Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Research — 4 Feb, 2021

By Nimayi Dixit
S&P Global Market Intelligence expects U.S. digital lender origination volumes to jump more than 20% per year over the next few years as the companies that weathered the initial shock of COVID-19 begin competing again for market share.
Origination volume in the first three quarters of 2020 among major digital lenders in the personal-lending-focused, small and medium-sized enterprises-lending-focused, and student-lending-focused segments plummeted 36% from year-ago levels. Volumes began to recover in the third quarter of 2020 after steep declines in the second quarter, but the recovery has been uneven among different companies, with some having already returned to pre-pandemic levels while others stagnate. S&P Global Market Intelligence expects the general upward trajectory to continue into the future though, with annual volumes in the industry projected to grow at a compound annual rate of 26% between 2020 and 2024.
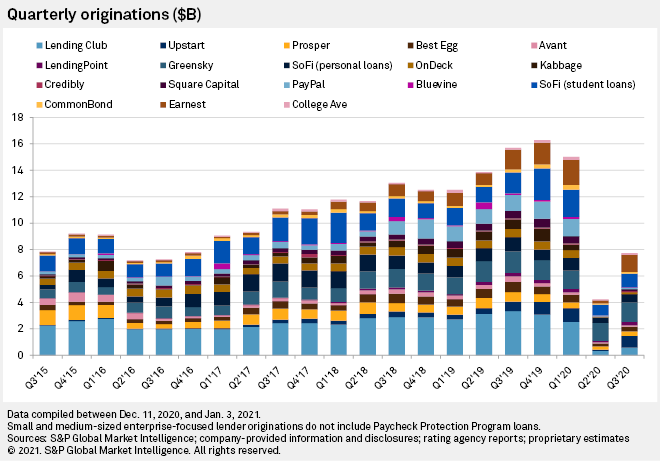
The pandemic dealt a serious blow to digital lenders
Origination activity plunged in 2020 as uncertainty around credit quality forced several lenders to tighten their underwriting standards and reduce approval rates. The spring of 2020 was particularly challenging. For example, at LendingClub Corp., the oldest and largest digital lender by cumulative originations, loans in forbearance peaked in May at about 16% of total loan balances. Meanwhile, the company tightened the screws on credit quality, with the average FICO rising to 721 in the second quarter of 2020 from 708 in 2019; while average incomes rose to nearly $108,000 from about $93,000.
Despite an improving credit outlook in the second half of the year, LendingClub had maintained model throughput at 40% to 50% below normal levels as of the end of the third quarter in an abundance of caution.
The funding environment also became challenging as the credit markets froze up in the immediate aftermath of the pandemic. Many loan investors, who digital lenders depend upon for liquidity, pulled back funding. Investors did return as the year progressed and the credit markets reopened, largely in response to various liquidity and lending facilities launched by the Federal Reserve.
Still, some government support may have negatively impacted digital lenders' originations by absorbing demand for credit. The Paycheck Protection Program, which aimed to bolster small businesses through government guaranteed loans with low interest rates, caused many digital lenders to apply for Small Business Administration approval so that they could facilitate the rescue loans. The major SME-focused digital lenders on S&P Global Market Intelligence's focus list originated $14 billion of the $525 billion PPP loans originated in the first round of PPP. Meanwhile, traditional, organic origination volumes in the first nine months of 2020 were down 61% compared to year-ago levels. That decline is greater than the decreases experienced by the personal and student-focused lenders.
Government stimulus and greater trepidation among consumers seems to have reduced demand for loans in other segments. Spending declined as lockdowns and economic pressure caused consumers to tighten their wallets. Visa Inc. processed nearly 8% fewer transactions in the second quarter of 2020 than in the first quarter; Mastercard Inc. processed 12% fewer transactions in the same time frame. Credit card loan balances at major issuers were depressed during the year, driven by lower spending volumes and decreased propensity among consumers to hold balances. This has likely decreased demand for personal loans which are often used to consolidate outstanding consumer debt.
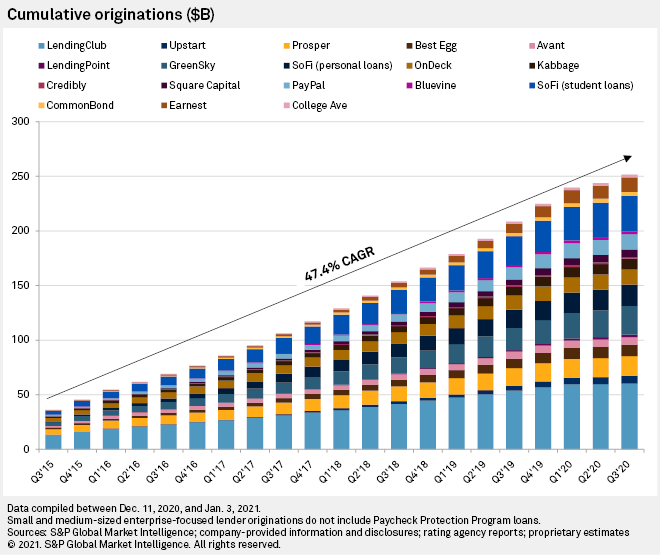
An uneven recovery
After a 72% quarter-over-quarter decline in the second quarter of 2020, the industry posted an 83% increase in originations in the following period. While volumes remained severely depressed relative to year-ago levels, signs of renewed origination activity and competition for market share were visible in the second half of 2020.
Some lenders had returned to near pre-pandemic origination levels by the second half of the year. Personal-focused lenders LendingPoint and Upstart Holdings Inc. actually grew origination volumes year-over-year in the first three quarters of 2020. LendingPoint posted an all-time high quarterly origination volume of $271 million in the third quarter. Upstart, which went public in December, posted an estimated 35% year-over-year increase in origination volume in the first nine months of the year. The company made nearly 81,000 loans in the third quarter, compared with about 12,000 in the second quarter.
The student-focused segment of our focus list has weathered the turmoil of the pandemic best among the three segments. Origination volume in the first nine months of 2020 was only 1% below 2019 levels, though volume for the group dropped by 74% between the first and second quarter of the year.
The segment's ability to stave off large year-over-year declines is attributable to its rapid growth prior to the pandemic. Between the first quarter of 2019 and 2020, the student-focused segment grew at a compound rate of over 14% per quarter compared to low single-digit growth rates for the other segments. The expansion was driven by the two largest companies in the group, Earnest Operations LLC, a subsidiary of Navient Corp., and Social Finance Inc.
The industry was not immune to consolidation though. Two of the largest SME-focused lenders sold in 2020. Despite being responsible for nearly half of the $14 billion PPP loans originated by the segment, Kabbage Inc. sold the bulk of its operations to American Express Co. in the summer of 2020. On Deck Capital Inc. sold to Enova International Inc. after struggling with complications induced by the pandemic.
OnDeck saw its 15-plus-day delinquency ratio nearly quadrupled in a single quarter, jumping to 39.5% in the second quarter of 2020 from 10.3% in the first quarter and 9.0% in the fourth quarter of 2019. The company was also engaged in a struggle with an activist investor during the spring of 2020.
Survivors rebounding from tough 2020
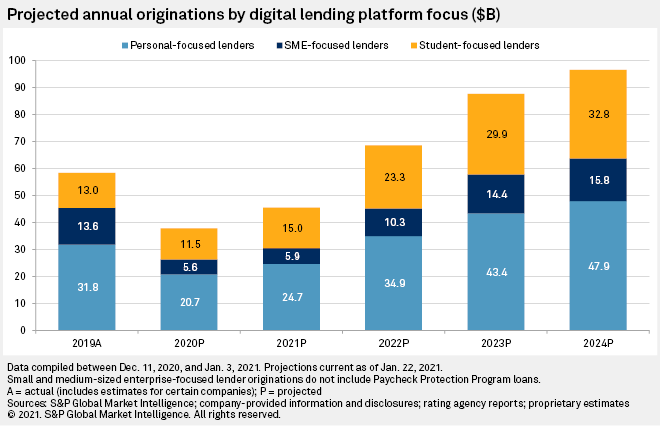
Lenders that have survived the storm will stand on stronger footing in 2021, as economists expect a strong rebound in economic activity this year, bolstered by the rollout of COVID-19 vaccines that allow economies to move closer to fully reopening. The resumption in business activity is expected to lead to considerable job gains and move unemployment closer to normal levels.
While GDP and unemployment are not expected to return to pre-pandemic levels for some time, a broader economic recovery should lead to a resurgence in originations for digital lenders. We've assumed that origination growth in 2021 will be roughly half the pace witnessed before 2020, but growth will accelerate notably in 2022 as consumers and the economy regain their footing. Though 2020 presented a significant blow to the industry, the group has already begun positioning itself to return to its upward trajectory and leave a notable mark on the financial services industry.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
Download the full report
Blog
Blog