Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Research — 24 Feb, 2022

By Nimayi Dixit
Introduction
Digital lender origination volumes across personal, student, and small and medium-sized enterprise lending rose above pre-pandemic levels in 2021 as stronger growth among personal-focused lenders helped the group rebound from a difficult 2020.

Personal-focused digital lenders originated an estimated 37% more in loans in 2021 relative to 2019. A healthy consumer credit environment, rising consumer demand and waning consumer stimulus created healthy demand for consumer credit. Personal-focused lenders were able to grow into this favorable environment without facing some of the headwinds that SME and student-focused lenders faced.
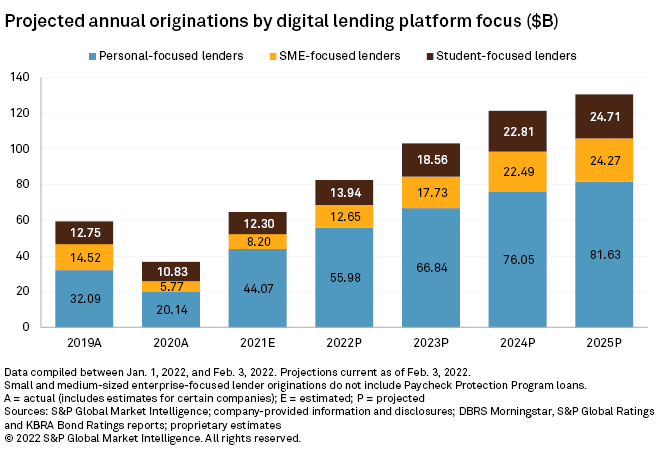
All three segments covered by S&P Global Market Intelligence grew origination volumes year over year in 2021. While inflation does pose some concerns, barring a significant shock to consumer demand in the near term, Market Intelligence projects a robust double-digit CAGR for the industry through 2025.

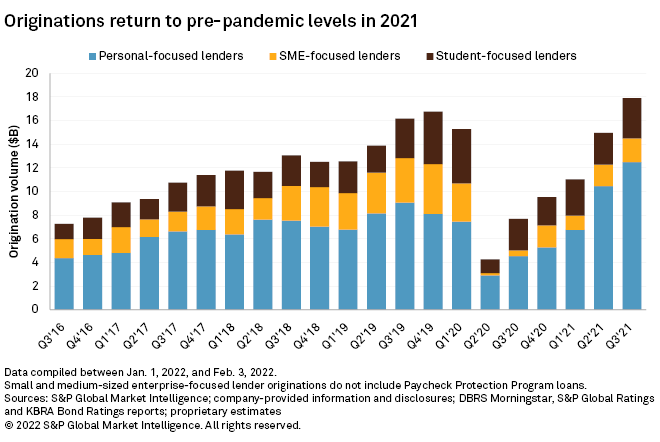
Economic recovery bolsters originations
The pandemic produced a historic contraction in origination volumes in 2020 for U.S. digital lenders servicing the personal, SME and student lending segments. Originations declined nearly 40% year over year.
But activity bounced back in 2021, as total originations across the 17 lenders covered by Market Intelligence are estimated to have grown over 75% year over year and over 8% relative to 2019 levels. The personal-focused lender cohort grew originations 37% relative to 2019 levels. SME-focused lenders originated about 44% less than they did in 2019 and student-focused are estimated to have originated nearly the same amount as they did in 2019.
Personal-focused lenders experienced a "Goldilocks moment" in 2021, where a confluence of macroeconomic factors produced rapid growth in demand for their products. Consumer balance sheet health improved in 2020 as consumers' savings reached historic highs and they diverted federal stimulus funds to pay off existing debt. Outstanding credit card debt declined precipitously during the year. As lockdowns eased heading into 2021, consumer spending increased, while waning government stimulus increased the demand for credit. Personal-focused lenders that navigated the turbulence of 2020 well were able to grow into the favorable credit and demand environment of 2021. Multiple lenders expanded volumes more than 100% year over year.
Businesses also benefited from the return of consumer spending in 2021. Though hiring and supply chain issues did create new problems in certain sectors, many industries noticed a marked improvement in activity relative to the lockdowns of 2020.
The pandemic created a very difficult environment for SME-focused lenders. Lockdowns and historic economic contraction produced great uncertainty in the credit profile of small businesses throughout the country. Financial technology lenders were forced to reduce origination volumes dramatically, with some companies such as Block Inc.'s Square Loans (formerly Square Capital) shutting down lending operations entirely in the second quarter of 2020. Kabbage Inc. and On Deck Capital Inc. sold their businesses.
Still, nearly $800 billion was lent out to small businesses through the Paycheck Protection Program, or PPP, between 2020 and 2021 to support them through the economic downturn, and fintech companies played a major role in the program. Lenders classified as "Fintechs (and other State Regulated)" originated over $6 billion in loans in 2020 under the program. In 2021, the group originated nearly $22 billion. However, the nearly $800 billion in PPP financing issued between 2020 and 2021 likely absorbed most of the loan demand from small businesses in those years, leaving little room for organic origination growth.
Organic origination volumes in our SME-focused group contracted by an estimated 60% in 2020. In 2021, volumes are estimated to have bounced back 42% from the 2020 lows but remained nearly 44% below 2019 levels.
Student-focused lenders faced a different headwind to organic origination growth. Under the Coronavirus Aid, Relief and Economic Security Act, a moratorium was placed on federal student debt payments. The deadline for this loan payment pause has been extended to May 2022. Federal student loans represent the vast majority of outstanding student loan debt and the payment pause has suppressed demand for refinancing, still the bread and butter of the student-focused digital lender cohort.
The headwind to demand dampened loan growth in 2021 despite a relatively robust credit environment. Despite this, we estimate loan originations returned to roughly 2019 levels in the year. A significant reshuffling also occurred amidst the chaos of the pandemic; Navient Corp., which originates loans primarily through its Earnest subsidiary, has established itself firmly as the dominant lender in the space, snatching the title from SoFi Technologies Inc. Navient originated $6 billion in student loans in 2021 compared to SoFi's estimated $3.72 billion. Navient was able to grow by focusing its marketing on private student loan borrowers rather than borrowers of federally backed loans. SoFi, meanwhile, has been focused on the diversification of its product offerings as it reengineers itself into a chartered banking institution.
Inflation may not alter outlook for future growth
Inflationary pressure is set up to be a major macroeconomic influence across the economy in 2022. The severity and duration of the pressure will determine its impact on the digital lending industry and its origination activity. Inflation could bolster demand for credit as consumers rely on it to support their purchases. However, if price increases depress overall consumer demand, that will have a negative impact on credit demand.
Experts are anticipating several rate hikes by the Federal Reserve in 2022, leading to an increase in the cost of debt. This could impact funding for digital lender loans as capital providers shift capital away from riskier assets. The increased cost of debt may also impact loan demand at the margins. However, loan yields on digital lender products, particularly personal and SME loans, can be quite high, often in the double-digits, implying that their customers may not be as rate sensitive as others. Many of the more mature players also enjoy robust yield spreads that may allow them to absorb rising funding costs instead of passing those on to borrowers.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
Segment