Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
13 Mar, 2023
By Rica Dela Cruz and Zuhaib Gull
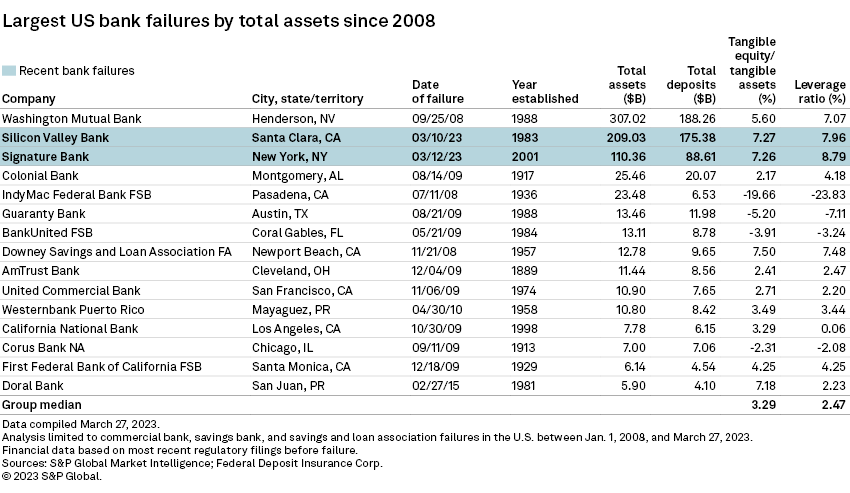
Signature Bank's downfall is the third-largest U.S. bank failure in history, ranking just below Silicon Valley Bank's recent collapse.
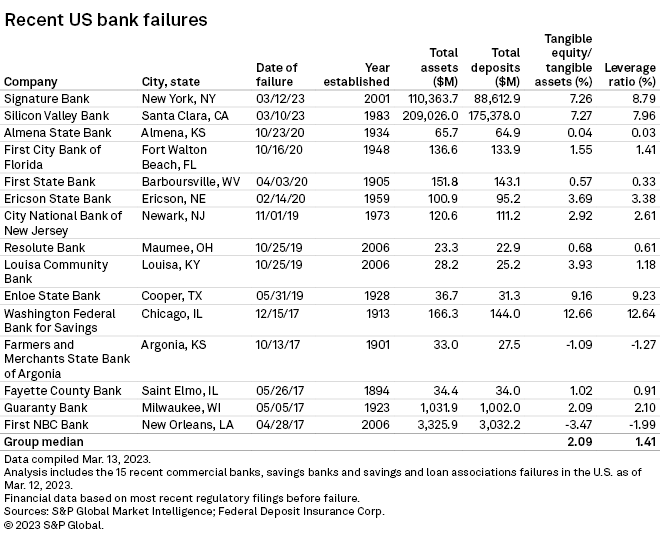
Signature Bank had $110.36 billion in assets and $88.61 billion in deposits as of the end of 2022, while Silicon Valley Bank had $209.03 billion in assets and $175.38 billion in deposits. That compares with the $307.02 billion of assets and $188.26 billion of deposits at Washington Mutual Bank at the end of its final quarter before its failure and sale to JPMorgan Chase & Co. in 2008.
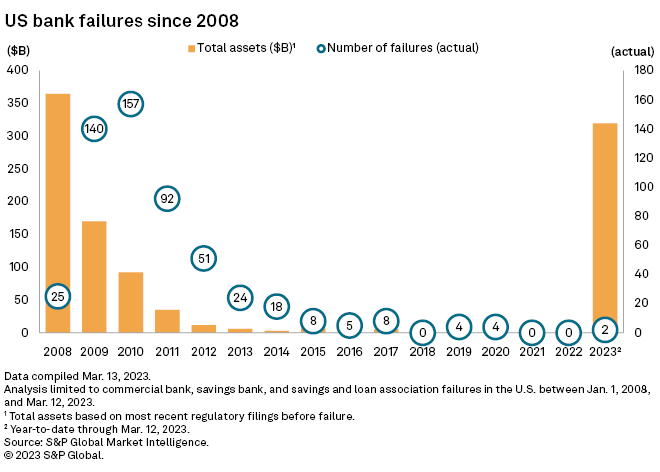
The New York Department of Financial Services took possession of Signature Bank on March 12 "to protect depositors" only two days after California's financial regulator closed Silicon Valley Bank. Regulators said all depositors at Signature Bank and Silicon Valley Bank will be protected. Signature Bank's collapse represents the second U.S. bank failure of 2023, and there were none in the prior two years, according to data from S&P Global Market Intelligence.
The total assets of the two failures in 2023 amount to 87.6% of the total assets from the 25 failures of 2008.
The cryptocurrency effect
Signature Bank had been under pressure since the cryptocurrency market collapse in 2022. During the year, cryptocurrency prices and volumes declined and FTX Trading Ltd., BlockFi Inc. and Voyager Digital Ltd. filed for bankruptcy, resulting in several banks experiencing heavy deposit losses related to digital assets.
Signature Bank and Silvergate Capital Corp., which recently decided to wind down its operations and liquidate its banking subsidiary, were two of the largest banks serving the cryptocurrency industry by deposit size.
On March 2, Signature Bank released a midquarter update, reporting lower spot deposit balances by about $826 million as of March 1 compared to levels at the end of 2022. The decline was driven mostly by a $1.51 billion decrease in deposits related to clients in the digital asset industry.
Following the update and before Signature Bank was shut down, analysts said the digital deposit outflows were in line with management's guidance in January, implying the company could raise the pace to cut more digital deposits by midyear.
On Signature Bank's fourth-quarter 2022 earnings call, co-founder, President and CEO Joseph DePaolo called for actionable regulatory guidance on cryptocurrency banking. Such guidance from the Federal Reserve, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corp. and the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency is needed to eliminate unqualified players and help rebuild the industry's confidence in banking for digital assets, DePaolo said.
* Download a template to view a list of bank failures in the U.S. since 1998.
* Download a template to generate a bank's regulatory profile.
* View an interactive list of failed banks.
Investor concerns amplify
There were 532 bank failures from 2008 through 2019. From 2020, there have been six failures, including Silicon Valley Bank and Signature Bank.
The news of Silicon Valley Bank's failure intensified the Street's concerns about funding, with banks such as First Republic Bank, PacWest Bancorp and Western Alliance Bancorp. facing questions about liquidity pressure due to their venture capital exposure.
First Republic Bank's stock price tumbled in premarket trading March 13 after the announcement of additional new liquidity from the Fed and JPMorgan failed to allay investor concerns. PacWest and Western Alliance issued updated financial figures following the declines in their respective stock prices.