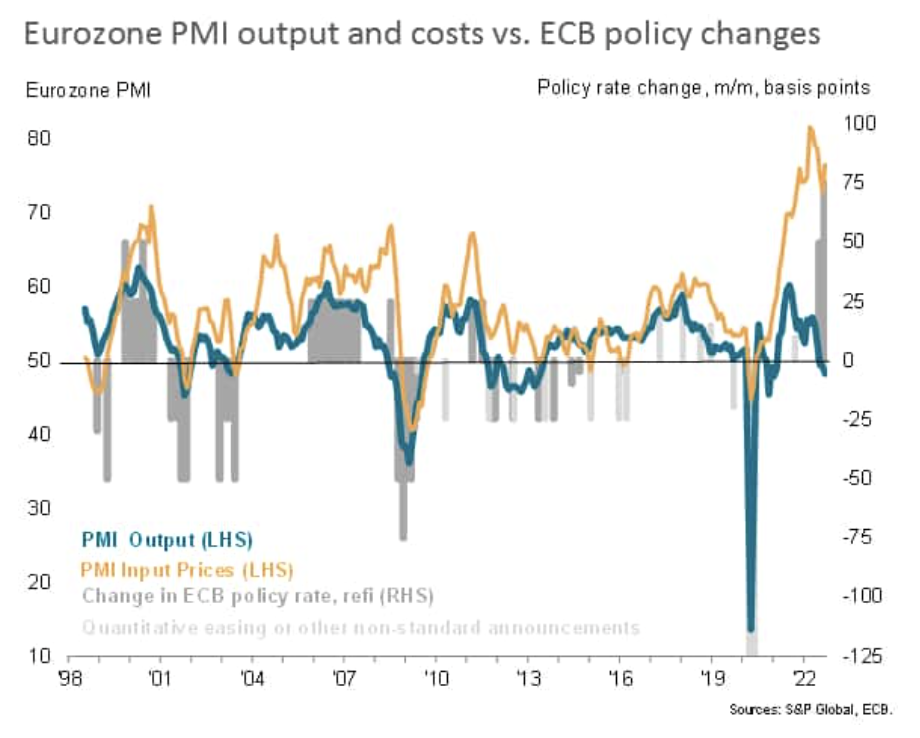
The Eurozone economic downturn deepened in September, with business activity contracting for a third consecutive month, according to preliminary survey data. Forward-looking indicators, such as new order inflows, backlogs of work and future output expectations, point to the decline gathering further momentum in coming months. At the same time, inflationary pressures picked up, fueled by rising energy costs.
—Read the article from S&P Global Market Intelligence
Access more insights on the global economy >
Shifting Dynamics In Private Equity Fundraising; Early Infotech Funding Slows
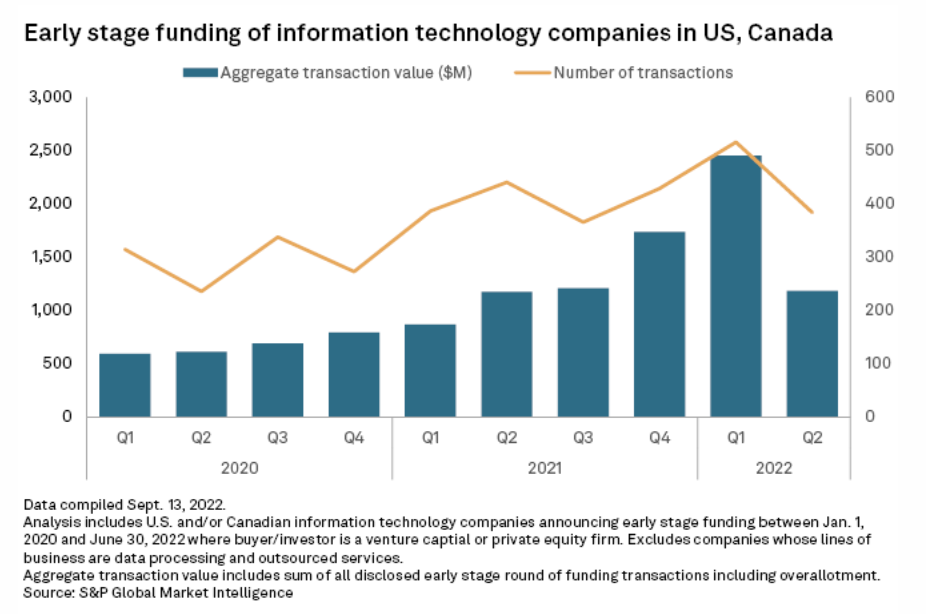
Private equity started the year with ambitious fundraising goals, but the past nine months have tempered expectations. Back in February, Hamilton Lane Inc. was touting the "15/15 club," a group of at least 15 buyout fund managers each aiming to raise $15 billion or more over the next 12 months. Private equity appeared on track to maintain the record-setting fundraising pace set by the asset class last year.
—Read the article from S&P Global Market Intelligence
Access more insights on capital markets >
China's Manufacturing Steel Demand Rebounds In August, Further Improvement To Be Modest
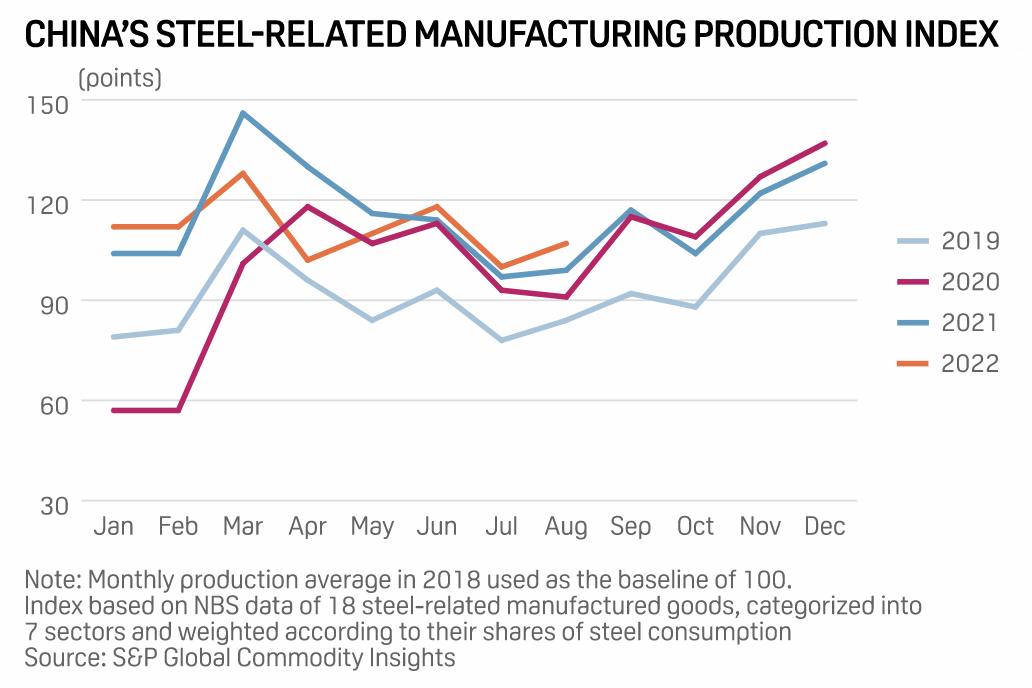
China's manufacturing steel demand rebounded in August and is expected to improve further in September and October on higher seasonal manufacturing activity, but market sources told S&P Global Commodity Insights that overall volume requirements are likely to remain modest amid a weak property sector and low household consumption. Evidence of this was also seen in August, when volumes were the third lowest so far in the year despite seeing a month-on-month growth.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on global trade >
New Jersey Expands Offshore Wind Power Capacity Goal To 11 GW By 2040
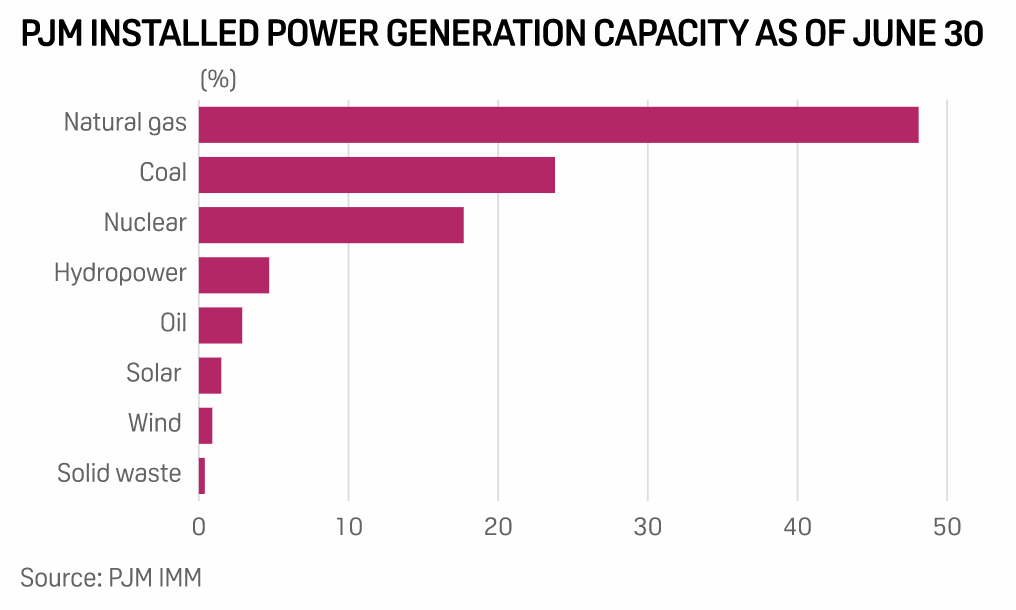
New Jersey Governor Phil Murphy has signed an executive order to increase the state's offshore wind goal by nearly 50% to 11 GW by 2040 and directed local regulators to assess the feasibility of further increasing the target. "With Governor Murphy's announcement that New Jersey will again raise its offshore wind goal, increasing its target from 7.5 GW by 2035 to 11 GW by 2040, the state has solidified itself as a national leader in driving forward this fast-growing industry," John Begala, vice president of federal and state policy of the Business Network for Offshore Wind, said in a statement emailed Sept. 22.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on Sustainability >
Global Fuels Market Outlook
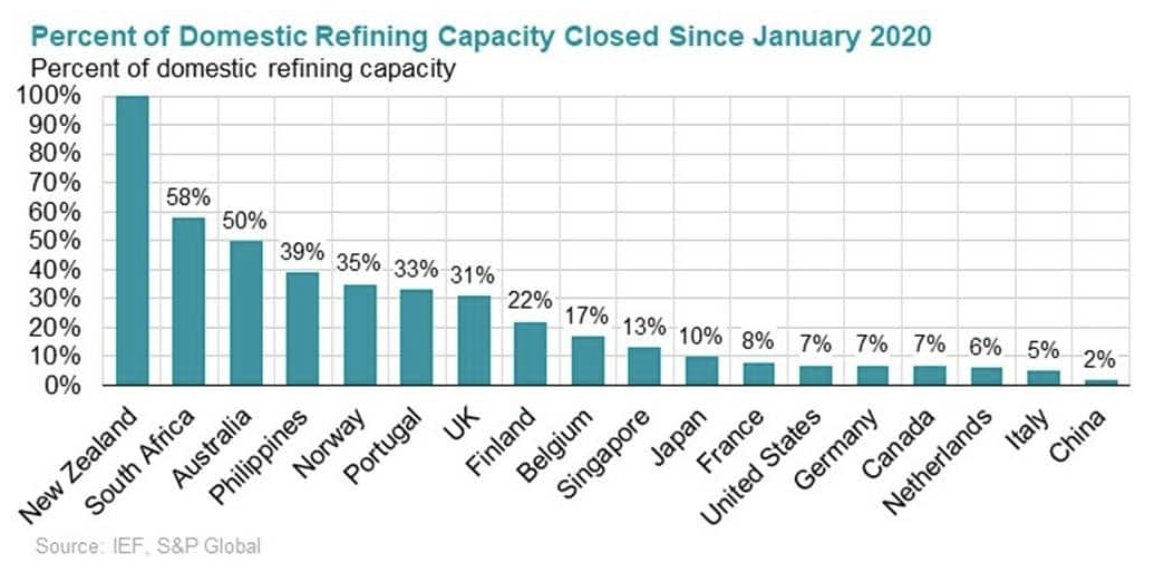
Global refined oil product markets are on track to remain tight until mid-decade, with the global downstream industry facing significant near-, medium- and long-term challenges, according to a new report by S&P Global and the International Energy Forum. Global oil refining capacity dropped for the first time in 20 years in 2020 and again last year, on pandemic-weakened margins, accelerated refinery closures and motivated conversions to biofuels or distribution terminals, according to an Oil Refining Industry Insights report issued last week.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on energy and commodities >
Dual Hong Kong Listings Still Attractive To U.S.-Listed Chinese TMT Companies
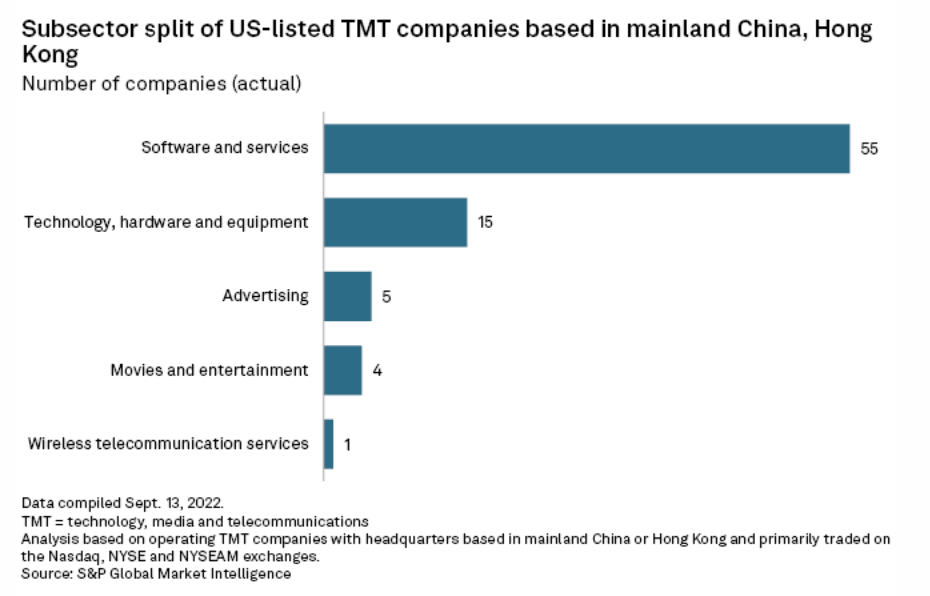
A recent agreement to allow U.S. scrutiny of Chinese accounting firms will not stop Chinese technology, media and telecom companies trading on the U.S. exchanges from seeking dual listings in Hong Kong. The U.S. Public Company Accounting Oversight Board, or PCAOB, which inspects and investigates public accounting firms around the world, recently struck a deal with the China Securities Regulatory Commission and China's Ministry of Finance to allow the auditing of registered public accounting firms headquartered in mainland China and Hong Kong.
—Read the article from S&P Global Market Intelligence
