Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
BLOG
Sep 03, 2020
Daily Global Market Summary - 3 September 2020
A significant and unexpected sell off in US tech companies drove all major US and most European equity markets lower on the day, while APAC markets closed mixed. US government bonds closed only modestly higher on the day despite the heightened volatility in equities, while European benchmark bonds closed mixed. iTraxx and CDX closed sharply wider across IG and high yield and oil/gold also closed lower on the day.
Americas
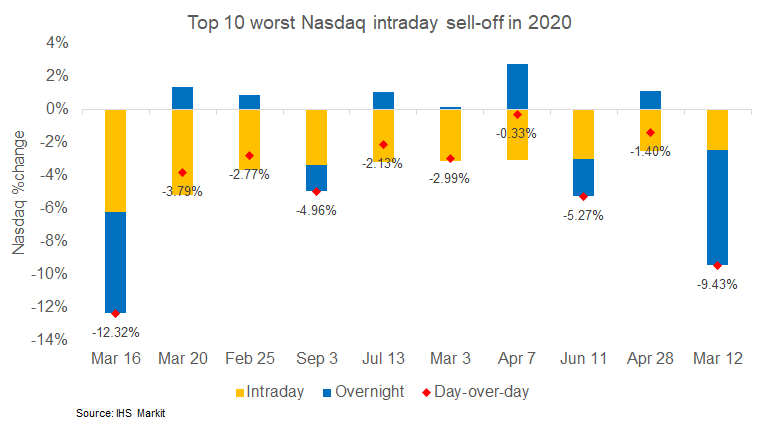
- US equity markets began to rapidly deteriorate beginning at 10:00am EST, with tech suffering the most losses on the day; Nasdaq -5.0%, S&P 500 -3.5%, Russell 2000 -3.0%, and DJIA -2.8%.
- Today was the Nasdaq's 4th worst intraday performance and 5th
worst day-over-day performance this year. The below chart shows the
Nasdaq's 10 worst intraday selloffs and those days' corresponding
overnight and day-over-day percent changes:
- 10yr US govt bonds closed -1bp/0.64% yield and 30yr bonds closed -2bps/1.36% yield. 10s did rally shortly after the release of the US jobless claims report to the day's lowest yield of 0.61% at approximately 11:30am EST.
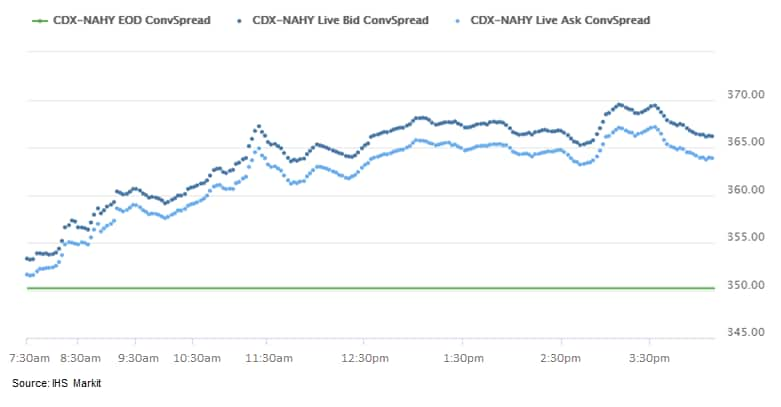
- CDX-NAIG closed +4bps/66bps and CDX-NAHY +11bps/362bps. Both IG
and high yield opened lower and continued to widen alongside the
selloff in equities.
- Gold closed -0.4%/$1,944 per ounce.
- Crude oil closed -0.3%/$41.37 per barrel.
- Seasonally adjusted US initial claims for unemployment
insurance, at 881,000 in the week ended 29 August, remained at
historically high levels, although well below the all-time high of
6,867,000 in the week ended 28 March. Under the old adjustment
methodology, this figure would have been roughly 1,020,000,
marginally up from the prior week's figure. (IHS Markit Economist
Akshat Goel)
- Beginning with this release, the method of seasonal adjustment has been switched from multiplicative to additive. Over the last several months, and especially in March, multiplicative adjustment has resulted in differences between adjusted and unadjusted figures that are too large to be reasonably accounted for by seasonality. Switching to additive adjustment will fix this issue. Historical data, prior to the data in this week's release, have not yet been revised to reflect this new methodology for seasonal adjustment.
- There were 13,254,000 seasonally adjusted number of continuing claims (in regular state programs) in the week ended 22 August. The seasonally adjusted insured unemployment rate in the week ended 22 August was 9.1%. Under the old adjustment methodology, the number of continuing claims would have been 14,045,000, a decrease of 447,000 from the prior week's figure.
- There were 759,482 unadjusted initial claims for Pandemic Unemployment Assistance (PUA) in the week ended 29 August. In the week ended 15 August, continuing claims for PUA rose by 2,597,557 to 13,570,327.
- In the week ended 15 August, 1,393,314 individuals were receiving Pandemic Emergency Unemployment Compensation (PEUC) benefits.
- The Department of Labor provides the total number of people claiming benefits under all its programs with a two-week lag. In the week ended 15 August, the unadjusted total rose by 2,195,835 to 29,224,546.
- In the week ended 22 August, US states reported 823,212 initial
unemployment claims, a decrease of 63,120 compared with the prior
week. Claims fell in all but 13 states but remain above
pre-COVID-19 levels throughout the country. (IHS Markit Economist
Alex Minelli and Fran Hagarty)
- Continuing unemployment claims, which lag initial claims by one week, numbered 13,726,619 in the week ended 15 August. Declines occurred in 48 states as continuing claims fell by 286,643 (2.0%) from the previous week.
- The insured unemployment rate, equal to continuing claims divided by covered employment, fell by 0.2 percentage point to 9.5% as 47 states saw a decrease in the week ended 15 August.
- Of the 13 states that saw an increase in initial claims, California saw the largest increase at 6,562, followed by Illinois (up 3,856) and Pennsylvania (up 1,926). States with increases of more than 1,000 claims cited increased layoffs in manufacturing, accommodation and food services, and retail trade.
- The largest decreases were seen in Florida (down 21,127), Texas (down 9,248), New Jersey (down 5,235), Virginia (down 3,715), and North Carolina (down 3,708).
- The significant decline in Florida's filings of initial claims
followed the state's efforts to combat the spread of COVID-19 while
supporting efforts to boost economic activity. Florida has
attempted to stem the bleeding in its leisure and hospitality
employment by calling for theme parks to expand capacity and
professional and college sports teams to allow limited fan
attendance in stadiums, and is starting a $13-million campaign to
encourage tourism within the state.

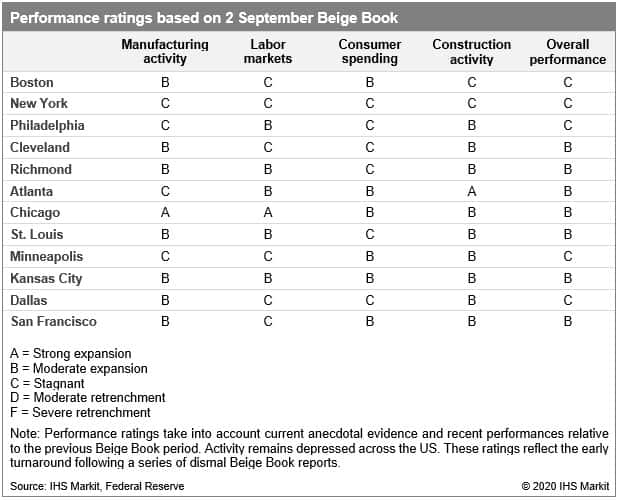
- Federal Reserve's Beige Book indicates economic activity
remains well below pre-pandemic levels as hiring in Northeast state
economies stagnates. (IHS Markit Economist James Kelly)
- Economic activity continued to increase in much of the country in July and August according to the US Federal Reserve's latest Beige Book report, containing anecdotal information from regional business contacts, but increasing COVID-19 outbreaks and heightened uncertainty around the course of the pandemic put the brakes on the recovery in Texas and resulted in stagnation in the Northeast.
- Hiring lost momentum over the summer as COVID-19 cases rose in the South and concerns around infection risk, childcare, and the coming school year limited employment growth in many regions. Retail sales dipped sharply in Texas as the pandemic ballooned while the ongoing travel recession limited consumer spending gains in tourism-heavy metros in California, the Northeast, and the South.
- The continued restart of automotive manufacturing plants boosted steel production in the Midwest, but weak activity in the Northeast and declining new orders elsewhere point to a slower end of the year.
- Homebuilding activity was modest outside the Northeast and was brisk in the West, but strong homebuyer demand overwhelmed the market in the South as low mortgage interest rates coaxed buyers into the market.
- Consumer spending rose in many parts of the country as auto sales remained strong, but retail sales and spending from tourism and travel was mixed. Tight inventories of new cars following the spring manufacturing shutdowns restrained sales in Texas, areas around the Great Lakes, and in New York, but used-car sales boosted dealership activity
- Labor markets expanded slightly but the pace of hiring ticked down noticeably in many parts of the country while employment levels remained far below pre-pandemic levels everywhere. While employment rose strongly in Illinois, Michigan, and areas around Lake Michigan, weak customer demand and increased uncertainty resulted in sluggishness in the rest of the Midwest.
- Manufacturing activity rose modestly in the Midwest and Great Lakes regions as automotive manufacturing plants continued to resume operations. Steel producers in Ohio, Missouri, and Kentucky saw boosts in activity, and many indicate they are running at full operation. Aviation and aerospace manufacturers and suppliers in the Northeast and Midwest continue to see weak business as travel remains depressed amid the ongoing pandemic and sharply reduced airline operations. Overall manufacturing activity in the Northeast was tepid and "slowed to a crawl" in New York.
- Construction activity struggled to keep up with demand for
homes in Georgia, Tennessee, and Florida as low mortgage interest
rates pushed many buyers into the real estate market. Surging home
sales in Virginia and the Carolinas led to many homes being sold
"sight unseen." A similar pattern continued to occur in the Midwest
and Great Lakes area as low rates and increasingly tight
inventories of single-family homes create a "sense of urgency."
Many homebuyers who expect to work remotely demonstrated their
desires for less-crowded suburban locales and larger living
spaces.
- The seasonally adjusted final IHS Markit US Services PMI
Business Activity Index registered 55.0 in August, up notably from
50.0 in July and slightly higher than the earlier 'flash' estimate
of 54.8. (IHS Markit Economist Chris Williamson)
- The latest expansion was strong overall and the quickest since March 2019. Firms often stated that the upturn in output was due to greater client demand and the further reopening of businesses.
- Cost burdens rose at a steep pace, despite the rate of inflation easing from that seen in July. Higher supplier prices and greater costs for equipment such as PPE drove input prices up.
- Greater pressure on capacity stemmed from a further accumulation of backlogs of work.
- With the exception of July's recent high, the pace of increase was the fastest since October 2018.
- US productivity (output per hour in the nonfarm business
sector) rose at a 10.1% annual rate in the second quarter, revised
up 2.8 percentage points. Hours worked fell at a 42.9% rate
(revised up 0.1 percentage point), while compensation per hour
surged at a 20.0% rate (revised down 0.4 percentage point). (IHS
Markit Economists Ken Matheny and Lawrence Nelson)
- The revisions to the large second-quarter swings in productivity, hours, and compensation per hour were close to our estimates. Unit labor costs rose at a 9.0% pace in the second quarter, revised down 2.2 percentage points from the previously reported.
- For the first quarter, growth in unit labor costs and compensation per hour were each revised down 0.2 percentage point. Growth in productivity and hours were not revised.
- The reference period for the source data the Bureau of Labor Statistics used in estimating first-quarter productivity predated most COVID-19-related job losses, which surged beginning in the week ending 21 March. To capture these losses, adjustments were made to March employment based on non-seasonally adjusted data for initial claims from the second half of March. There were no such adjustments made for the BLS's estimate of second-quarter productivity. Further information is contained here.
- Data on productivity and costs were severely impacted by fallout from the COVID-19 pandemic, so the implications of recent quarterly data for longer-run trends are unclear. Productivity growth firmed prior to the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. During 2019, productivity rose 1.9%, up from an average of 1.2% over the three years through 2018. Over the first two quarters of 2020, productivity rose at a 4.8% annual rate. We expect productivity growth to ease in coming quarters.
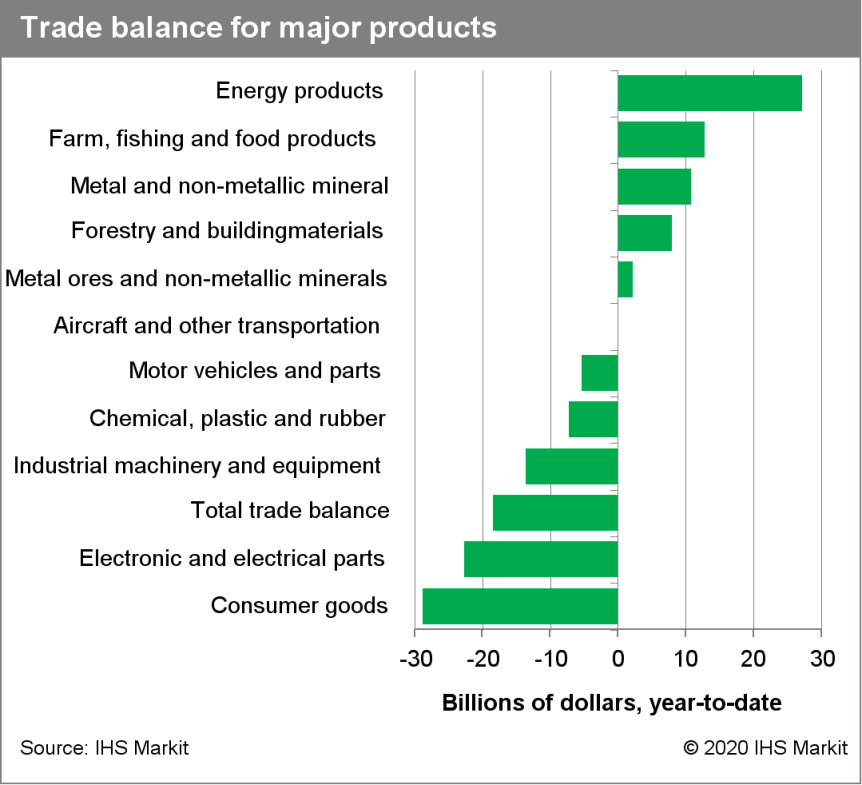
- The US nominal trade deficit widened in July by $10.1 billion
to $63.6 billion, close to our estimate. Underlying the headline
number, nominal exports rose 8.1% and nominal imports rose 10.9% in
July. (IHS Markit Economist Kathleen Navin)
- The gains in exports and imports marked the second consecutive month of increases in each, following sharp declines this spring amidst the global pandemic. Still, the levels of nominal exports and imports remain roughly 20% and 10% below their levels at the end of last year, respectively.
- In the details of today's report, both imports and exports of transport services continued to turn up in July. Imports of travel services also rose slightly, while exports of travel services continued to ease.
- These areas of trade were hit particularly hard by the pandemic as air travel was all but shut down for much of March and April and as the recovery remains slow. We look for trade in these sectors to gradually improve over the coming months.
- The data on trade through July suggest stronger growth of both exports and imports in the third quarter. On balance, this raised our forecast for the change in net exports in the third quarter. In addition, the details of this report suggest more domestic spending on capital goods in the third quarter, so we also raised our forecast of equipment spending.
- California could become the first US state to develop its own generics after the Democratic-led state legislature approved bill SB-852, according to Kaiser Health News (KHN). If signed into law, the bill would authorize the state's health agency to partner with one or more drug companies by January 2021 to manufacture or distribute a range of generic or biosimilar products, including at least one insulin product. The legislation would also pave the way for California to produce its own line of generic products in the future, according to the source. These state-developed generics would be widely available to both public and private buyers within the state, and startup funding of USD1-2 million - together with staff costs estimated in the low hundreds of thousands of US dollars - would be obtained from taxpayer money. The drugs that lead to the biggest savings for the state and consumers will be targeted, including generics that treat chronic and high-cost conditions, as well as those than can be delivered through mail order. California's healthy agency will have 18 months to identify a list of drugs that could be manufactured by the state, with a report due by July 2022. By the following year, the state must determine whether it is able to manufacture its own generics and biosimilars. (IHS Markit Life Sciences' Margaret Labban)
- US regulatory agency the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has launched an interactive web tool so that the public can see the results of autonomous vehicle (AV) tests ( https://www.nhtsa.gov/automated-vehicles-safety/av-test-initiative-tracking-tool). The interactive, web-based test-tracking tool has been launched as part of the NHTSA's Automated Vehicle Transparency and Engagement for Safe Testing Initiative (AV TEST Initiative). The tool enables the public to access the information submitted by various companies and US state authorities on ongoing self-driving vehicle testing. The information on the testing is submitted voluntarily to the NHTSA, with the test-tracking tool enabling the data to be viewed according to several filters, including testing location, company, state information, and company information. The NHTSA states that it intends to update the tool frequently "as participants add or modify their information, as new participants are added, and as data fields are added or modified". The information on the testing sites may be displayed according to vehicle type and road type, as well as location. On an interactive map, red dots represent locations where companies have reported carrying out AV testing or demonstrating automated driving systems (ADS). Clicking on a dot pulls up information on to the screen, which can include the testing status, vehicle type, type of testing activity, road type, whether there is a safety driver, use (public or test team, for example), owner of the AV technology, and site co-ordinator. If a company has submitted information on a specific test route or zone, a user can zoom in on the map to the see that specific route or zone of operation. When the NHTSA announced the initiative in June, it was stated that nine companies and eight US states had pledged they would participate. The companies include Beep, Cruise, Fiat Chrysler Automobiles (FCA), Local Motors, Navya, Nuro, Toyota, Uber, and Waymo and the US states include California, Florida, Maryland, Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Texas, and Utah. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- Motional, a joint venture (JV) between Hyundai and Aptiv, has announced an expansion to autonomous vehicle (AV) dataset nuScenes. Created in 2019, nuScenes, was the first publicly available AV dataset and the platform is organized into 1,000 urban street scenes collected from Boston (US) and Singapore. The expanded data set now includes nuScenes-lidarseg that adds 1.4 billion annotated LiDAR points to provide a detailed picture of a vehicle's surroundings. The second dataset, nuImages, created in response to user demand, involves 100,000 annotated images to generate an extensive range of unpredictable and challenging driving conditions. Karl Iagnemma, president and CEO of Motional, said, "Safety transcends competition. The belief that passenger safety must take priority over any competitive advantage is at the heart of nuScenes." (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Canada's trade surplus with the United States widened by $0.1
billion to $2.9 billion. The trade deficit with the rest of the
world increased by $1.0 billion to $5.3 billion. (IHS Markit
Economist Patrick Newport)
- Nominal exports surged 11.1% month on month (m/m) on strength from motor vehicles and parts and aircraft; real exports rose 8.9% m/m. Nominal exports increased 11.1% m/m to $45.4 billion, $2.9 billion below February's level as 10 of 11 production sections were up. Motor vehicle and parts exports exceeded February's level, jumping 37.0% m/m to $8.2 billion as the auto industry ramped up production and shortened its regular July shutdown period, allowing it to sell more to (and buy more from) the United States. Energy products exports rose 18.9% m/m—the third straight increase—on higher prices and volumes of crude oil.
- Nominal imports pressed up 12.7% m/m on ballooning imports of
motor vehicles and parts; real imports increased 11.1% m/m. Nominal
imports jumped to $47.9 billion, $2.0 billion below February's
pre-pandemic level. Motor vehicles and parts imports, nearly
hammered to the ground earlier in the COVID-19 crisis, shot up
50.3% m/m to $8.1 billion, which is 11.2% below February's level;
imports of passenger cars soared 71.9% m/m, while engines and parts
registered an also impressive 38.7% m/m gain.
- Light-vehicle sales in Mexico were 77,092 units in August, a
decline of 28.4% year on year (y/y), according to brand-level sales
data published by the National Institute of Statistics and
Geography (Instituto Nacional de Estadistica y Geografia: Inegi).
(IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- The results in August represented a month-on-month (m/m) improvement and were the third consecutive month of reduced y/y sales declines. Compared with July, light-vehicle sales in August increased 5.8%.
- Light-vehicle sales declined 31% y/y in July, more than 40% y/y in June, and 59% y/y in May, when only about 42,000 units were sold.
- As are other countries, Mexico is seeing declining demand amid the COVID-19 pandemic and the country's stay-at-home orders and lockdown and social-distancing measures taken in April and May.
- Although the COVID-19 virus outbreak remains a concern, Mexico did not renew its stay-at-home orders in August.
- Despite the collapse in sales, brands' rankings remained relatively consistent. Nissan maintains its lead in the Mexican market. In August, Nissan sold 16,540 units, down 26.4% y/y (Infiniti sold 54 units, down 46.0% y/y and down 5 units from July).
- Nissan was followed in the rankings by General Motors, which sold 12,115 units (down 27.6% y/y).
- Volkswagen (VW) held third place with 7,355 units sold (down 36.9% y/y). VW brand Audi reports its results separately and saw a small 2.4% y/y sales decline to 920 units.
- In fourth place, Toyota sold 6,532 units in August (down 28.3% y/y).
- Chinese automakers BAIC and JAC had been making stronger sales efforts in the Mexican market, and JAC sold 370 units in August; however, BAIC's sales dropped to 141 units, from 293 units in August 2019.
- Mexico's light-vehicle sales declined in 2018 and 2019, and in 2020, the market was soft prior to the COVID-19 situation. Prior to the pandemic, IHS Markit had expected a market decline of 2.6% to 1.280 million units in 2020. However, our August forecast round, factoring in the COVID-19 disruption as well as ongoing recovery efforts, instead sees the country's full-year light-vehicle sales falling 28.8% to about 940,847 units.
- Local sources reported that the FSO Nabarima is taking on water and at risk to sink in the Gulf of Paria, offshore Venezuela. The FSO has approximately 1.3 million barrels of oil onboard, and is in "very poor condition", with water flooding in the lower decks. It is understood that the oil will be transferred to another vessel. The Nabarima FSO is installed at the Corocoro field, operated by PDVSA and Eni.
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- European equity markets were all higher on the day until the sharp sell-off in US equities began, resulting in all major markets closing lower except for Spain +0.1%; Italy/UK -1.5%, Germany -1.4%, and France -0.4%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed mixed; Italy +2bp, UK/France flat, and Germany -2bps.
- iTraxx-Europe closed +2bps/52bps and iTraxx-Xover +18bps/324bps.
- Brent crude closed -0.8%/$44.07 per barrel.
- Eurozone retail sales volumes declined by 1.3% month on month
(m/m) in July, a weaker outcome than expected (market consensus
+1.5% m/m according to Reuters' survey), albeit in an exceptionally
uncertain environment and following exceptionally strong increases
in prior months. There was also a downward revision to June's
initially reported m/m surge in sales volumes (from 5.7% to 5.3%).
(IHS Markit Economist Ken Wattret)
- In level terms, retail sales volumes have rebounded relatively strongly from the COVID-19 shock. Sales in July were just 1.2% below February's, even factoring in the latest weaker-than-expected data.
- The overall recovery in retail sales again masks divergent trends across spending categories, however. Sales of textiles, clothing and footwear fell by over 10% m/m in July, for example, and remained more than 23% below their February level even after exceptionally large 223% and 35% m/m gains in May and June respectively as COVID-19-related restrictions eased.
- In contrast, mail order and internet sales in July were more than 9% above their February level in July, despite large back-to-back m/m declines in the latest two months. The substitution effects that benefited this area of sales during the lockdowns has been followed by a partial correction as containment measures have been lifted, although the long-standing shift in trend towards increased mail order and internet sales remains intact
- The strong carryover effect stemming from exceptionally large gains in May and June's retail data means that the third quarter will still experience a very high q/q growth rate in retail sales despite July's downward surprise. By way of illustration, no change in the level of sales in both August and September would yield a q/q rise in the third quarter of 8.2%, a record high (following a 5.2% q/q drop in the second quarter).
- Bank of England governor Andrew Bailey anticipates that UK GDP
will be about 1.5 percentage points lower than it would have been
without the COVID-19 virus in the long run. The Bank's deputy
governor believes that Bailey's prediction is a "good starting
point". (IHS Markit Economist Raj Badiani)
- Bank of England governor Andrew Bailey told the Treasury Select Committee in the UK parliament that the "UK economy could suffer worse scarring from the coronavirus crisis than originally predicted in August."
- Bailey argues that the outlook for the UK economy faces a "record level" of uncertainty, making the recovery path difficult to predict. He acknowledges that consumers will remain risk averse when deciding to re-engage with the economy, fearing the continued risk of infection from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) virus. The danger is that behavioral changes represent a risk to the economy if many people continue to work from home or refrain from visiting attractions or physical shops.
- Overall, Bailey anticipates that long-run UK GDP will be about 1.5 percentage points lower than it would have been without the COVID-19 virus. However, he noted that "there was broad agreement on two things. One, there's a very high degree of uncertainty … and there's a very big downside skew".
- At this stage in the COVID-19 cycle, the Bank of England is not making any assumptions about continued local lockdowns, the risk of a second wave of COVID-19 infections, or the arrival of a vaccine.
- Volvo Cars has announced the launch of the Care by Volvo subscription service in the United Kingdom, following a successful regional trial. The company claims that the service is designed for customers who are looking for convenient access to the brand's cars. The service's monthly subscription payment allows customers to choose any model from the current Volvo line-up, with benefits such as scheduled servicing, wear-and-tear maintenance, replacement tires, and roadside assistance. Monthly payments start from GBP559 (USD743.5) for an entry-level XC40 T3 Momentum. Conor Horne, the UK head of Care by Volvo, said, "Our subscription offer also makes for easy budgeting because it covers all the essentials apart from fuel, with the option of adding insurance." Automakers have been testing subscription services in varying forms in recent years, as the industry expects vehicle-ownership models to change in the future, and ultimately, customers to pay for miles travelled, rather than purchase a vehicle. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- The UK chemical industry has welcomed an announcement by the UK government that under the country's post-Brexit version of the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) legislation, called UK REACH, deadlines for the full submission of data to underpin substance registration dossiers will be staggered over a period of six years, instead of the previously announced two-year timeframe. These deadlines start from 28 October 2021. The proposal to introduce a six-year timeframe, based on tonnage, for the future registration of chemicals in the UK, follows an evidence-gathering exercise carried out by the government to understand better the impact of UK REACH on the chemical sector and its supply chains. The Department for Environment, Food, and Rural Affairs (Defra), a UK government body, says that under the proposal, data for products made or imported in volumes of 1,000 metric tons/year or more must be submitted within two years, data for substances produced or imported in quantities of 100 metric tons/year or more must be submitted within four years, and data for products made or imported in volumes of 1 metric ton/year or more must be submitted within six years. Substances that are carcinogenic, mutagenic, or toxic for reproduction and made or imported in volumes of 1 metric ton/year or more and substances that are very toxic to aquatic organisms and produced or imported in volumes of 100 metric tons/year or more are subject to the two-year timeframe.
- Skoda has launched its first electric vehicle (EV) in the form
of the Enyaq iV at a launch ceremony in Prague (Czechia). In terms
of styling, the Enyaq has a clean and modern sport utility vehicle
(SUV)/crossover shape with a large blanked-off grille, which is not
unlike BMW's kidney-grille shape in design, with slim and crisp LED
front headlights and a prominent front bumper. (IHS Markit
AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
- It also features a squared-off roofline with quite a raked rear hatchback. The curved rear bumper runs from the lower edge of the rear lights, finishing in a contrasting lower section with a black finish.
- The model is 4,648 mm long, 1,877 mm wide, and 1,618 mm tall; it has a wheelbase of 2,765 mm and has good trunk (boot) capacity of 585 liters.
- Infotainment functions are controlled via a 13-inch touchscreen mounted on top of the dashboard.
- In terms of variants, the entry-level model, the Enyaq iV 50, has a gross lithium-ion battery capacity of 55 kWh (net: 52 kWh).
- The rear-mounted electric motor has an output of 109 kW, offering a maximum range of up to 340 km on the Worldwide harmonized Light vehicle Test Procedure (WLTP) measurement. This increases to up to 390 km in the 132-kW Enyaq iV 60 fitted with a 62-kWh battery (net: 58 kWh).
- The rear-wheel-drive Enyaq iV 80, delivering 150 kW, has the highest range of up to 500 km on the WLTP cycle.
- Its 82-kWh battery (net: 77 kWh) is also used by the two versions equipped with a second electric motor, and which are therefore equipped with four-wheel drive - the 80X and the vRS, which deliver 195 kW and 225 kW, respectively.
- The top-of-the-range model accelerates from 0 to 100 km/h in just 6.2 seconds and has a top speed of 180 km/h.
- The maximum range of both all-wheel-drive variants is 460 km.
- The Enyaq iV is a well-designed and attractive electric crossover and is the first Volkswagen (VW) Group EV based on the MEB architecture to be built outside Germany.
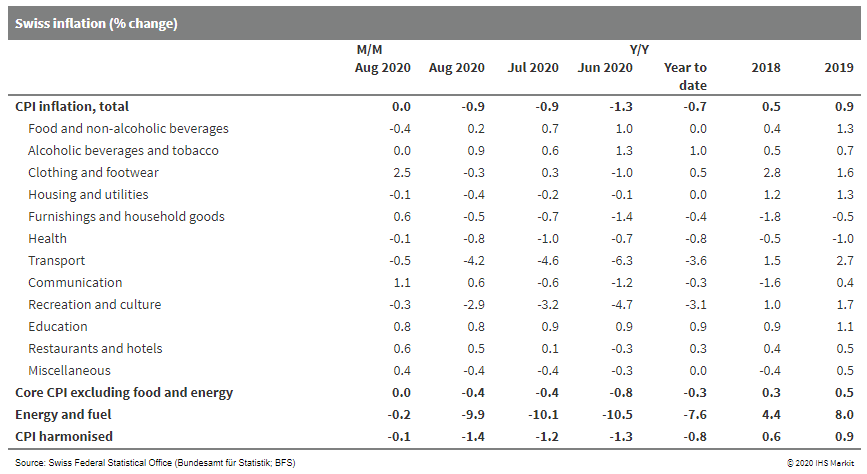
- Swiss inflation continues to follow a stabilization tendency
that began in June. The downward trend towards deflation of -1.3%
during the first half of 2020, owing to falling oil prices and
concurrent Swiss franc appreciation, has started to reverse. Base
effects will support this tendency, but sustained positive rates of
inflation will only be seen from around mid-2021. (IHS Markit
Economist Timo Klein)
- According to the Swiss Federal Statistical Office (SFSO), Swiss consumer prices remained flat month on month (m/m) in August, slightly firmer than the long-term average for this month. Firmer oil prices and Swiss franc weakening against the euro contributed to this result.
- The annual rate of the consumer price index (CPI) held steady at -0.9%, which compares with a cyclical low of -1.3% year on year (y/y) in May and June.
- The EU-harmonized measure, with its somewhat different composition, was softer than the national data, posting readings of -0.1% m/m and -1.4% y/y in August (the latter down from July's -1.2%). Base effects play an important role here - we expect September's annual rate to rebound to around -0.8%.
- Seven of the 12 main Classification of Individual Consumption by Purpose (COICOP) categories of goods and services in the national data posted a rising annual rate and only four categories a declining one (while "miscellaneous goods and services" held steady at -0.4% y/y).
- The main upward influences, taking relative weightings into account, came from transport, health, communication, hotels/restaurants, and recreation and culture.
- Prices for food and housing/utilities were the main offsetting factors to the downside. Energy prices were little changed in August (-0.2% m/m), leading to just a slight rise in their annual rate from -10.1% to -9.9%.
- The split between goods (0.2% m/m and -1.6% y/y, the latter down from -1.5% y/y in July) and services (0.0% m/m and -0.4% y/y, the latter up from -0.5% in July) reveals only small differences during August, but disinflationary pressure continued to stem mainly from goods.
- Prices of domestic goods remained flat m/m, while those of
imported goods increased 0.1% m/m, leading to a slight increase in
domestic inflation from -0.1% to 0.0% and constant imported
deflation at -3.4% y/y. The latter will rise in the coming months
as base effects exert upward pressure.
- Russia is set to revive 12 million hectares of unused agricultural land as well as create the necessary infrastructure to increase the country's agricultural exports. "It is necessary to conduct a large-scale inventory of land, to identify specific land plots most suitable for agriculture. Our task is to provide farmers with no less 12 million hectares of new agricultural land," said deputy prime minister Viktoria Abramchenko at a meeting of the Board of the Ministry of Agriculture. According to Abramchenko, the task of bringing unused agricultural land into circulation, as well as creating the necessary infrastructure for living and working in the countryside, will help increase Russian agricultural exports. This compliments the state program already in place since 2020, which sets a goal to double Russian agricultural exports to USD45 billion by 2024. This, as the Deputy Prime Minister noted, will improve the situation with housing, infrastructure, education and healthcare in rural areas, and bring the standard of living of the rural population closer to the urban standard. "For the implementation of the state program in 2020, the government has allocated RUB36 billion. Next year the amount is planned to reach RUB34 billion. By the end of this year, within the framework of the program, more than 140,600 thousand square meters of housing will be commissioned or purchased, 90 projects for development of rural areas will be implemented, almost 4,000 socially significant projects for their improvement. This is only a small part of all measures aimed at improving the quality of life of citizens in the countryside," she said. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Jana Sutenko)
- Zambia's real GDP fell by 0.3% y/y during the first quarter of
2020. IHS Markit expects the downturn to worsen during the second
quarter as COVID-19-virus lockdown measures are accelerated. (IHS
Markit Economist Thea Fourie)
- The Zambia Statistics Agency (ZamStats) reported 24.5% y/y growth in the agricultural, fishing, and forestry sectors during the first quarter following a 61.9% y/y expansion in the previous quarter. Other resilient sectors during the same period include information and communication (a 20.7% y/y increase), financial and insurance (an 8.9% y/y increase), transport and storage (increase by 4.6% y/y), and real estate (a 3.5% y/y increase).
- A slowdown in output in some of the largest sectors in the Zambian economy negatively affected overall real GDP during the first quarter.
- ZamStats reported a 9.6% y/y fall in wholesale and retail trade (18.5% of GDP), an 8.5% y/y slowdown in construction activity (9.1% of GDP), an 8.6% y/y contraction in electricity and water output (1.6% of GDP), and a 1.0% y/y decrease in other services (including government services, accounting for 24.8% of GDP).
- Mining production, dominated by copper, decreased by 2.0% y/y during the first quarter and contributed 10.7% to total GDP.
- The second-quarter headline GDP growth will continue to be
supported by resilient output in the agriculture, fishing, and
forestry sectors, while the latest data released by Zambia's
Ministry of Finance show a 15.9% y/y rebound in copper production
during the second quarter of 2020 from a 3.8% y/y contraction in
the first quarter of the year. The recovery in copper production
mirrors the rebound in global copper prices over the period.
Together, these two sectors account for roughly 20% of real GDP
and, therefore, are unlikely to shield the economy from the steeper
decline expected in other sectors of the economy in the second
quarter of the year.
Asia-Pacific
- APAC equity market closed mixed; South Korea +1.3%, Japan +0.9%, Australia +0.8%, India -0.2%, Hong Kong -0.5%, and Mainland China -0.6%.
- According to official data from the Australian Bureau of
Statistics (ABS), the slump in economic activity during the June
quarter (the second quarter) was led by private consumption as it
detracted a big 6.7 percentage points from growth. The 7.0% quarter
on quarter (q/q) seasonally adjusted plunge in real GDP growth was
the largest since the series began in 1959 and confirmed
Australia's first technical recession since 1991. Policymakers will
be focused over the next few months on how much more stimulus can
be provided to help lift the economy. (IHS Markit Economist Bree
Neff)
- The ABS also reports that the household savings rate surged to 19.8% during the quarter, the highest level since 1974 as in real (inflation-adjusted) terms households spent 86% q/q less on transportation services, 56.1% q/q less at hotels and dining out, 15% q/q less on other recreation and culture, and 25% q/q less on the operation of vehicles as they stayed at home.
- Private-sector fixed capital formation expenditures in real terms were surprisingly only down by 6.6% q/q, with the only component to record an increase being new non-dwelling engineering construction, probably because of rising iron ore and gold prices encouraging some mining-sector expansion.
- Dwelling construction spending was down by 7.3% q/q and spending on equipment and machinery was down 7.0% q/q, with both being the worst results since the early 2000s.
- Government spending did mitigate some of the pain, but there was no way it would completely offset what happened in the private sector. Government consumption spending contributed 0.6 percentage point to growth, while fixed capital formation by the government, including public corporations, contributed 0.1 percentage point. What was notable was that most of the support came from local and state governments, with their consumption and fixed capital formation contributing 0.5 and 0.2 percentage point, respectively.
- Australia's primary income-account deficit tends to be the main driver of the country's current-account deficits, but it narrowed for a fifth consecutive quarter during the June quarter, this time by another 44% q/q. A 26% q/q plunge in primary income outflows arose as investment income outflows from portfolio flows dropped 53% q/q and from foreign direct investment by 18% q/q. Primary income-account inflows also weakened during the quarter, but by a smaller 16% q/q.
- The June quarter result was modestly stronger than IHS Markit had expected. We had held the forecast down in part out of an abundance of caution as regional GDP figures had surprised significantly on the downside in the June quarter. Even with the stronger figure for the June quarter, we are unlikely to dramatically upgrade our forecast for 2020, which in August stood at -6.1%. Most likely our forecast will remain in the mid- to 5% range.
- New vehicle sales in Australia decreased by 28.8% year on year
(y/y) to 60,986 units during August, according to data from the
Federal Chamber of Automotive Industries (FCAI). (IHS Markit
AutoIntelligence's Nitin Budhiraja)
- The sport utility vehicle (SUV) segment posted a sales decline of 17.0% y/y to 32,278 units, while passenger car sales fell steeply to 14,758 units, down by 42.8% y/y.
- In August, sales of light commercial vehicles (LCVs) totalled 11,234 units, down by 35.9% y/y, while heavy commercial vehicle (HCV) sales were 2,616 units, down 20.7% y/y.
- During the month, Toyota was the best-selling brand with sales of 12,449 units. In second place was Mazda with sales of 6,921 units, followed by Hyundai with 4,525 units, Kia with 4,521units, and Mitsubishi with 4,308 units.
- The top-selling vehicle was the Toyota RAV4, followed in the rankings by the Ford Ranger, Mazda CX-5, Toyota Land Cruiser, and Toyota Corolla.
- The state of Victoria, which is currently under Stage 4 Restrictions, recorded a 65.9% y/y decrease in sales to 8,347 units last month.
- FCAI chief executive Tony Weber said, "The industry has moved swiftly to implement robust COVID Safe protocols to ensure the health and wellbeing of employees and customers is preserved. However, it is particularly difficult for our members and their Victorian dealer networks under the current Stage 4 Restrictions, and this is reflected in the reduced sales figures."
- On a year-to-date (YTD) basis, sales were down by 20.4% y/y to 575,906 units.
- Australian firm Ceres Tag has begun development of a smart
collar for pets to monitor health and wellbeing. Ceres was able to
turn its attention to the pet sector after COVID-19 meant it could
not extend its pre-commercial trials on 1,000 cattle across
Australia and New Zealand. The firm is currently developing a smart
ear tag for livestock and is also working on Ceres Wild - an ear
tag for wildlife. Ceres anticipates its Ceres Companion Collar
technology will reach the market by 2022. The company described the
collar as "the smartwatch for man's best friend", as well as being
able to further strengthen the pet-human bond. (IHS Markit Animal
Health's Daniel Willis)
- The Ceres Companion Collar will include a low power operation when the animal is at home or with the owner, and the ability to switch to satellite communications - including GPS location - when the animal journeys further afield;
- A smartphone app to interact with the collar to detect specific behaviors such as food and drink intake, sleeping, panting and barking, as well as alerting health concerns to the owner, caregiver or veterinarian;
- Algorithms that measure health and performance metrics, which can be added to the algorithm store for users to customize what they measure; and
- A charging dock that will also synchronize additional collar data, such as when an animal has escaped and then been retrieved, to the cloud and keep the collar updated with the latest software.
- The Ceres Companion Collar will be able to automatically switch from a short-range indoor and yard monitoring system to an unlimited range outdoor satellite-based system when a dog or cat is taken outside or to larger open areas. The firm claims other systems are normally unable to provide this range of coverage. This benefit will allow Ceres to gain access to 80% of the animal monitoring market that is currently not catered for, the company told IHS Markit Animal Health.
- The China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM) on 3
September released estimates of new vehicle sales in China in
August prior to its monthly briefing. According to CAAM, new
vehicle sales in China are expected to reach 2.18 million units in
August, up 11.3% year on year (y/y) and 3.2% month on month. (IHS
Markit AutoIntelligence's Abby Chun Tu)
- Breaking down the figures by vehicle type, passenger vehicle (PV) sales are expected to grow 4.4% y/y during August, while commercial vehicle (CV) sales are expected to rise 37.5% y/y.
- During January-August, new vehicle sales in China are expected to reach around 14.54 million units, down 9.7% y/y.
- PV sales are expected to decrease 15.5% y/y during the first eight months, while CV sales are expected to grow 16.9% y/y.
- IHS Markit expects more details to be released by CAAM in the coming week.
- Chinese automaker Geely Auto has submitted an initial public offering (IPO) prospectus to the China Securities Regulatory Commission. According to the prospectus, Geely Auto plans to raise CNY20 billion (USD2.93 billion) by listing its shares on the Shanghai Stock Exchange Sci-Tech Innovation Board, also known as the STAR Market. The share offering will make Geely Auto the first automaker to be listed on the NASDAQ-like stock exchange. Of the total funds raised, the company plans to allocate CNY8.4 billion to product development, CNY3 billion to technology development, CNY3 billion for business acquisition, and CNY6 billion for liquidity improvement. Geely says its new modular platforms, the B-segment Modular Architecture (BMA) and the Compact Modular Architecture (CMA) platforms, will support its product expansion. In addition, model development based on older platforms will continue. Geely says the funds allocated for acquisitions will be used to acquire plants and businesses that complement its business development and to secure resources. The automaker is also looking to boost investment in critical auto technologies, including new energy vehicles (NEVs), vehicle automation, and connected cars. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Abby Chun Tu)
- Japan Polyethylene, an affiliate of Mitsubishi Chemical, has decided to shut down a low-density polyethylene (LDPE) plant at Kamisu, Japan, from May 2021. The production capacity of the plant is 62,000 metric tons/year. Japan Polyethylene says that the supply and demand situation has deteriorated due to new global expansions. It has also seen a financial burden from repair costs. The company will also stop production of ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) copolymers at its Oita plant. According to IHS Markit, the production capacity of EVA there is 60,000 metric tons/year. According to IHS Markit, the company produces LDPE at Oita, with a production capacity of 125,000 metric tons/year; Kurashiki, 118,000 metric tons/year; Kawasaki, 145,000 metric tons/year; and Kamisu, 168,000 metric tons/year. It also produces high-density PE, with a combined capacity of 422,000 metric tons/year. IHS Markit says that Japan is a highly developed market, with very little to no opportunity for large consumption surges. In recent years, production of LDPE in Japan has declined. Although it grew in 2019 owing to increased exports to China, in the next five years production will grow moderately at about 1%/year. By 2024, China is expected to add more than 2 million metric tons of capacity and is expected to have an above-average annual capacity growth rate—9%—between 2019 and 2024, adds IHS Markit.
- Tata Motors has reported in a filing with the Bombay Stock
Exchange (BSE) that its domestic sales reached 35,420 vehicles
during August, up 21.6% year on year (y/y). (IHS Markit
AutoIntelligence's Isha Sharma)
- Of this total, passenger vehicle sales stood at 18,583 units (up 154.0% y/y), while commercial vehicle (CV) sales reached 16,837 units (down 23.0% y/y).
- Within the CV segment, sales of medium and heavy commercial vehicles (MHCVs) fell by 48.6% y/y to 2,746 units, intermediate and LCV truck sales dropped by 36.5% y/y to 2,001 units, and sales of passenger carriers declined 68.0% y/y to 720 units.
- Sales in the small CV cargo and pick-up segment reached 11,370 units, up 2.6% y/y.
- This is Tata's sharpest increase in the passenger vehicle segment in more than a year and can be mainly attributed to pent-up demand and a low base of comparison.
- Proton's sales surged by 24.7% year on year (y/y) to 11,378
units during August, accounting for approximately 21.6% of the
Malaysian new vehicle market, according to data released by the
company. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
- Proton claimed that three of its models led their respective segments. The Saga was the automaker's best-selling vehicle during August with 4,784 units sold - the second best-selling vehicle in A-sedan segment. The X70 sport utility vehicle (SUV) was the best-selling vehicle across all the SUV segments in Malaysia with sales of 2,791 units last month. The Persona sedan continued to be the most popular B-segment sedan with 2,411 units sold, and the Exora multi-purpose vehicle (MPV) topped the C-MPV market with 630 units sold. The Iriz hatchback stood in third position in the B-hatchback segment with sales of 762 units last month.
- In the year to date (YTD), the automaker's sales stood at 61,672 units, 46 units more than the automaker's sales in the same period last year.
- It is estimated to have captured 21.7% of the Malaysian new vehicle market in the YTD. "Proton is pleasantly surprised by how quickly we have been able to recover the lost sales during the [movement control order] MCO period, as it only took us three months to get back on track. By exceeding our YTD volume in August 2019 we are quietly confident of recovery from the headwinds of COVID-19. The positive effect this has on the company, our employees and the vendor community cannot be understated and we hope to continue this trend until the end of the year so as to give the automotive industry ecosystem a strong boost," said Proton Edar CEO Roslan Abdullah.
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-3-september-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-3-september-2020.html&text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+3+September+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-3-september-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Daily Global Market Summary - 3 September 2020 | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-3-september-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+3+September+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-3-september-2020.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}




