Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
WHITEPAPER — Aug 28, 2023
The U.S. Department of the Treasury's Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) and the U.S. Department of Commerce's Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) issued a joint alert regarding the proliferation of certain 'high priority goods' being exported and transshipped to Russia in order to support its war effort in Ukraine.
The alert, issued in May 2023, identifies 9 Harmonized System (HS) Codes which should be used by financial institutions and others for enhanced customer due diligence purposes. The 9 HS Codes are as follows;
Similar regulation covering goods across HS Codes 84 and 85 have also been implemented by the European Union and United Kingdom.[1]
One of the major challenges to identifying strategic and battlefield goods in international trade is the lack of standardisation when describing products in documents such as a bill of lading, airway bill or invoice. Furthermore, the usage of the HS code in trade documents is low, the associated description of a certain HS code contains phrases not often found in the same documents and many goods and items are described in various ways, making the identification of potential military end-use items a challenge.
Directly incorporating the 9 HS Codes and their descriptions into a risk and compliance screening programme will yield a particular set of results and has the potential for missing some items classified in the High Priority List because the HS Code is not specified or the goods are described in a different manner. The correlation between a HS Code and an Economic Classification Control Number (ECCN) is not always definitive or one-to-one.
In order to assimilate the High Priority List into a screening programme it is necessary to determine the potential ways of describing these items outside of just the HS Code or a single keyword. Similarly, understanding where the key export partners of these items are based and which countries the goods are shipped too will assist in the understanding of how and where risk is likely to be found. This paper will seek to identify certain countries that are recent partners of U.S. exports for High Priority List goods, how they have been described in U.S. export bill of lading documents and how they are shipped.
The following charts highlight exports of the 9 HS Codes described in the FinCEN/BIS Alert as being the key items currently used within Russian weapon systems and found on the battlefield in Ukraine.
These charts are categorized by individual HS Code and capture the trade of U.S. exports to the top 15 countries where the percentage change in the growth of trading partners is highest. Percentage change for all the following charts is calculated as the difference between March 2023 and March 2022.
New trading partners for U.S. exports in 2022 and 2023 for High Priority Items can assume the potential for transhipment hubs or reexport zones for goods and items now known as battlefield electronics. As mentioned in the FinCEN/BIS alert, current behavioural or red flag indicators now stress the need to understand entities and individuals shipping goods from the High Priority List for the first time. Individual countries can also offer a general indication to support this hypothesis.
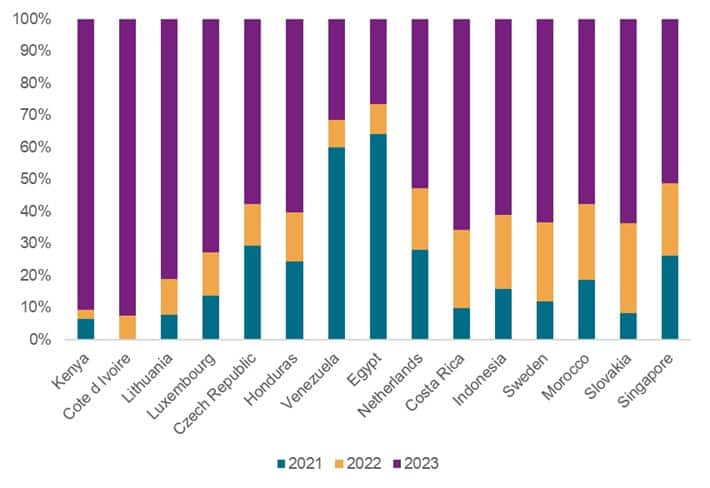
Source: S&P Global Market Intelligence (Global Trade Analytics Suite). Date as of July 10, 2023
For 'Processors and Controllers' defined with HS Code 854231 above, Cote d'Ivoire has emerged as a new U.S. trading partner in 2022 and 2023 despite there being no trade data supporting this corridor in previous years. Kenya and Lithuania also indicate a greater emphasis in 2022 and 2023 for receiving goods in this category.
Click here to read and download the full paper.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[1]https://finance.ec.europa.eu/system/files/2023-06/230623-list-high-priority-battlefield-items_en.pdf and https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/russia-sanctions-common-high-priority-items-list
Subscribe to our complimentary Global Risk & Maritime quarterly newsletter, or listen to Maritime and Trade Talk podcast for the latest insight and opinion on trends shaping the shipping industry from trusted shipping experts.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
How can our products help you?
