Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
ECONOMICS COMMENTARY
Sep 10, 2018
Global growth close to two-year low in broadening slowdown
- Global PMI at second-lowest since November 2016
- Slower developed and emerging market growth
- Exports and consumer sector see steepest slowdowns
- Prices rise sharply
Global economic growth edged lower in August, according to the latest PMI surveys, down to its second-weakest for nearly two years. The surveys also brought signs of an export-led slowdown spreading to other parts of the economy, including weaker growth of business investment and consumer spending.
The headline JPMorgan Global Composite PMI, compiled by IHS Markit, fell from 53.7 in July to 53.4, its second-lowest since November 2016.
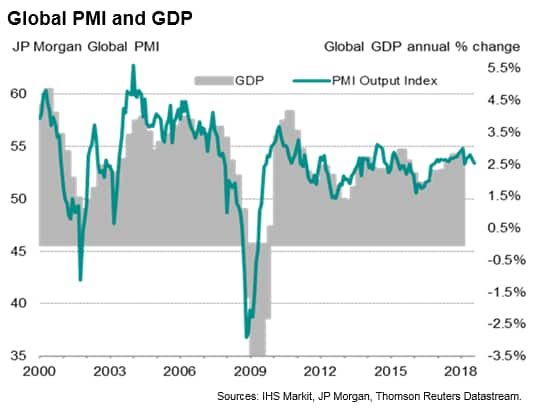
On one hand, despite the fall, the latest reading is only marginally below the 53.8 average seen in 2017 and remains indicative of global GDP rising at a solid annual rate of 2.5% (at market exchange rates). Future expectations improved slightly, albeit still the second-lowest seen so far this year.
On the other hand, manufacturing output growth continued to run at one of the weakest rates seen over the past two years, stymied by a further near-stagnation of global trade flows. Global export orders barely rose for a fourth consecutive month in August.
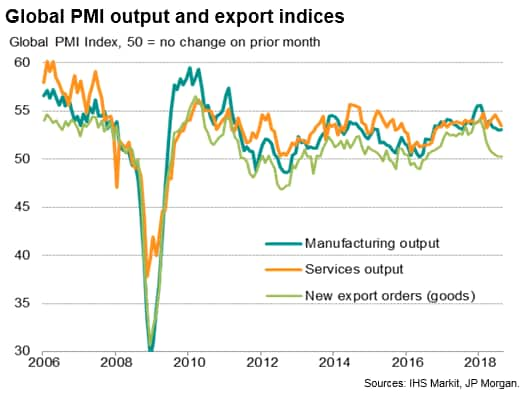
Furthermore, in a sign of weakness spreading beyond the export sector, August also saw worldwide service sector business activity grow at the slowest pace for five months, also registering one of the softest performances seen over the past two years.
Slower developed and emerging markets
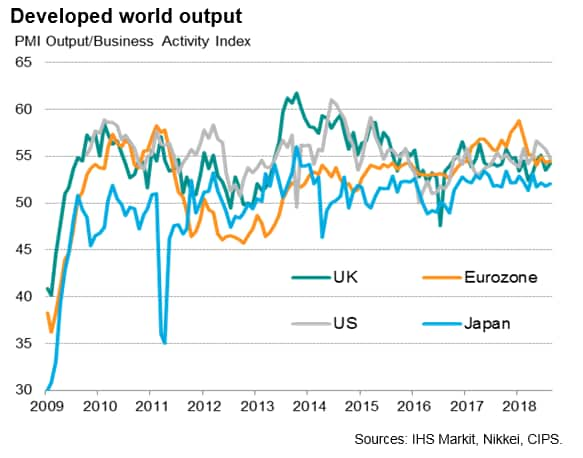
Developed world output growth hit the second-slowest since November 2016, reflecting weakened services expansion alongside relatively subdued manufacturing growth. The US was the best-performing major developed economy for the fourth successive month, though an easing in the rate of growth meant the gap closed with the UK and Eurozone. Japan again saw the weakest (albeit still solid) expansion.
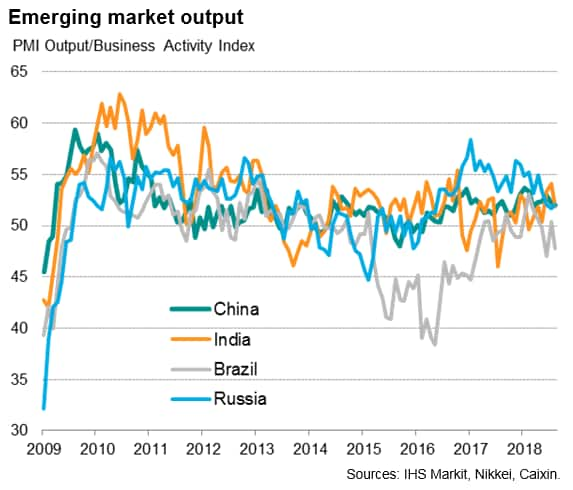
Emerging markets meanwhile grew at the slowest pace since last October, as weaker services growth matched a factory sector stuck in a low gear. Of the four largest emerging markets, only Russia saw faster growth. Growth slowed in both China and India, but Brazil was the worst performer, suffering the second-largest output decline seen in the past year-and-a-half.
Broader weakness
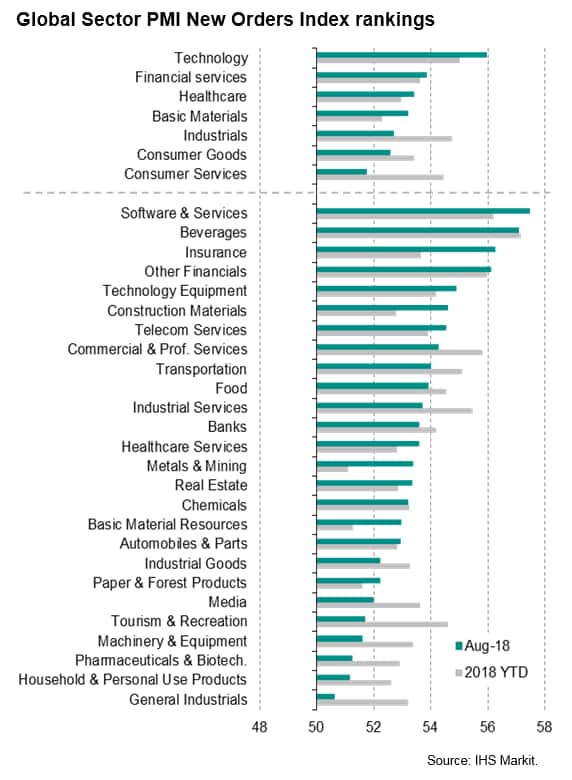
Global sector PMI data allow us to drill down into detailed industry trends, and highlight how the slowdown has broadened-out in recent months.
So far this year, new order growth has waned compared to last year for most broad industry categories covered by the PMI surveys. The main exception is consumer services, which hitherto had been a key area of support to the global economic upturn. However, comparing the latest three months to August with the prior three months, it's consumer services that has lost the most growth momentum, suggesting even this sector is now starting to struggle.
The consumer goods and consumer services sectors in fact registered the weakest expansions for five and ten months respectively in August, with household products, tourism & recreation and media sub-sectors seeing especially sluggish demand growth.
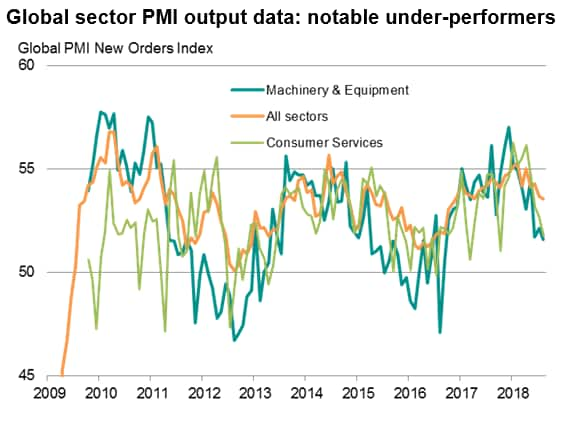
A further sector notable in terms of its slowdown is machinery & equipment manufacturing, as this sector is a bellwether of wider capital spending. The machinery sector has seen order book growth cool sharply since the start of the year, culminating in August with the smallest monthly gain in new orders since September 2016.
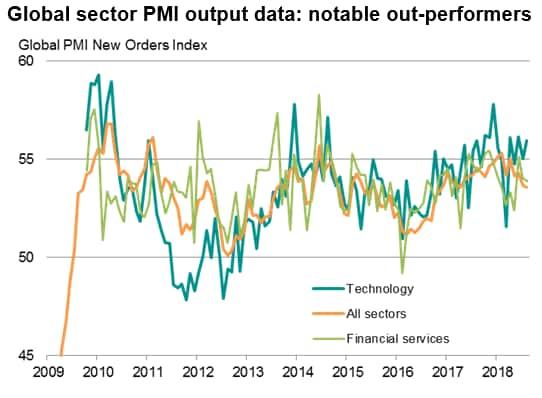
Not all sectors are struggling, however, with technology and (to a lesser extent) financial services being notable out-performers in August.
Higher prices
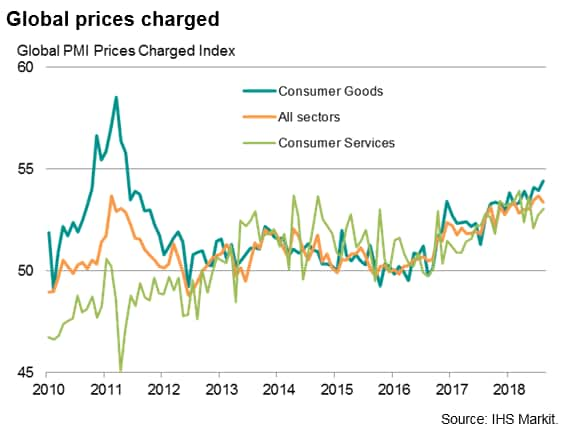
While slower export growth has been commonly attributed by PMI respondents to rising concerns regarding tariffs and trade wars, some of the recent slowing in demand has also been linked to rising prices. Average prices charged for goods and services rose globally at the joint-fastest rate seen since the global financial crisis in July, easing only modestly in August. However, the rate of increase of average prices charged for consumer goods accelerated further in August, highlighting how rising costs are feeding through to higher consumer inflation, sending hawkish signals for monetary policy.
© 2018, IHS Markit Inc. All rights reserved. Reproduction in
whole or in part without permission is prohibited.
Chris Williamson, Chief Business Economist, IHS
Markit
Tel: +44 207 260 2329
chris.williamson@ihsmarkit.com
Purchasing Managers' Index™ (PMI™) data are compiled by IHS Markit for more than 40 economies worldwide. The monthly data are derived from surveys of senior executives at private sector companies, and are available only via subscription. The PMI dataset features a headline number, which indicates the overall health of an economy, and sub-indices, which provide insights into other key economic drivers such as GDP, inflation, exports, capacity utilization, employment and inventories. The PMI data are used by financial and corporate professionals to better understand where economies and markets are headed, and to uncover opportunities.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fglobal-growth-close-to-two-year-low-in-broadening-slowdown.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fglobal-growth-close-to-two-year-low-in-broadening-slowdown.html&text=Global+growth+close+to+two-year+low+in+broadening+slowdown+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fglobal-growth-close-to-two-year-low-in-broadening-slowdown.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Global growth close to two-year low in broadening slowdown | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fglobal-growth-close-to-two-year-low-in-broadening-slowdown.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Global+growth+close+to+two-year+low+in+broadening+slowdown+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fglobal-growth-close-to-two-year-low-in-broadening-slowdown.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}




