Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Language
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
S&P Global — 20 Jul, 2023 — Global
By S&P Global
Start every business day with our analyses of the most pressing developments affecting markets today, alongside a curated selection of our latest and most important insights on the global economy.
The Surprising Environmental Benefit of Burning Ammonia
Ammonia is a handy little inorganic compound formed from one nitrogen atom and three hydrogen atoms. A small amount of the ammonia produced today is used in household cleaning products or as an antimicrobial agent for foods; 88% is used for fertilizer, which is crucial for feeding the over 8 billion humans living on Earth. In fact, one of the biggest sources of conflict that led to the collapse of the Black Sea grain deal this week is Ukraine’s refusal to transport Russian ammonia through a pipeline that crosses Ukrainian territory. But the feature of ammonia that is most exciting to investors is that it can be used as a fuel source. And since ammonia only comprises nitrogen and hydrogen, it doesn’t emit carbon during combustion.
While the combustion of ammonia does not emit carbon, the production of ammonia frequently creates a great deal of carbon emissions as most ammonia comes from natural gas. Ammonia derived from natural gas is called gray ammonia, a significant contributor to global greenhouse gas emissions that makes up about 1%-2% of global carbon emissions. Some ammonia producers reduce these emissions through carbon capture and sequestration at the production site, resulting in blue, or low-carbon, ammonia. The other major variant is green ammonia, which is produced using renewable energy and draws hydrogen from water and nitrogen from the air.
While ammonia can be burned directly in an engine, it will have superior energy density if the hydrogen is first separated from the nitrogen and then burned as a pure gas. This type of combustion creates environmentally inoffensive emissions of water and nitrogen gas. Because it is relatively easy to derive pure hydrogen from ammonia, ammonia is often used as a carrier to store and transport hydrogen. Due to the tiny size of the hydrogen atom, attempts to store or transport pure hydrogen gas end up with a lot of leakage. Ammonia has been identified as a potential low-carbon bunker fuel for transport ships. This type of ammonia use can leverage existing infrastructure for marine fueling and fuel storage.
The “color” of ammonia favored in different regions is often determined by the local environment, regulations and government incentives, and the availability of feedstocks. In the US, blue ammonia is gaining in popularity due to the availability of natural gas and credits for carbon capture and sequestration facilities under the Inflation Reduction Act. Europe, traditionally a heavy user of gray ammonia, is looking at alternatives because the price advantages of gray hydrogen will shortly be undone by the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism. The Gulf countries and Australia are looking like early leaders in green ammonia due to their abundant sunshine. While green ammonia cannot currently compete on price with blue or gray ammonia, large-scale production facilities will create efficiencies that should bring down the price.
“The development of the wider industry suffers from complexities around competitiveness. The technological use is proven and its known,” said Ryan Monis, director of chemical consulting at S&P Global Commodity Insights, during a recent “Chemical Week” podcast. “But the problem that we see today is that the production costs of renewable energy are prohibitive to produce green ammonia at the same cost as gray ammonia.”
Today is Thursday, July 20, 2023, and here is today’s essential intelligence.
Written by Nathan Hunt.
Inflation And Growth Signals: What To Watch For In The Upcoming July PMI Surveys
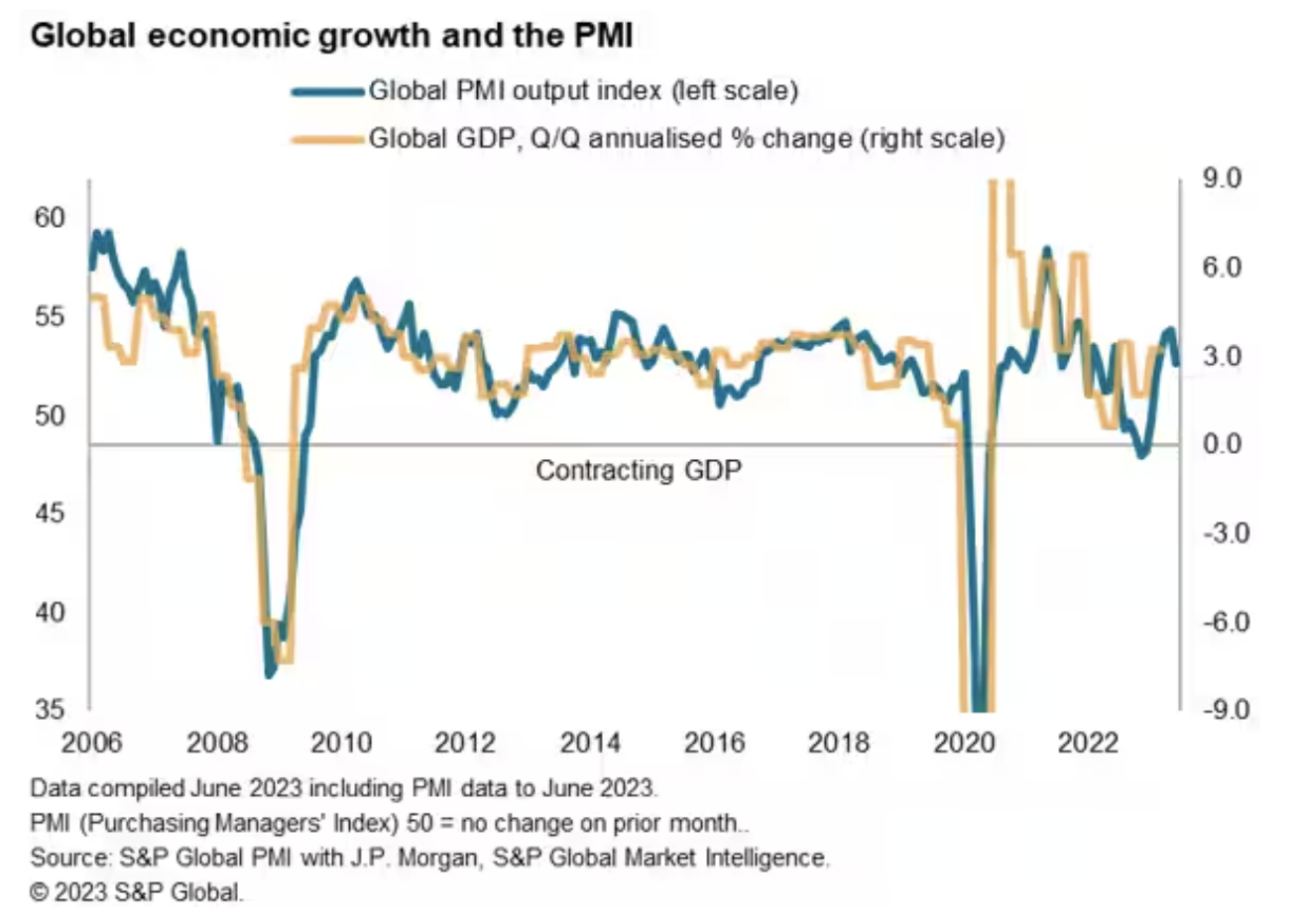
How fast is inflation falling, and how resilient is economic growth? Further insights into these two key issues facing policymakers and markets around the world will be provided by the upcoming PMI surveys, commencing with flash PMI data for the major developed economies on July 24 and followed by final data in early August. The surveys will provide details on industrial prices, service sector inflation, the detailed sectoral pattern of demand — notably the recent upswing in consumer services spending — as well as clues as to whether labor markets are continuing to hold up, pushing wages higher.
—Read the article from S&P Global Market Intelligence
Access more insights on the global economy >
Covered Bonds Outlook Midyear 2023: Rising Interest Rates Will Test Asset Performance

As the COVID-19 recovery fades and higher rates start to dampen demand, eurozone economic activity may contract around the turn of the year, but S&P Global Ratings doesn’t expect unemployment to rise sharply. The medium-term outlook is brighter due to fiscal stimulus and a more supportive monetary policy.
—Read the report from S&P Global Ratings
Access more insights on capital markets >
Shipowners Urged To Up Digitalization Game For GHG Cuts By 2030
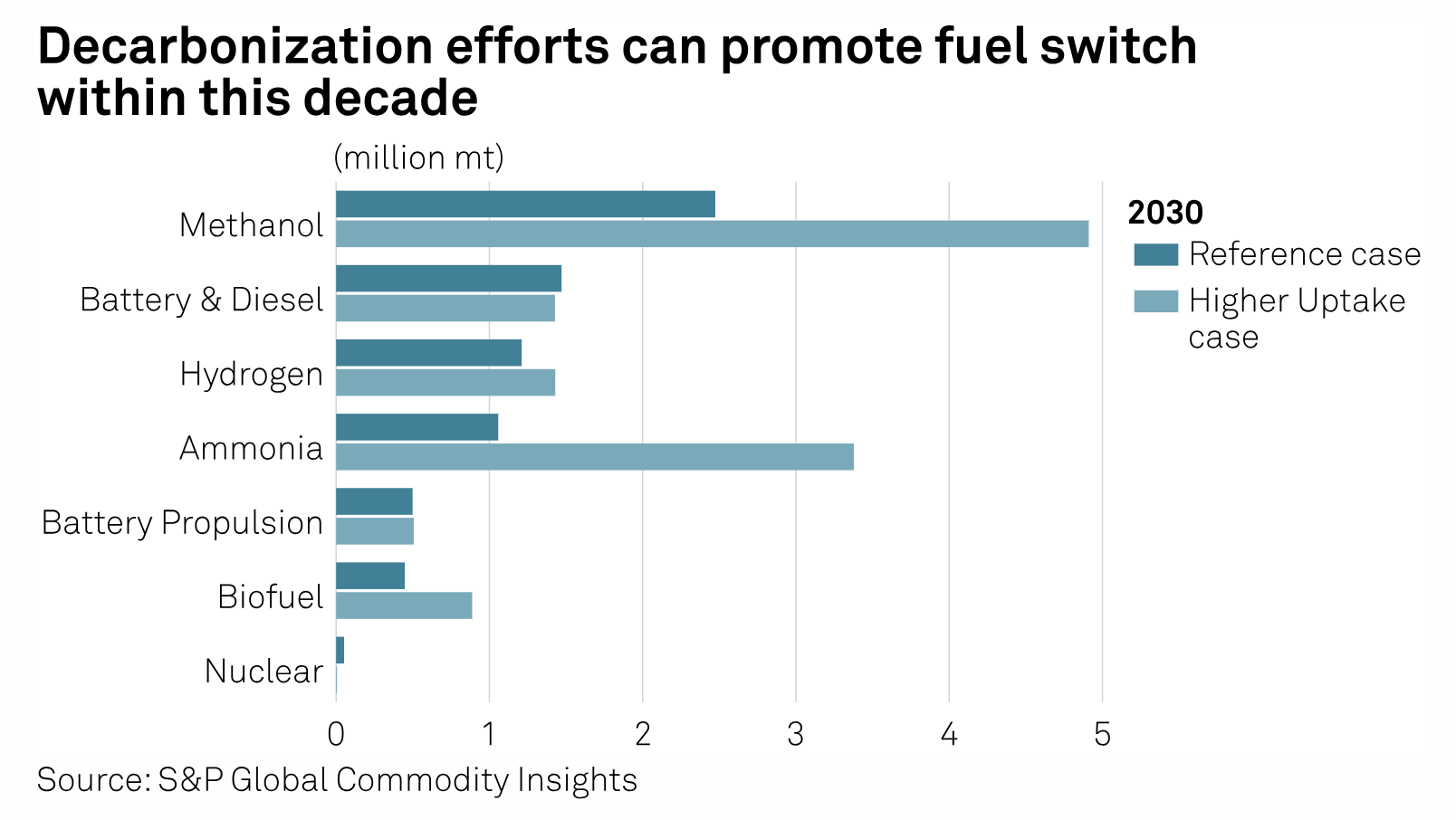
Shipowners can achieve decarbonization at scale within this decade with speed optimization and energy-saving equipment, according to maritime professionals — but the industry might need to digitalize data collection first. Currently, shipping companies rely on the so-called noon reporting, in which a ship's chief engineer manually compiles information on sailing speed, vessel location, bunker inventories and weather conditions daily to gauge operational conditions.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on global trade >
Follow The ESG Leaders
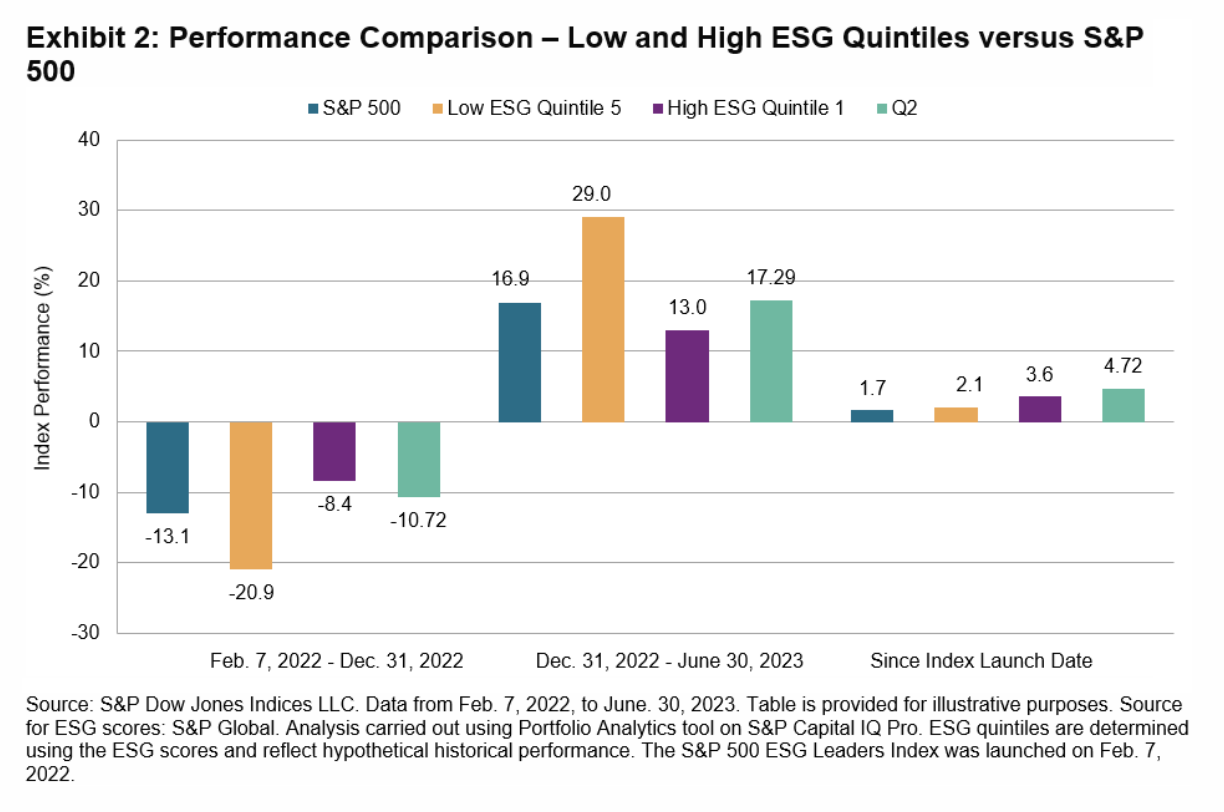
The S&P 500 ESG Leaders Index is constructed using securities from the S&P 500 ESG Index that meet stricter sustainability criteria, while maintaining similar overall industry group weights as the S&P 500. The S&P 500 ESG Leaders Index takes its underlying index up a notch by applying additional exclusionary screenings based on business activities such as shale energy, nuclear power, alcoholic beverages and gambling.
—Read the article from S&P Dow Jones Indices
Access more insights on sustainability >
North American Power: Electric Utility Capex Growth Is Expected To Remain Robust, But Where Is The Investment Going?
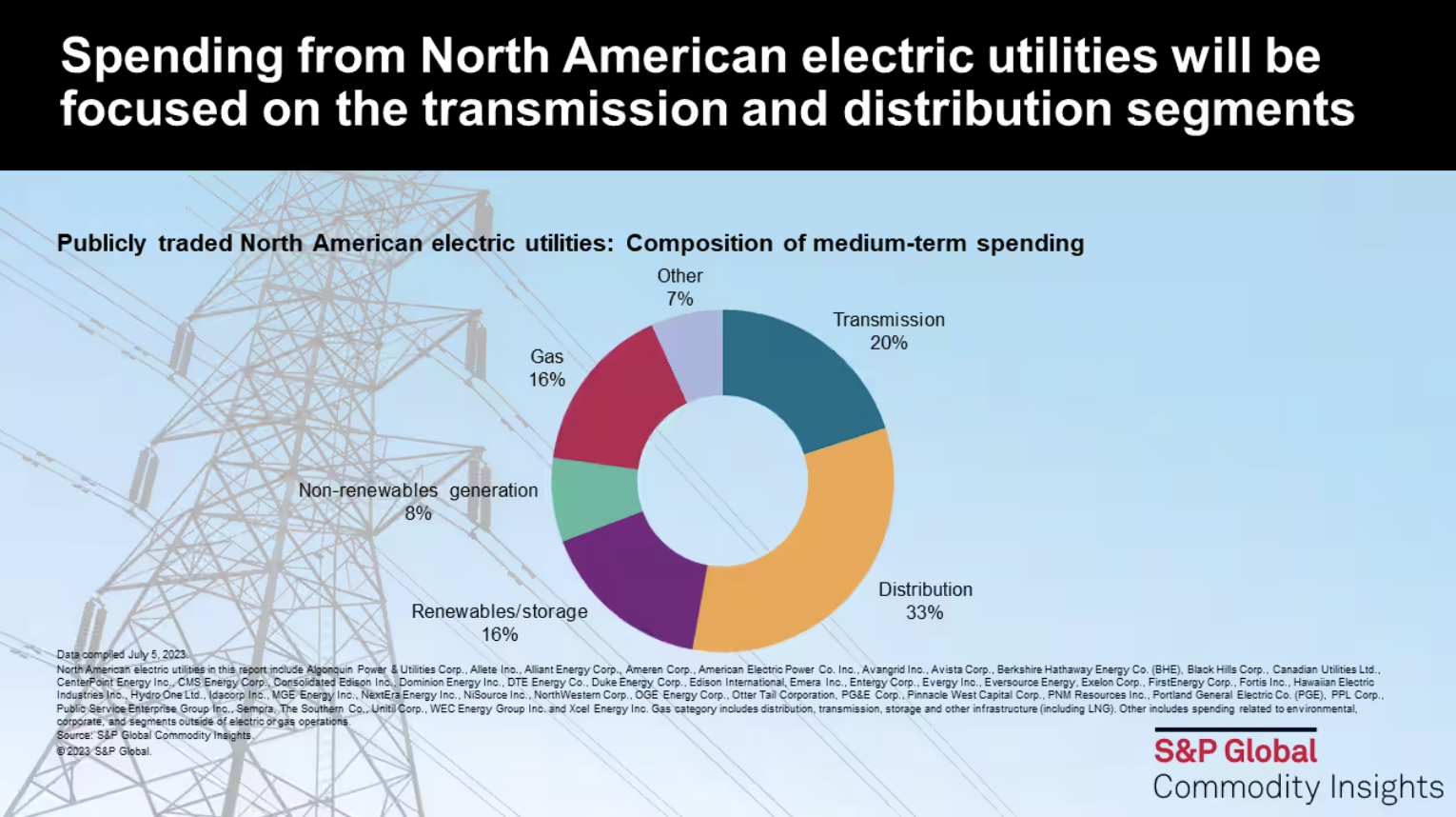
For the largest publicly traded US and Canadian electric utilities, overall capital expenditure has increased at a 7% compound annual growth rate since 2010; meanwhile, aggregate capex for this group of companies is expected to continue to rise at a similar rate through the medium term. An examination of company guidance and stated capital investment plans from this peer group indicates that rather than capacity expansion, much of this spending is targeted on infrastructure upgrading and replacement.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on energy and commodities >
Industry Top Trends Update Asia-Pacific: Gaming
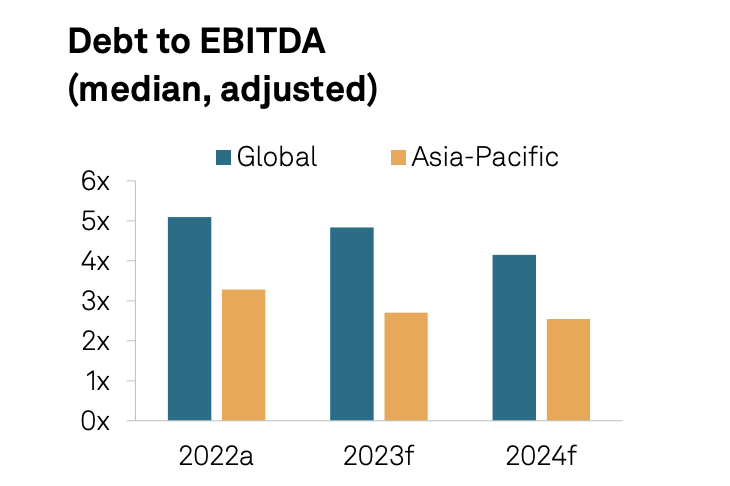
Gaming revenue in most Asian markets should largely recover to pre-pandemic levels in 2023 and may surpass it in 2024. A stronger-than-expected Macao recovery should help operators to deliver faster improvement in cash flows and more rapid deleveraging. Regulatory risks persist across Asia.
—Read the report from S&P Global Ratings
Content Type
Location
Segment
Language
