Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Language
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
S&P Global — 25 Sep, 2023 — Global
By S&P Global
Start every business day with our analyses of the most pressing developments affecting markets today, alongside a curated selection of our latest and most important insights on the global economy.
A Year of Growing Pains for Voluntary Carbon Markets
No one involved in the voluntary carbon market thought it was perfect. For years, it has been an open secret that quality concerns and a lack of integrity were leading to abuses in voluntary carbon markets and keeping supplies of carbon credits artificially elevated. With too many carbon credits of dubious quality flooding the market, it became impossible for supply and demand to generate a reasonable price.
This year, a complementary pair of global integrity initiatives have fundamentally changed pricing in voluntary carbon markets (VCMs). On the supply side, the Integrity Council for the Voluntary Carbon Market’s Core Carbon Principles Assessment Framework was introduced by sellers of carbon credits to establish integrity. On the demand side, the Voluntary Carbon Markets Integrity Initiative’s Claims Code of Practice established guidelines for the appropriate application of carbon credits. While carbon pricing has remained sluggish since these integrity initiatives were introduced, industry observers believe that greater integrity in VCMs will allow the market to grow. Three experts on VCMs from S&P Global Commodity Insights — Eklavya Gupte, Dana Agrotti and Silvia Favasuli — joined the “Future Energy” podcast to discuss recent developments in VCMs and how carbon credits can regain credibility.
“This market has experienced exponential growth between 2018 and 2021 both on the supply and demand side,” Agrotti said on the podcast. “It was really in 2023 where these high-profile integrity attacks started coming to the market, especially targeting the nature-based segment. … The question of whether the market can recover really hinges on the development of integrity initiatives.”
The Verified Carbon Standard of the world’s largest certifier of voluntary carbon credits, Verra, has been criticized in recent years due to doubts about the efficacy of the program's carbon offsets. This has resulted in integrity and quality concerns that have negatively affected the liquidity and pricing of carbon credits. To address the issues, Verra tweaked the certification to reflect new labels established under Article 6 of the Paris Agreement on climate change, which sets rules for global trade in greenhouse gas reductions and, as a result, plays a critical role in the development of voluntary carbon credits.
"We need to get credibility in the market, and we think that it is really important to have progress on carbon markets at [the 2023 UN Climate Change Conference (COP28)]," COP28 Director-General Majid al-Suwaidi told S&P Global Commodity Insights. "We think that all of these solutions [carbon taxes and carbon prices] are useful and helpful. The carbon markets, let's be frank, have had a few years of lost time in a way."
“Since the start of the year, we’re seeing one main trend in particular, which has been the increasing spread between the nature-based avoidance type of credit and the nature-based removal type of credit,” S&P Global Commodity Insights’ Favasuli said on the podcast. “Our nature-based avoidance price assessment in January this year was assessed at around $12. … The natural carbon capture, which is our assessment for nature-based removal credit, was just $1 above at $13. [At] the start of September, the spread between these two prices [was] up to $9.”
Carbon removal credits derive from climate mitigation strategies that remove CO2 emissions from the atmosphere. These types of credits are poised to become a huge market and are created through a wide range of approaches, including direct air capture coupled with durable storage, soil carbon sequestration, biomass carbon removal and storage, enhanced mineralization, ocean-based CO2 removal, and afforestation/reforestation.
The important thing to remember about VCMs is that they are voluntary; companies buy these credits by choice, and not because they are mandated by regulation. Regulated compliance carbon markets have grown in recent years to an estimated $900 billion. VCMs are much smaller and valued at about $2 billion. Some market observers believe that VCMs may eventually disappear into compliance carbon markets as more regulation and initiatives such as the EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism come into effect. The EU’s mechanism will establish a carbon tax on imports of selected energy-intensive materials and products into the region, starting in 2026.
Today is Monday, September 25, 2023, and here is today’s essential intelligence.
Written by Nathan Hunt.
Japan's Growth Momentum And Inflation Pressures Ease In September
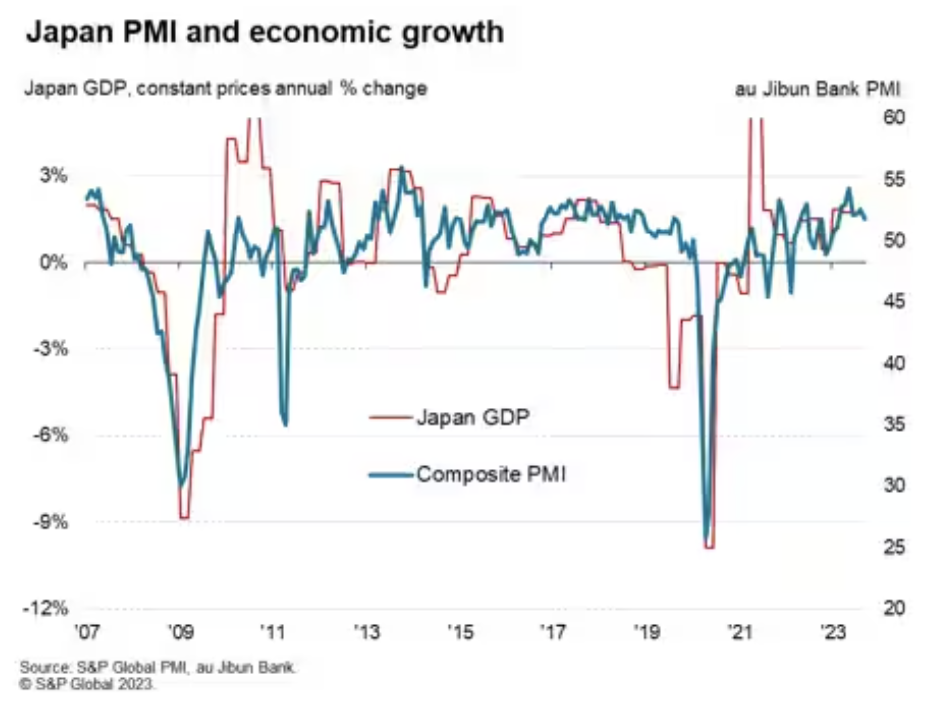
Japan's private sector economy continued to grow in September, extending the sequence of expansion that commenced at the start of 2023. That said, the pace of improvement slipped to the weakest in seven months according to flash PMI data. Slower service sector growth, attributed in part to a renewed decline in new business from abroad, and a quicker fall in manufacturing output underpinned the latest slowdown. Moreover, business confidence further declined in September, foreshadowing weaker conditions to come.
—Read the article from S&P Global Market Intelligence
Access more insights on the global economy >
Emerging Markets Real Estate Issuers Stand Their Ground
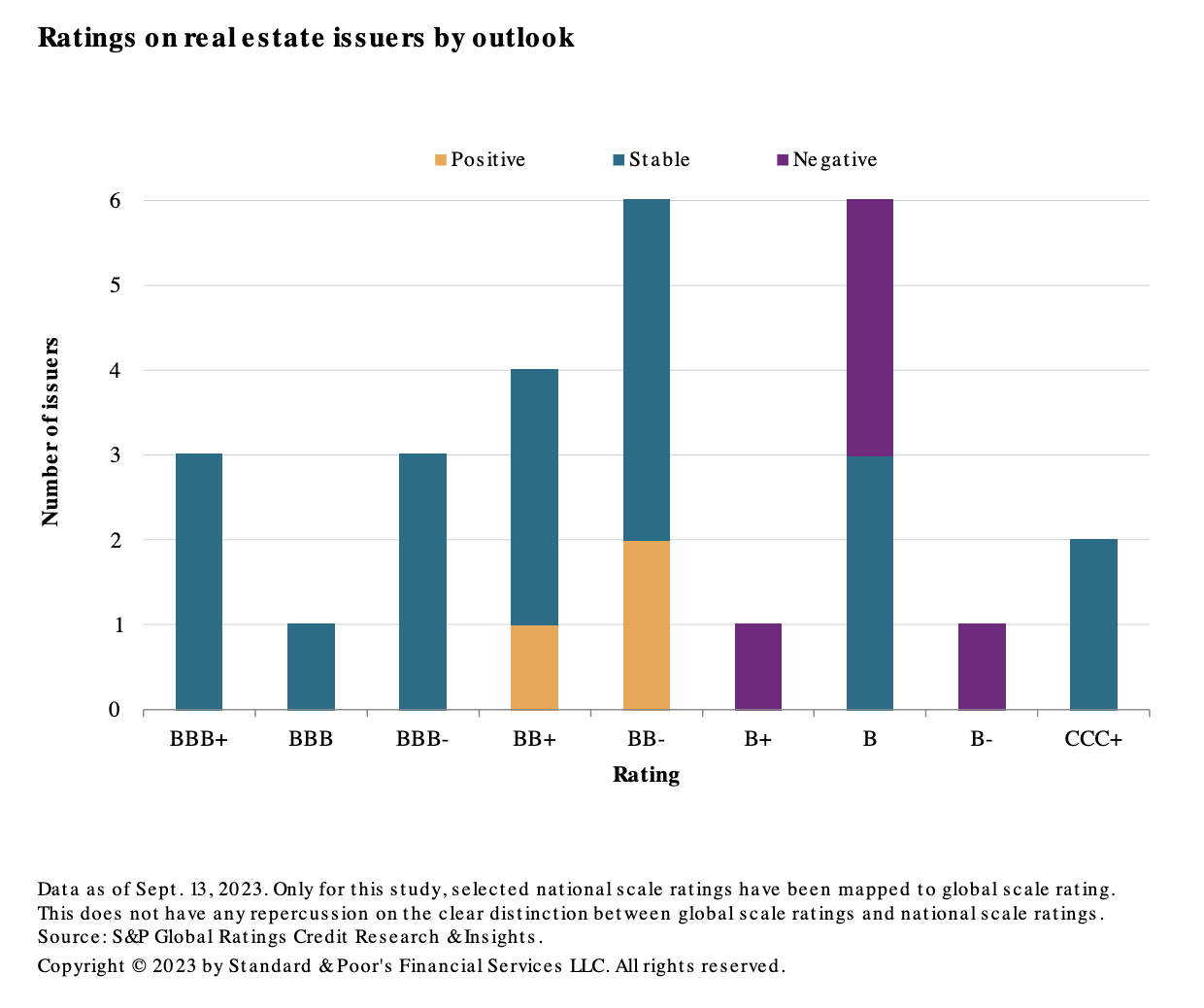
The real estate sector has seen better days. Tighter lending conditions led to an increase in refinancing risk for real estate investment trusts (REITs), while higher mortgage rates reduced homebuilders' revenues and profits. The US and Europe are among the most affected regions, but emerging markets also grapple with declining real estate valuations. It's not all doom and gloom, though. S&P Global Ratings expects the real estate companies in its rated emerging market universe will exhibit credit rating resiliency through the end of 2023. They will benefit from idiosyncratic budgetary buffers and, in certain jurisdictions, support from governments and domestic banking sectors.
—Read the report from S&P Global Ratings
Access more insights on capital markets >
Russian Diesel Export Ban To Hit Turkey, Brazil Hardest But Curbs Seen Short-Lived
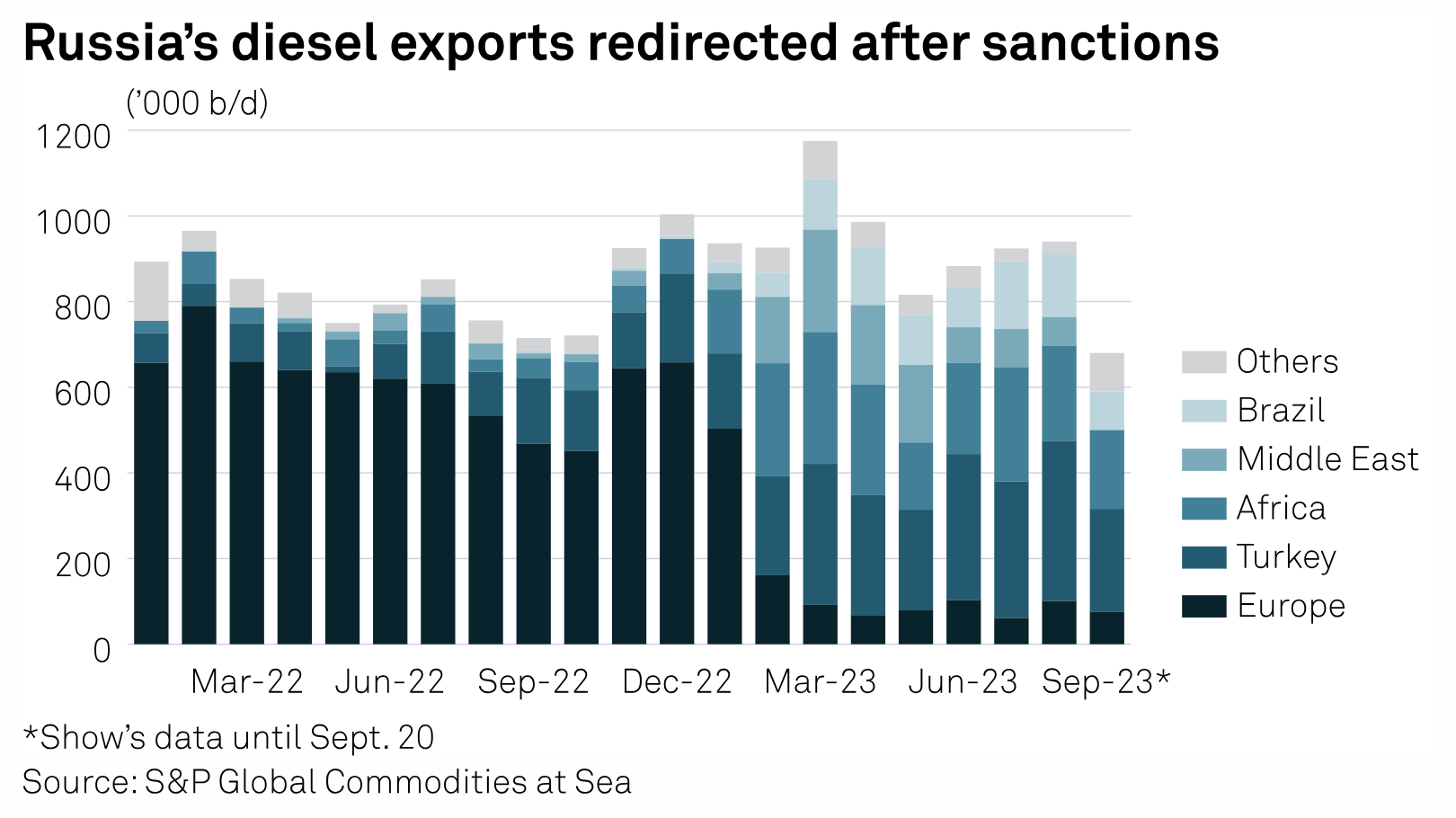
Russia's move to temporarily ban nearly all its exports of diesel and gasoline to ease surging domestic fuel prices is set to hit flows to Turkey and Brazil, but market watchers expect the curbs to be short-lived. Announced with immediate effect on Sept. 21, by far the biggest impact of the ban will be on global diesel markets, as Russia has been exporting almost 1 million b/d of diesel this year, compared with gasoline flows of around 150,000 b/d.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on global trade >
Listen: At Climate Week NYC, Using Collaboration To Tackle Supply Chain Emissions
This week the ESG Insider podcast is on the ground at Climate Week NYC for a special series of interviews from the sidelines of The Nest Climate Campus. In this episode, hosts Lindsey Hall and Esther Whieldon sit down with Amina Razvi, CEO of the Sustainable Apparel Coalition (SAC). SAC is a nonprofit alliance for the consumer goods industry. It launched in 2009 when Walmart and Patagonia brought together peers and competitors from across the sector to develop a standardized approach to measuring sustainability performance and to drive collective action.
—Listen and subscribe to ESG Insider, a podcast from S&P Global Sustainable1
Access more insights on sustainability >
India's Soybean Harvest May Dip In 2023-24 Despite Increased Acreage: Survey
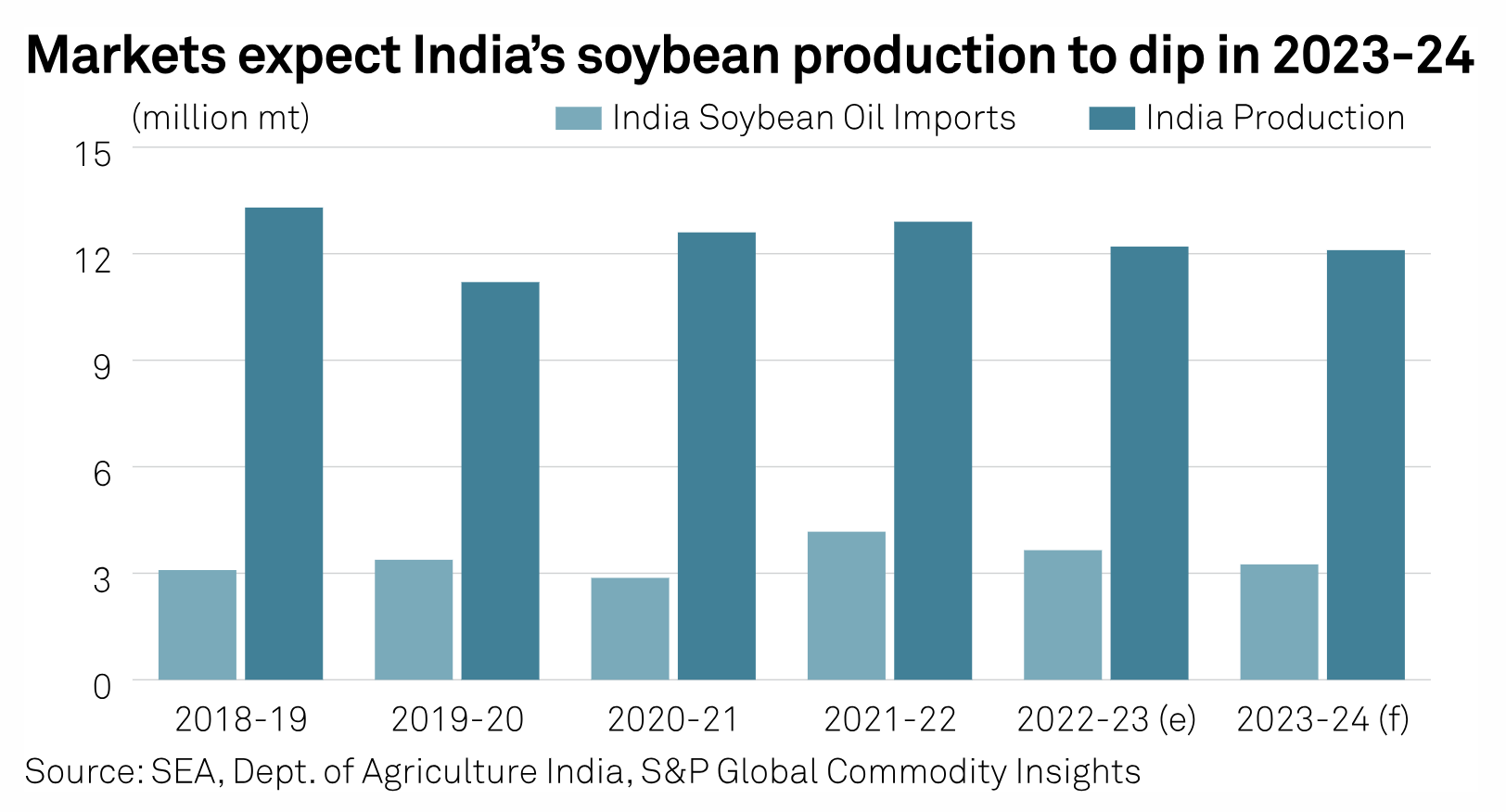
A steep rainfall deficit in August may push India's soybean yields and harvest lower than government's expectations in marketing year 2023-24 (October-September) despite an increase in acreage, according to market participants polled by S&P Global Commodity Insights. According to the annual soybean survey conducted among 13 trade participants and analysts, India's soybean output in MY 2023-24 is seen slightly lower on the year at 12.1 million mt, down from an estimated 13.1 million mt in MY 2022-23.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on energy and commodities >
Listen: Next in Tech | Episode 134: Observability and new operational models
Managing complex application environments successfully requires not only insights into both application behavior and the infrastructure that’s supporting them but also the ability to correlate all of that data. Analyst Mike Fratto returns to the podcast to explore observability, an approach to effectively managing new application patterns that steps beyond traditional methods. From the cloud native world, it’s gaining wider traction and simplifying operations with observability pipelines.
—Listen and subscribe to Next in Tech, a podcast from S&P Global Market Intelligence
