Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Our Methodology
Methodology & Participation
Reference Tools
S&P Global
S&P Global Offerings
S&P Global
Our Methodology
Methodology & Participation
Reference Tools
S&P Global
S&P Global Offerings
S&P Global
Aug 15, 2022

By Adam Speck
HPAI, also known Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza or H5N1, is a contagious virus that has a high mortality rate among poultry. It infects the gastrointestinal and respritory systems of the bird, causing vital organs to cease to function. HPAI spreads via infected animals that transmit the virus through their saliva, mucus, and feces, as well as through farm equipment and vehicles. Due to the densely populated nature of poultry holding facilities, HPAI tends to spread rapidly and can wipe out a large percentage of the flock in a very short period of time. This can lead to a sudden drop in supply and a sharp rise in the price of related products. As a result of the the potential economic, social and psychological damage that can be caused by the presence and threat of HPAI, the USDA has established guidelines to actively track and mitigate the impact on the industry. The recommended form of action is culling, which is a rapid depopulation of infected birds in order to minimize the spread of HPAI to healthier members of the flock. The immediate impact of HPAI in North America has been reflected across all related poultry and egg markets since its initial identification in Dec 2021.
Although the impact of HPAI has been prevalent in the poultry and eggs sector as a whole, the individual sector impact has varied as the spread of the virus continues.
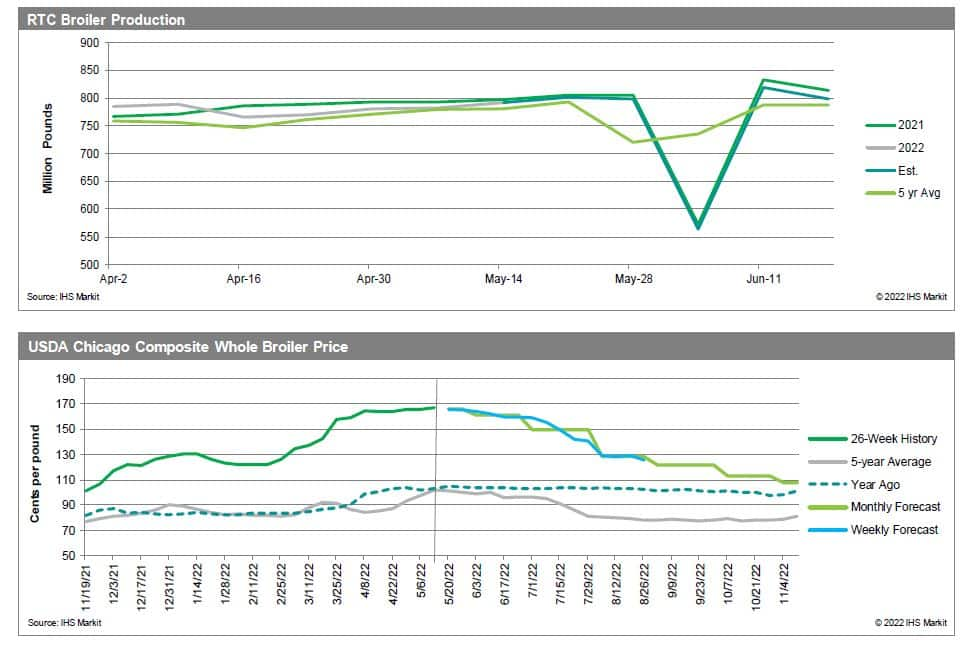
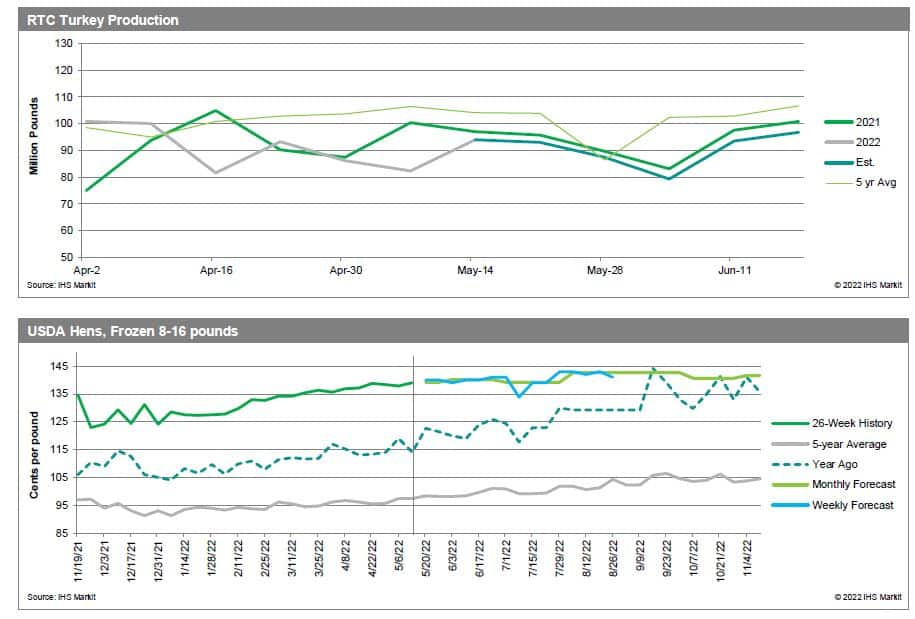
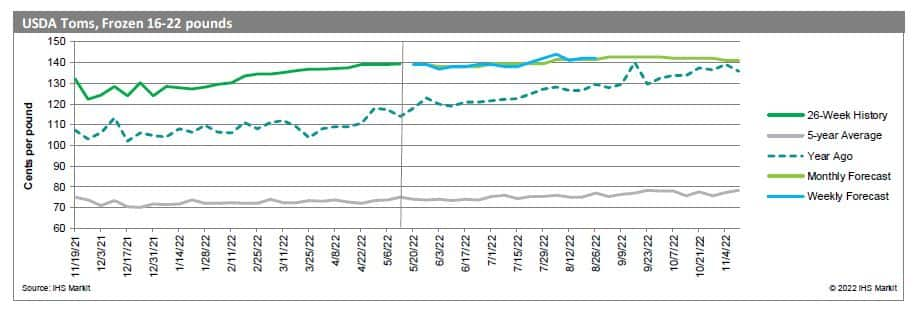
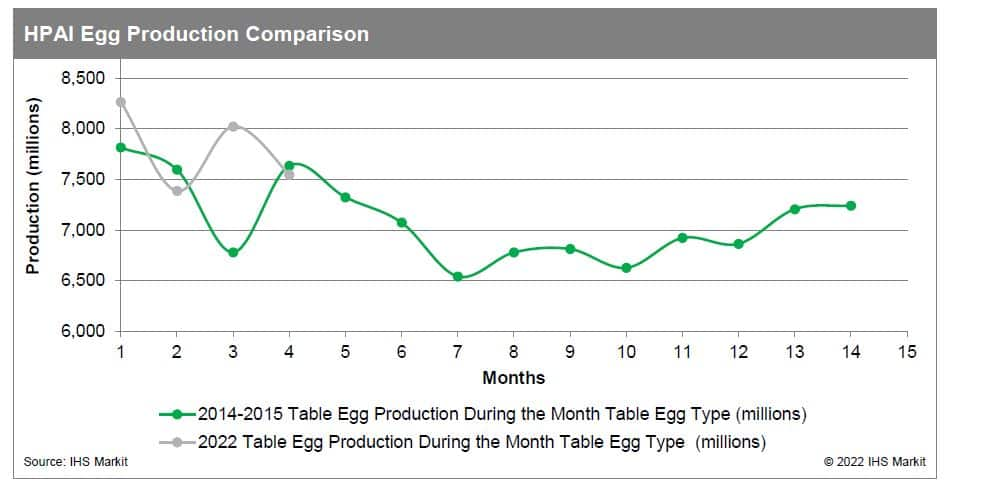
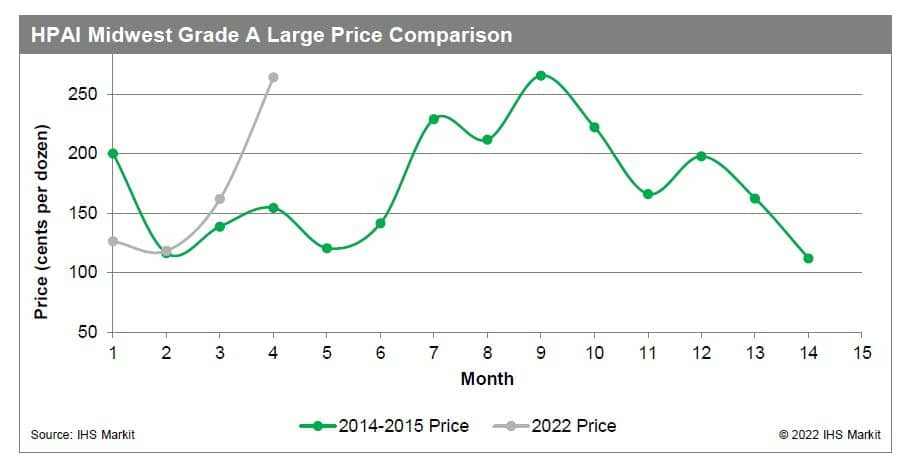
The previous HPAI outbreak in the United States occurred during 2014-2015, when similar behavior in trends across all poultry and egg markets occurred. Depopulation was still implemented at the time as the primary form of mitigation against the outbreak of the disease. Egg production declined sharply from May to December 2015, with the layer inventory falling to 2011 levels. As a result, prices increased sharply, with the benchmark egg price reaching a 61% premium from the previous year at its peak. Both processing and consumer grade eggs saw similar price action during the initial outbreak, but the spread between the two narrowed from May to August 2015 due to larger price increases in processing eggs, fueled by strong demand from commercial operations. Monthly egg exports declined by nearly 50% at the onset of the outbreak and resulted in a $41 million loss in export income. Turkey production endured a similar drop but began recovery in mid 2015 and returned to pre-HPAI levels by early 2016. Price fluctuations were relatively muted, with a slight increase occurring after the outbreak period, but returned back to pre-HPAI levels by December 2016. Monthly exports declined by nearly 40% and resulted in a $177 million loss in export income. Broiler production was not impacted by the spread of the virus and continued its sideways trend for the duration of the outbreak. Similarly, prices also trended sideways with a slight bias towards the downside throughout and past the outbreak period. Monthly exports also continued the regular trend and had no discernable impact on income. Egg production remains considerably elevated in 2022 when compared to the 2014-2015 level. Similarly, Midwest Grade A Large prices are trending higher this year when compared to the previous HPAI outbreak.
Posted 15 August 2022 by Adam Speck, Senior Economist, Livestock, S&P Global Energy
This article was published by S&P Global Energy and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.