Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Language
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
S&P Global 17 Apr, 2024 Global
By S&P Global
Start every business day with our analyses of the most pressing developments affecting markets today, alongside a curated selection of our latest and most important insights on the global economy.
India's Unique Energy Transition To Harness Coal, Other Natural Resources
India is uniquely positioned to capitalize on the global push to decarbonize. While the country's growing energy demands have seen green aspirations take a back seat to economic growth, a recently released interim budget for 2024–25 suggests that those priorities may be shifting. New initiatives in the budget show how India plans to leverage technology and its natural resources to manage the energy transition.
In January, the government funded an 85 billion-rupee initiative to promote coal gasification projects. With the release of its new interim budget, the government intends to have 100 million metric tons of coal gasification and liquefaction capacity established by 2030, according to Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman. Though not inherently environmentally friendly, coal gasification would give India more energy independence and allow the country to reduce imports of natural gas, methanol and ammonia, according to Sitharaman. It would also afford the opportunity to employ carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS) technologies, which is easier during gasification than when burning coal.
CCUS development was not specifically funded in the interim budget, but India's abundant coal reserves make it likely that the government will find ways to tap into this resource as part of the transition to renewable energy. Speaking with S&P Global, New Era Cleantech Solution Managing Director Balasaheb Darade likened India's coal reserves to the Middle East's oil supply and said the country is "bound to use it" while it works to adopt clean energy. Darade believes that the government could encourage CCUS by removing a tax of 400 rupees per metric ton on coal projects that use the technology. Developing CCUS expertise would also benefit other hard-to-decarbonize industries, such as cement and iron, which contribute significantly to the Indian economy.
The interim budget also seeks to make fuller use of waste from India's agricultural sector. The country produces 500 million metric tons of agricultural residue annually, and 200 million metric tons go unused, according to Ashvin Patil, founder and director of Biofuels Junction. This waste could be converted into valuable biofuels. In presenting the interim budget, Sitharaman outlined a plan to increase demand for agricultural residue via a phased mandatory blending of biogas in piped and compressed natural gas. The government will support the supply side through financial assistance for the equipment necessary to collect the raw materials used in biogas production.
India is also exploring green hydrogen production, which could be the linchpin in a strategy to decarbonize the country's industrial sector. Speaking at India Energy Week in February, Prime Minister Narendra Modi highlighted India's National Green Hydrogen Mission, which aims to make the country a center for hydrogen production and exports. Green hydrogen could also be used by India's iron industry to produce direct-reduced iron or as an energy source in other industrial sectors.
While such initiatives reflect a commitment to a clean energy future, India must strike a delicate balance between economic growth and net-zero goals as the country's energy demand is set to double by 2045. Proposals in the new interim budget — such as a rooftop solarization plan that would provide savings for households while decarbonizing the electric sector — show how the Indian government intends to square these seemingly competing priorities.
Today is Wednesday, April 17, 2024, and here is today’s essential intelligence.
- Written by Adam Rihner.
US Investors' Risk Appetite, Outlook On Returns Suffer Setback In April
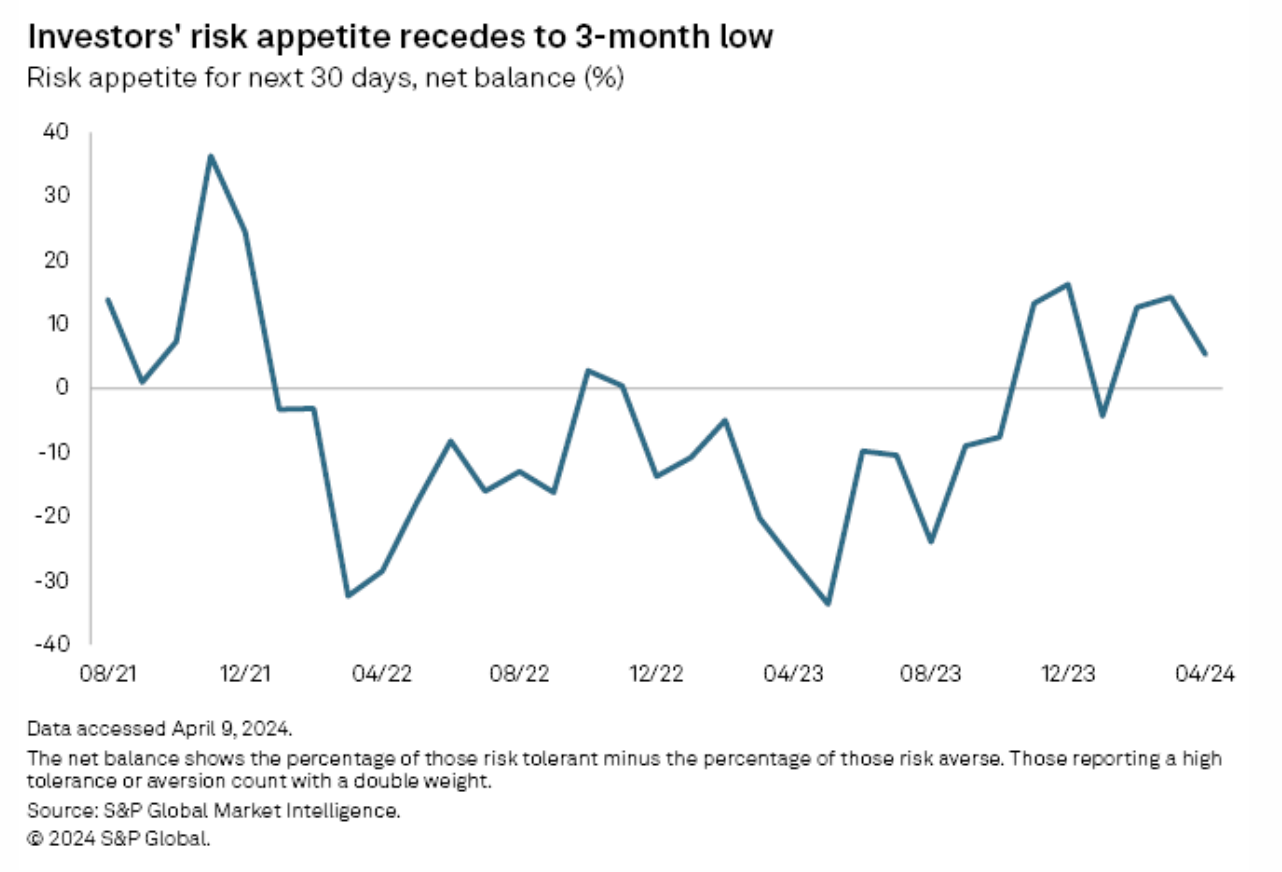
Equity investors grew less risk tolerant in April amid a worsening outlook on near-term equity market returns, according to the latest results from S&P Global's Investment Manager Index survey. US equity investors' risk appetite declined from 14% in March to 5% in April, remaining in mildly risk-tolerant territory for a third consecutive month.
—Read the article from S&P Global Market Intelligence
Access more insights on the global economy >
U.S. Home Price Overvaluation Softens As Wage Growth Outpaces Home Price Gains

S&P Global Ratings has updated its home price overvaluation assessment and the related Federal Housing Finance Agency Home Price Index (FHFA HPI) inputs, based on fourth-quarter 2023 data. Our assessment fell slightly to 14.3% as per capita income growth outpaced home price appreciation (HPA). However, it is still comparable to our last reading, which was an overvaluation of 15.6% at the national level based on third-quarter 2023 data. The non-seasonally adjusted All-Transactions FHFA HPI was close to flat (up 0.04%) between third- and fourth-quarter 2023, while the Purchase-Only Index decreased 0.29% on an unadjusted basis.
—Read the article from S&P Global Ratings
Access more insights on capital markets >
China Q2 Copper Concs TC/Rcs To Be Stable Amid Tight Supply, Smelters' Output Cuts
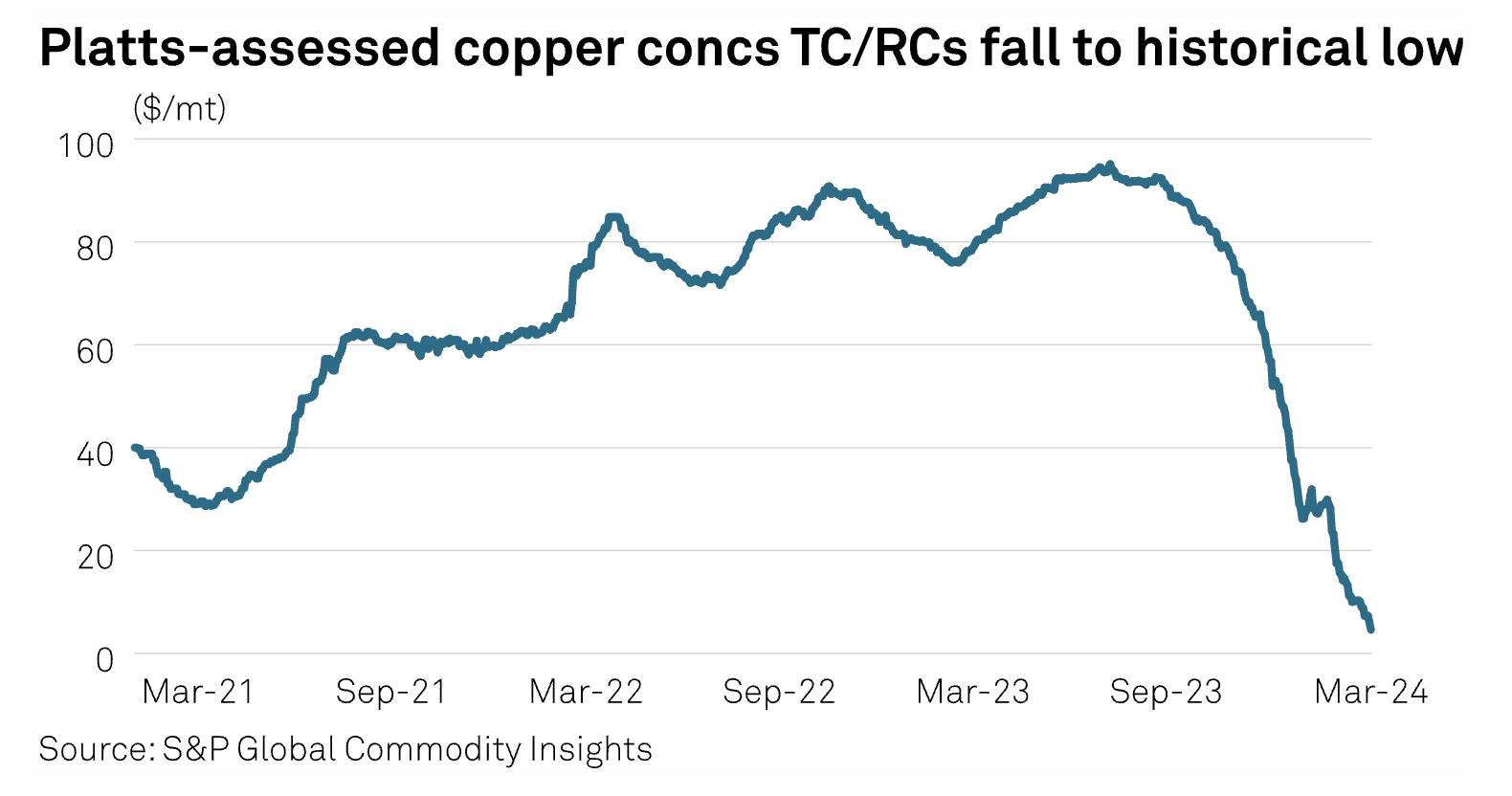
China's clean copper concentrate treatment and refining charges are likely to stay stable amid tight miner supply and lower smelter stocks in the second quarter of 2024. However, market sources also said they would await fresh indicators for clearer direction. Supply disruptions in Chilean copper mines such as Los Bronces, which is curtailing output to reduce costs, as well as Spence mine, which is facing high-moisture content, and delayed shipments of Indonesian-origin copper concs due to heavy rain have all contributed to smelters' lower inventory levels and low spot availability.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on global trade >
Listen: How Plastic Impacts Companies, Investors, Public Health And The Environment

Ahead of Earth Day on April 22, we’re launching a miniseries of the ESG Insider podcast looking at plastic. We’ll explore how plastic impacts human health and the environment, how companies and investors are approaching the topic, and what to expect from international plastic treaty negotiations starting April 23. In today's episode, we hear about the health and environmental impacts of plastics from Dr. Philip Landrigan, Director of the Program for Global Public Health and the Common Good at Boston College. He was lead author of a major scientific study the Minderoo-Monaco Commission on Plastics and Human Health published in 2023.
—Listen and subscribe to ESG Insider, a podcast from S&P Global Sustainable1
Access more insights on sustainability >
Asia-Pacific Energy Transition: Adapting To Looming Execution Risks
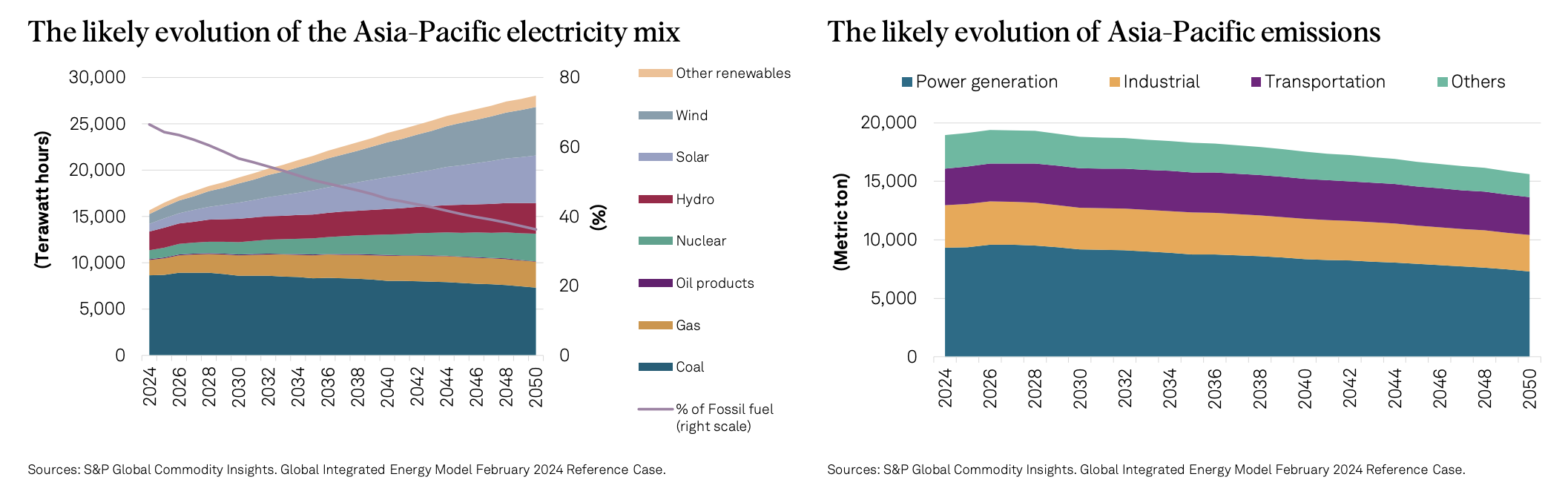
Energy transition plans are being revised as countries move to execution, with extended reliance on coal plants (China) or new coal plants (India), delayed retirement of coal plants (Australia), and a focus on alternate sources, such as gas (Vietnam), or hydro/geothermal (Indonesia).
—Read the article from S&P Global Ratings
Access more insights on energy and commodities >
Listen: Next In Tech Episode 162: The Cloud Native Journey

While getting to a cloud native development pattern is a goal for most organizations, it can be a significant journey to transform both infrastructure and processes. Analyst Carl Lehmann joins host Eric Hanselman to explore the paths that can move enterprises forward. DevOps approaches can speed development, Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) can change ways of managing risk and platform engineering can simplify tool sets, but adoption does not always follow a straight line.
—Listen and subscribe to Next in Tech, a podcast from S&P Global Market Intelligence
