Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
BLOG
Jun 25, 2020
Daily Global Market Summary - 25 June 2020
US and European equity markets closed modestly higher on the day, while APAC closed lower. European credit indices closed slighter wider and US high yield ended the day tighter. Most European benchmark government bonds traded higher on the day, while US yields were slightly higher. Texas and California are reconsidering their plans to fully reopen their economies as COVID-19 cases in those states continue to grow rapidly, which will likely create additional headwinds for the US markets ahead of next week's quarter-end.
Americas
- US equity markets closed in positive territory and at the highest levels of the day; Russell 2000 +1.7%, DJIA +1.2%, and Nasdaq/S&P 500 +1.1%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed +1bp/0.69% yield.
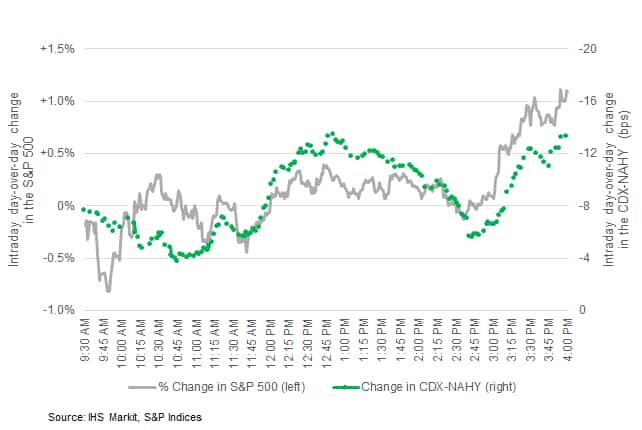
- CDX-NAIG closed flat/78bps and CDX-NAHY -13bps/501bps. The
below chart is the intraday change in the S&P 500 and CDX-NAHY
from yesterday's close (spread change axis is reversed to better
align visually with the S&P performance). The graph indicates
CDX-NAHY peaked at 12:51pm EST then widened out by as much as 8bps
by 2:43pm EST before closing only slightly below the day's best
level:
- Crude oil closed +1.9%/$38.72 per barrel.
- Texas paused reopening plans Thursday, as new coronavirus cases and hospitalizations increased in many U.S. states. California Gov. Gavin Newsom warned a potential influx of coronavirus-related hospitalizations could impact reopening plans. Coronavirus-related hospitalizations in the state increased by 32% in the last 14 days, with more than 4,200 people in hospitals, he said Thursday. As testing expands across the state, the rate of positive tests has increased to 5.6% in the last seven days, the Democratic governor said. (WSJ)
- The Fed has released stress test results today with dividend
action points for banks. Large banks are required to cap dividend
payments - by not paying more than an average of their most recent
four quarters. (IHS Markit Dividend Forecasting)
- All large banks will be required to resubmit and update their capital plans later this year to reflect current stresses, which will help firms re-assess their capital needs and maintain strong capital planning practices during this period of uncertainty. The Board will conduct additional analysis each quarter to determine if adjustments to this response are appropriate."
- During the third quarter, no share repurchases will be permitted. The Board is also capping dividend payments to the amount paid in the second quarter and is further limiting them to an amount based on recent earnings. As a result, a bank cannot increase its dividend and can pay dividends if it has earned enough income."
- The Fed's analysis on the potential impact of the pandemic showed that, in the most extreme scenario, 34 banks would face $700 billion of loan losses, versus the $560 billion of loan losses under the traditional stress tests, which was based on a scenario set in February. (FT)
- Seasonally adjusted US initial claims for unemployment
insurance, at 1,480,000 in the week ended 20 June, remained at
historically high levels, although well below the all-time high of
6,867,000 in the week ended 28 March. This was the 14th straight
week with claims in seven figures. (IHS Markit Economist Akshat
Goel)
- The seasonally adjusted number of continuing claims (in regular state programs), which lag initial claims by a week, fell by 767,000 to 19,522,000 in the week ended 6 June. This is well below the all-time high of 24,912,000 in the week ended 9 May and indicates that as businesses reopen, furloughed workers are cautiously getting recalled.
- The insured unemployment rate in the week ended 6 June stood at 13.4%.
- There were 728,120 unadjusted initial claims for Pandemic Unemployment Assistance (PUA) in the week ended 20 June. In the week ended 6 June, continuing claims for PUA rose by 1,672,153 to 11,046,401.
- While continuing claims for regular state programs have declined in the past three weeks, not everyone getting off these benefits is heading back to work. Individuals who have exhausted regular benefits are eligible for up to 13 weeks of extended benefits under the Pandemic Emergency Unemployment Compensation (PEUC). In the week ended 6 June, 851,983 individuals were receiving PEUC benefits with 38 states accepting claims for PEUC so far.
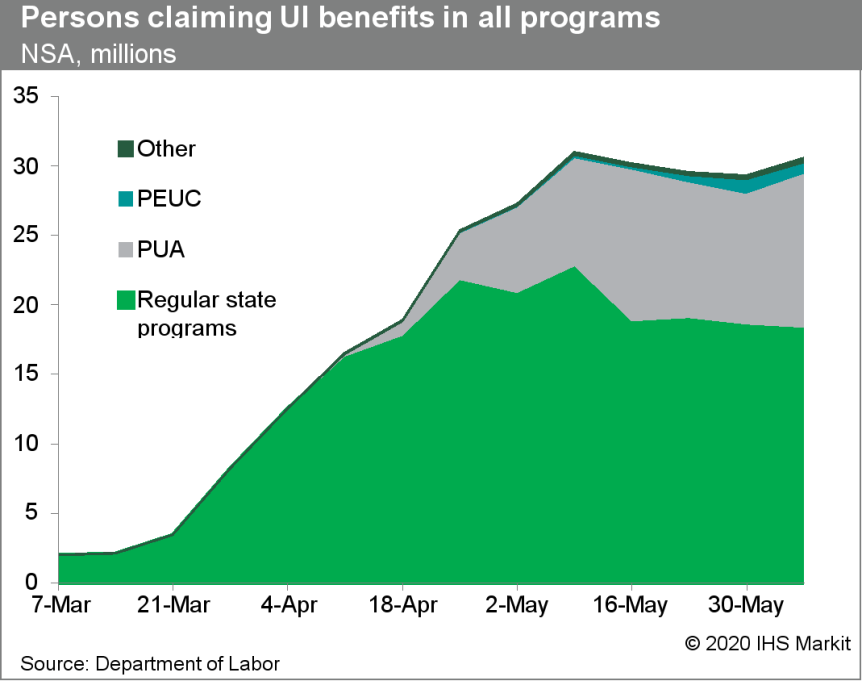
- The Department of Labor provides the total number of people
claiming benefits under all its programs with a two-week lag. The
unadjusted total for the week ended 6 June was 30,553,817, an
increase of 1,294,309 from the previous week. Sixty percent of this
total is from regular state programs and 36% from the PUA
program.
- US manufacturers' orders for durable goods rose 15.8% in May,
while shipments rose 4.4% and inventories rose 0.1%. The increase
in orders outpaced both IHS Markit's assumption and the consensus
expectation. (IHS Markit Economists Ben Herzon and Lawrence Nelson)
- The 4.4% increase in shipments of durable goods mirrored a previously reported 3.8% increase in manufacturing industrial production. Both measures remain well below their pre-pandemic levels, but their increases in May support our view that the trough in GDP was in April.
- Most of the increase in orders was in transportation equipment, with nearly one-half in nondefense aircraft and parts and about one-quarter in motor vehicles and parts.
- Of note was the first positive reading on orders for nondefense aircraft and parts since February. New orders are reported net of cancellations, so negative readings over the prior two months indicate elevated cancellations then. In May, then, either cancellations subsided or gross new orders turned up (or some combination of the two).
- The US goods deficit widened by $3.6 billion in May to $74.3
billion. This was in contrast to expectations for a narrowing.
Moreover, the combined inventories of wholesalers and retailers
fell 3.6% in May; we had penciled in no change. (IHS Markit
Economists Ben Herzon and Lawrence Nelson)
- Nominal goods exports declined 5.8% in May and are down 34.6% cumulatively since February, as global recession has led to plunging demand for US exports.
- Nominal goods imports declined 1.2% in May and are down 16.4% since February, reflecting falling domestic demand.
- Some of the unexpected weakness in the goods balance was in capital goods, which implies more domestic spending on equipment, so we lessened our forecast of the annualized decline in business fixed investment in equipment by about 5 percentage points to a 30.7% decline.
- The weakness in the combined inventories of wholesalers and retailers was mainly in retail, which accounted for about 84% of the total decline. This reflected a surge in retail sales in May, roughly 60% of which came out of inventories.
- US chemical volumes are expected to drop nearly 10% this year as global economic activity contracts due to the impacts of COVID-19, according to the American Chemistry Council's (ACC) Mid-Year 2020 Chemical Industry Situation and Outlook. Volumes should recover in 2021 with a return to pre-COVID output levels in the US by the second half of 2021. "As key end-use and export markets struggle, US chemical volumes will contract as well," said Martha Moore, senior director of policy analysis and economics at ACC. "Chemical volumes will fall 9.3% this year, while shipments will decline by 13.5%," Moore said. "In 2021, volumes will rebound 12.3% and shipments will increase by 14.5%." ACC forecasts a decline in basic chemicals volumes of 8.9% in 2020 with a 14.2% rebound in 2021.Of the major basic chemical segments, plastic resins fare the best with an expected decline of only 5.6% in 2020. In specialties, the 2020 decline is expected to be 13.6% in 2020, followed by a 10.6% gain in 2021. US chemical capital spending is set to decline 17.6%, to $29.0 billion, in 2020, but grows 15.7% in 2021 to $33.5 billion. "It'll be 2022 or even beyond when you get back to prior peak levels of capital spending as companies are trying to preserve cash," Swift said. "They're doing that by delaying or extending some of these projects."
- General Motors (GM) has decided to cancel a planned third shift at its plant in Spring Hill, Tennessee, United States, over weak market demand. After reports surfaced that GM would indefinitely delay a return to three-shift production at its Spring Hill plant, the automaker and the United Auto Workers (UAW) union confirmed that GM had decided to drop the plan for the shift instead. An Automotive News report quotes a GM spokesperson as saying, "We believe the best way to react to this unforeseen change in our market is to reduce output and operate on two shifts effective immediately. This adjustment allows the plant to maintain stable production, protect the value of our brands in any sales environment, and to provide the smallest impact to the plant employment going forward." The move will mean the laying off about 680 full-time and temporary employees. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- The Central Bank of the Argentine Republic (Banco Central de la República Argentina: BCRA) on 24 June released its latest monthly banking bulletin covering April 2020. The report shows several updates to key sector ratios. On the solvency side, the capital adequacy ratio (CAR) stood at 21.9% and the tier-1 capital ratio at 20.0%. Regarding asset quality, the non-performing-loan (NPL) ratio for the month was not released. However, the report gives a new breakdown of the main sectors that contributed to its rise to 5.3% in March. Corporate NPLs rose significantly to 7.5%, up by 3.6 percentage points compared with the same month of 2019. Most of this rise stemmed from industry (NPL of 12%), construction (10.9%), and trade (10.2%), while services (2.8%) and agriculture (2.6%) recorded the lowest NPLs. As for liquidity, foreign-currency deposits contracted by 1.9% month on month (m/m), or 41% year on year (y/y), while local-currency deposits increased by 7.3% m/m. (IHS Markit Banking Risk's Alejandro Duran-Carrete)
- Brazilian imports of dairy products in the first five months of 2020 (January-May) plunged to the lowest since 2010. Brazil spent USD95.24 million on purchases of dairy products (milk, cream and milk products other than butter or cheese), which is 30% lower than in the same period in 2019. This is the second lowest level since 2010, when import value reached USD89.7 million, according to data from the Foreign Trade Secretariat (Secex). The decrease is due to the Brazilian real's strong depreciation against the US dollar. Volumes declined 35% compared to the same period last year, at an average price of USD2.91 per kilo (+ 7.4% year -on-year). The main supplier Argentina accounted for 63% of the total amount, with the value totaling USD60.3 million. Fit was followed by Uruguay, with a 13% share in the total value. The US has also supplied Brazil with a sizeable amount, accounting for 7.24% of the total import value in January-May. It is interesting to note that imported products were shipped mainly to the state of Sao Paulo, one of the main consumer hubs in the country, which purchased 45.6% of the total landed in Brazil. At the same time, Sao Paulo was responsible for just over 43% of dairy exports from Brazil. The country's exports topped USD20.2 million in the first five months of this year, 23.4% higher year-on-year, however, in volume, the growth was more modest, at 13.6%, with being sent to foreign markets 10.3 million tons, at an average price of USD 1.96 per kilo (+ 8.3%). Algeria was the main destination of Brazilian exports, accounting for 15% of the total, but South America remained the key destination with USD6.24 million worth of Brazilian products purchased in January-May. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodity's Ana Andrade)
Europe/Middle East/ Africa
- European equity markets closed higher across the region; Spain/France +1.0%, Germany +0.7%, and Italy/UK +0.4%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed higher across the region, except for Italy +4bps; Germany/UK -3bps, France -2bps, and Spain -1bp.
- 5yr UK govt bonds closed at a -0.05% yield, which is the first time that maturity has closed with a negative yield.
- iTraxx-Europe closed +1bp/69bps and iTraxx-Xover +2bps/396bps.
- Brent crude closed +1.5%/$41.12 per barrel.
- Russian Federal State Statistical Service (RosStat) confirmed
the real GDP growth rate at 1.6% y/y during the first quarter of
2020, while also providing the breakdown of the value added. (IHS
Markit Economist Lilit Gevorgyan)
- As expected, the extractive sector was a key drag on the economic activity, falling by 0.5% y/y during January-March 2020. This weakness was mainly due to a 1.7% y/y decline in the sector's activity in March.
- RosStat slightly revised down the first-quarter growth rate for the manufacturing, to 3.6% y/y from 3.8% y/y, compared to a 3.9% y/y gain in the last quarter of 2019. The sector's growth eased to 2.6% y/y in March, from annual increases of 5.0% in February, and 3.9% in January.
- Growth impulse came from food production, which expanded by around 9.0% y/y in March. However, the manufacturing of air travel and transport equipment, as well as electronics, shrunk by one-quarter.
- Russian manufacturing had a strong start to the year, when compared to a 1.4% contraction for the same period in 2019, implying that the recent data also benefited from the statistical low base.
- Retail and wholesale trade had healthy gains, up by 4.9% y/y in the first quarter of 2020, a notable improvement when compared to the 3.3% fall in the same period a year ago. However, trade volumes declined in the first quarter when compared to 6.4% y/y gains in the fourth quarter of 2019.
- Clearly, the retail and wholesale sales have benefited from the low statistical base effect of 2019, although rising real incomes and wages have also contributed to the strong performance.
- Total services, which make up 60.2% of the value-added decelerated to 2.0% y/y in the first quarter from 3.3% in the fourth quarter of 2019. A closer look at services breakdown suggests that the main drag came from 4.4% y/y drop in transport and storage.
- Bayer today announced a series of agreements to resolve legacy Monsanto litigation, including a payment of $10.1-10.9 billion (€9.1-9.8 billion) to address current and future claims alleging that glyphosate, a widely used herbicide first introduced by Monsanto in 1974, causes cancer. Funded from free cash flow and the recent divestiture of Bayer's animal health business, Bayer says the settlement brings closure to about 75% of the current Roundup litigation—involving approximately 125,000 filed and unfiled claims overall—for $8.8-9.6 billion, which also includes an allowance expected to cover plaintiffs with whom the company has not yet reached an agreement. Bayer inherited the Roundup liability with its $63-billion takeover of Monsanto in June 2018. Moody's notes that while the settlement removes significant uncertainty for Bayer, it comes at a high price. "[The settlement] will delay the company's deleveraging trajectory as proceeds from asset disposals and free cash flow generation will now be used to fund settlement payments, instead of reducing debt stemming from the financing of the transformative Monsanto acquisition," says Moritz Melsbach, Moody's Assistant Vice President. Bayer also announced that it has resolved legacy Monsanto litigation related to dicamba drift for up to $400 million the most recent polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) water litigation exposure for approximately $820 million.
- Moody's today published a downgrade of BASF's long-term and short-term credit ratings from "A2/P-1/review for downgrade" to "A3/P-2/outlook stable." The reasons for these changes include the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and related uncertainty. Moody's says the downgrade reflects BASF's rating ratios that had already been weak for the A2 rating when entering the COVID-19 outbreak, which also limits the potential for improvement in case of a recovery in 2021. "With expected 2021 numbers the company would not be in line with requirements to maintain an A2 rating, such as a Moody's-adjusted EBITDA margin that Moody's expects to reach levels of only around 13% in 2021; high gross leverage with debt/EBITDA of 3.7 times [x] in 2021, even though this is still a considerable improvement from the expected 4.5x in 2020; and the emerging negative free-cash-flow [FCF] profile that Moody's expects will become a feature of BASF as the company embarks on a large capital spending program in Asia and in the area of battery materials, coupled with an expectation of continued high dividend payouts. Moody's estimates negative FCF of about €1.0 billion in 2020, around €2.0 billion in 2021, and €2.8 billion in 2022."
- Austrian industrial production (including construction)
declined by 15.1% month on month (m/m) in seasonally adjusted,
EU-harmonized terms during April, reflecting the lockdown enforced
to contain the COVID-19 virus and following a somewhat curtailed
March decline of 7.0% m/m (initially reported as a 9.5% drop). The
combined drop during March-April of 21.1% compares with a larger
25.2% decline in neighboring Germany during this period. (IHS
Markit Economist Timo Klein)
- Production excluding construction, i.e. largely manufacturing, declined by a similar 15.3% m/m in April, following a 6.1% m/m fall in March (revised up from a 7.8% drop; see table below for further details). This translates into a combined plunge of 20.5% during these two months, while construction output weakened even more (by 23.0% versus the February level).
- In year-on-year terms, calendar-adjusted production excluding construction fell 22.0% in April, which compares favorably with declines of 30.1% in Germany and 28.0% in the eurozone as a whole.
- During its session on 24 June, the Czech National Bank (CNB)
policy council voted unanimously to keep the base interest rate
stable at 0.25%. Inflation was slightly above expectations in
April-May (mainly because of higher core inflation) and is
currently one of the highest in the European Union. (IHS Markit
Economist Sharon Fisher)
- Amid continued high economic uncertainty, confidence indicators showed mixed results in June, with large month-on-month (m/m) increases in services and trade confidence matched by weakening industrial and construction sentiments. Consumer confidence improved moderately owing to an improving outlook for household finances, inflation, and unemployment.
- All confidence indicators were down sharply compared with February's levels, with the largest drops reported in the services and industrial sectors, and consumer and trade sentiments experienced more modest declines. Owing to a worsening assessment of current demand, industrial confidence decreased in June to the lowest level since early 2009.
- In terms of industry, the automotive sector struggled the hardest, with production down by 35.7% year on year (y/y) in the first five months of 2020. After plunging by nearly 90% y/y in April owing to closures at major factories, the number of vehicles produced dropped by 52% y/y in May, according to the Czech Automotive Industry Association.
- Czech services have been hit hard by a decline in tourism, and it is unclear how many foreign visitors will arrive despite the recent opening of borders to "safe" European countries.
- The CNB expects inflation to fall to the 2% target by the end of 2020. The inflation outlook was viewed as balanced, with fiscal policy presenting upside risks and the exchange rate having an anti-inflationary impact.
- South Africa's public-sector debt-to-GDP ratio is expected to
reach 81.8% by March 2021. Higher taxes, government spending
rationalization and stronger growth are necessary to stabilize the
public-sector debt trajectory over the medium term. (IHS Markit
Economist Thea Fourie)
- South African Finance Minister Tito Mboweni presented the 2020 Supplementary Budget to parliament on 24 June, showing the budget deficit widening to an estimated 15.7% of GDP in fiscal year (FY) 2020/21 - well above the 6.8% of GDP assumed in February.
- The National Treasury's estimates show that the government's tax revenue will be ZAR300 billion (USD16.8 billion) below target during FY 2020/21. "This is mainly due to revised revenue projections and pay-outs from the Unemployment Insurance Fund (UIF)," the National Treasury reported. As of mid-June, UIF payments totaling ZAR23 billion were made to 4.7 million workers affected by the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Total government spending (including debt servicing costs) is expected to exceed ZAR2 trillion during FY 2020/21. The supplementary budget makes provision for an additional ZAR21.5 billion of healthcare spending and ZAR12.6 billion for services at the front-line of the government's response to the pandemic, to enable increased screening and testing. An additional ZAR25.5 billion has been allocated to vulnerable households and ZAR6.1 billion for youth employment programs.
- Finance Minister Mboweni warns that tax measures to the amount of ZAR40 billion will have to be implemented over the next four years, while the government will have to find spending adjustments totaling ZAR230 billion over the next two years.
- The National Treasury expects South Africa's GDP to contract by 7.2% during 2020, while headline inflation is expected to average 3.0% this year.
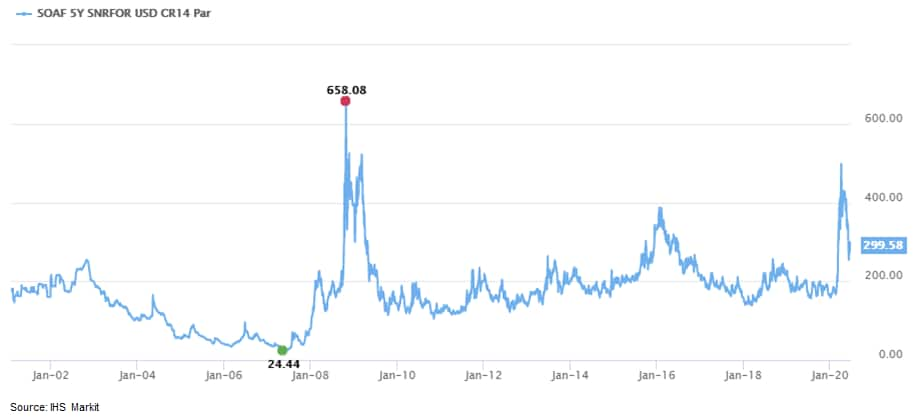
- 5yr CDS spreads on the Republic of South Africa almost breached
500bps on 3 April and were at the widest level since March 2009.
Spreads have since tightened in almost 200bps to close at 305bps
today:
Asia-Pacific
- APAC equity markets closed lower across the region; Australia -2.5%, South Korea -2.3%, Japan -1.2%, Hong Kong -0.5%, and India -0.1%.
- China saw a 7.5% y/y growth in foreign direct investment (FDI)
in May, slowing from 8.6% y/y in April, according to the Ministry
of Commerce (MOC). The cumulative FDI in the first five months
remained in 3.8% contraction y/y. (IHS Markit Economist Yating Xu)
- By sector, high-tech sectors and new economy remain attractive to foreign investors. FDI into high-tech industries grew by 2% y/y through May.
- Information services saw a 42.3% y/y expansion with e-commerce businesses notching up gains of 67.9% y/y and innovation and design service increasing by 49.8% y/y.
- According to China Daily citing an online statement by the Ministry of Commerce (MOC) on 18 June, China plans to significantly lower the threshold for foreign investors' strategic investment in listed companies to introduce more overseas capital and practical management experience as part of the efforts to improve the governance structure of listed firms.
- The total asset requirements for non-controlling shareholder foreign investors will be reduced from having USD100 million to USD50 million and for wholly-owned foreign investors from managing USD500 million to USD300 million. The lockup period for foreign investors' shares will be adjusted from three years to 12 months.
- Gaztransport and Technigaz (GTT) has received an order from China Huanqiu Contracting & Engineering Co. (HQC) for the design of two membrane full containment LNG storage tanks. The two tanks, each with a net capacity of 220,000 m3, will be the largest land storage tanks in China, according to GTT. The onshore storage tanks will be located in the Tianjin south port Industrial Zone in China and are planned to be commissioned during the last quarter of 2022. (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Dag Kristiansen)
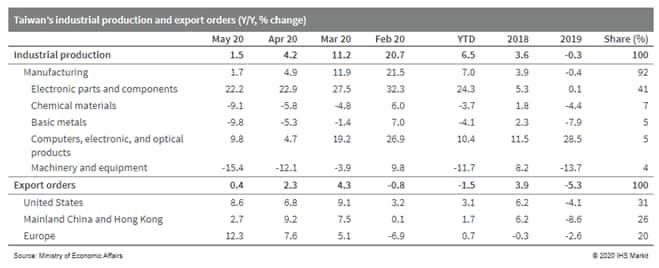
- Taiwan's export orders, representing a leading indicator of
actual exports, increased in May for the third straight month,
although the gain nearly flattened. Export orders were up by 0.4%
year on year (y/y), slowing from a 2.3% y/y expansion in April.
(IHS Markit Economist Ling-Wei Chung)
- The gain in May was bolstered by a 22.2% y/y surge in orders of information and communication products and a 13.4% y/y jump in orders of electronic products, as the technology sectors benefitted from booming demand for products and equipment related to working from home and remote education.
- Orders of non-technology sectors slumped by more than 20% y/y in May, led by drops in orders of mineral products, chemicals, base metal, and plastic products.
- Meanwhile, boosted by booming technology demand, orders from Europe increased at a double-digit pace for the first time in five months, jumping 12.3% y/y, accelerating from a 7.6% y/y expansion in April. This was followed by an 8.6% y/y increase in orders from the US and a 2.7% y/y gain in orders from mainland China and Hong Kong SAR.
- Orders from ASEAN dropped 6.0% y/y in May, faster than a 3.9% y/y decline in April. Orders from Japan also contracted, down 8.1% y/y, accelerating from a 4.7% y/y decrease in April.
- Concurrently, supported by rising export orders, industrial production (IP) increased 1.5% y/y in May, although the pace of gain decelerated from a 4.2% y/y expansion in April. It also marked the slowest increase in seven months, barring a seasonal disruption in January.
- Output of the key electronic component industry jumped 22.2%
y/y, marking the sixth month of a double-digit expansion. It was
boosted by a 36% y/y surge in production of integrated circuits,
maintaining the above-30% y/y increasing trajectory since the
beginning of 2020.
- Toyota's latest corporate governance report revealed that it holds 10.25 million shares of Uber Technologies, reports Reuters. These shares are valued at JPY31.15 billion (USD293 million) as of 30 March, which represents around 0.6% of Uber's outstanding shares. Toyota, DENSO ,and SoftBank that jointly invested USD1 billion in Uber's autonomous vehicle unit, the Advanced Technologies Group. Toyota has also previously partnered with Uber in 2018 to offer an on-demand autonomous ride-hailing service. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- The US Commerce Department has stated that it has begun its investigations into the imports of automotive tires from Taiwan, Thailand, South Korea, and Vietnam to check whether these tires are being sold in the US market at less than fair values, reports Reuters. The Department will also be investigating to determine whether unfair subsidies were provided to tire manufacturers in Vietnam for the production of passenger vehicle and light truck tires. The investigations are being conducted in response to petitions filed during May 2020 by the United Steelworkers (USW) representing US tire plant workers. The United States reportedly imported approximately USD4-billion worth of tires from these four markets in 2019, out of which tires worth USD2 billion were from Thailand. The USW has also stated that the imports of tires from these countries have risen by almost 20% since 2017 and have now crossed 85 million tires. In 2015, the USW won orders on imported automotive tires from mainland China, which has led to a sharp reduction in tire imports from the region. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-25-june-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-25-june-2020.html&text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+25+June+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-25-june-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Daily Global Market Summary - 25 June 2020 | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-25-june-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+25+June+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-25-june-2020.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}




