Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Blog — 13 Sep, 2023

By Sidiq Dawuda
Business Description:
Lordstown Motors Corporation (NASDAQ: RIDE) – (LMC) was an American electric vehicle motor company headquartered in Lordstown, Ohio. The primary vehicles it focused on developing were electric full-size pickup trucks for fleet customers in the United States. LMC, at its highest growth point, had a steady cash flow and an end-of-year revenue of $244 million, successfully raising capital of $182 million in 2022.1 On June 27th, 2023, the company along with its affiliates filed for Bankruptcy under the Chapter 11 US Bankruptcy Act.
Bankruptcy Summary:
In April 2023, LMC allegedly breached a $170 million investment with electronics company Foxconn, formally called Hon Hai Precision Industry Co., Ltd. (TWSE:2317). In addition, it received a warning from NASDAQ that it would be delisted as its share price fell towards the $1 minimum on the 7th of March. Foxconn and LMC disagreed on the terms of their business arrangement, leading to the investment ending as soon as the first deal was concluded. Important to note, the Credit Analytics probability of default (PD) of LMC was significantly higher than that of the benchmark for the Automobile Manufacturing Industry for a significant amount of time. In addition to the unstable macroeconomic environment, LMC failed to meet customer demand leading to flagging revenues and a rise in PD. Upheavals in the senior management and leadership of the company, added to the uncertainty surrounding its creditworthiness, with both the CEO Steve Burns and CFO Julio Rodriguez resigning from their posts on the 14th of June.[1] Following this, the company restructured under Chapter 11, to finalize its efforts to sell its remaining vehicles, and related assets.
Fundamental Probability of Default Analysis:
In Figure 1 below, shows S&P Global Market Intelligence’s Credit Analytics, one-year Fundamental Probability of Default (PDFN) shows how LMC’s credit score has been significantly impacted by sales performance and market sentiment. There is a clear increase of approximately 30% from the PD of 7.7% in March 2021 to the final PD as the firm approached bankruptcy. Undertaking a 3-year analysis, the PD in Jan 2021 was 52.17%, rapidly increasing to an approximate PD of 76.37%. This highlighted the worsening creditworthiness of LMC with PD deteriorating over consecutive periods. Prior to the company going into administration, our models had raised red flags warning investors it was risky for them to maintain their exposure to the company.
Figure 1: Analysis of Fundamental Probability
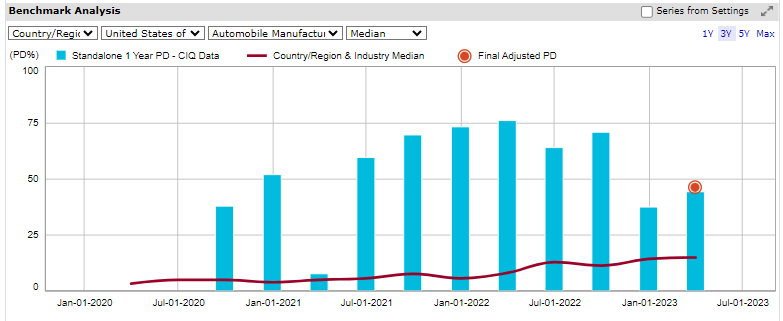
Source: Credit Analytics from S&P Global Market Intelligence. Data as of July 18, 2023. For illustrative purposes only.
Figure 2 separates the business and financial risk. The business risk is related to the business model in terms of the industry and region of the company. With respect to the financial risk, it can be explained by the high share of debt (and consequently low equity) given its asset base, which left it vulnerable to the macroeconomic headwinds that buffeted the economy and industry. The most significant factor which had impacted the company’s PD was the total equity. The company’s total equity was $212.62M in comparison to $2469.71M for the comparable country and industry median. As the risk increased, there was a direct impact on the PD which increased by over 101%. Sales growth also had a punitive impact on the credit strength of LMC with 0% growth over the last 2 reporting periods. In addition, many of the other financial and business risk drivers such as the EBIT-to-revenues and Retained Earnings to Total Assets ratios were contributing to the deterioration of the PD with the company considered to have the worst business risk classification, namely “vulnerable” and to be “significantly leveraged”. The poor sales performance and failure of its partnership with Foxconn led to LMC faltering. The PDFN provided an early signal of deterioration, well in advance of the eventual bankruptcy filing.
Figure 2: Fundamental Probability of Default

Source: Credit Analytics from S&P Global Market Intelligence as of July 24, 2023. For illustrative purposes only.
Exhibit 3: Key Market Developments
|
Date |
Event Type |
Headline |
|
Jul-06-2023 |
Index Constituent Drops |
LMC dropped from NASDAQ |
|
Jun-30-2023 |
Index Constituent Drops |
LMC dropped from S&P TMI Index |
|
Jun-30-2023 |
Index Constituent Drops |
LMC dropped from S&P Global BMI Index |
|
Jun-29-2023 |
Delistings |
LMC NASDAQ Delisting Notice |
|
Jun-28-2023 |
Bankruptcy - Other |
Motion for Joint Administration Approved for LMC |
Source: S&P Global Market Intelligence as of July 19, 2023. For illustrative purposes only.
Rising default rates and economic headwinds are putting a spotlight on the importance of robust, forward-looking models that combine both financial and macroeconomic variables to provide a clear and transparent view of a company’s credit risk profile. RiskGauge™ from Credit Analytics not only pinpoints a company’s potential weaknesses but also provides a wider market context that enables informed conclusions and decision-making.
This blog is written and published by S&P Global Market Intelligence, a division independent from S&P Global Ratings. Lowercase nomenclature is used to differentiate S&P Global Market Intelligence credit scores from the credit ratings issued by S&P Global Ratings.