Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
BLOG
Aug 14, 2020
Daily Global Market Summary - 14 August 2020
APAC equity markets closed mixed today, while Europe was lower across the region and US markets were close-to-unchanged despite the flurry of economic reports. Benchmark government bonds were slightly better across Europe and the US, except for US 30yr bonds which closed even lower after an already challenging week. iTraxx and CDX indices closed wider across IG and high yield, with oil, gold, and silver also lower on the day. US retail sales improved in July, but came in lower than expected, and US consumer sentiment appears to be in a concerning holding pattern that is only slightly above April's nadir.
Americas
- US equity markets closed mixed; Nasdaq -0.2%, Russell 2000 -0.1%, S&P 500 flat, and DJIA +0.1%. There was a sudden, but modest, rally across the US equity markets that began at 3:50pm EST, with the S&P 500 increasing +0.3% from its lowest point of the day during those final 10 minutes of the trading session.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed -1bp/0.71% yield and 30yr bonds +2bps/1.45% yield, which is +14bps and +21bps week-over-week, respectively.
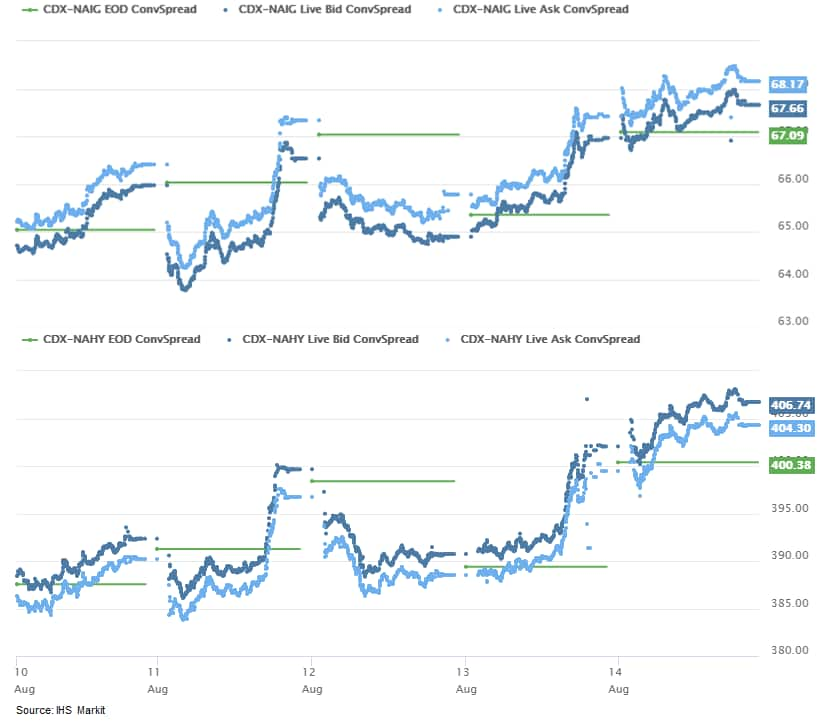
- CDX-NAIG closed +1bp/68bps and CDX-NAHY +5bps/406bps, which is
+3bps and +18bps week-over-week, respectively.
- Crude oil closed -0.5%/$42.01 per barrel.
- Gold closed -1.0%/$1,949 per ounce and silver -5.9%/$26.09 per ounce.
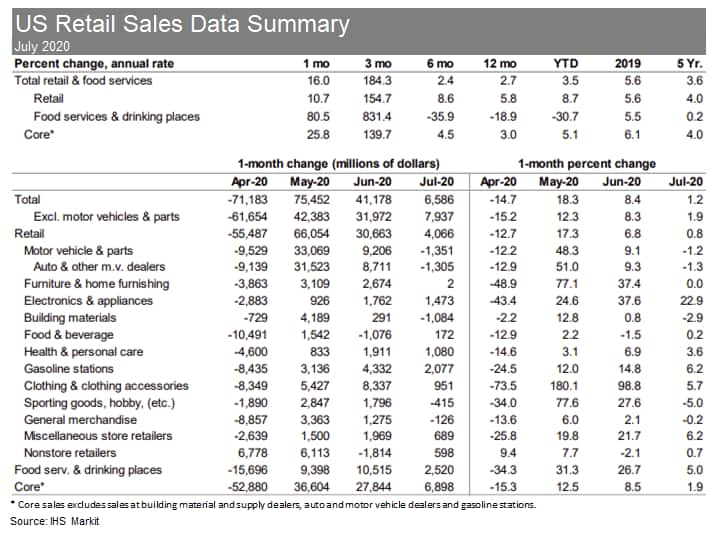
- Total US retail trade and food services sales increased 1.2% in
July, following an upwardly revised surge of 8.4% in June. (IHS
Markit Economists James Bohnaker and David Deull)
- Core retail sales through July were stronger than expected, suggesting more real PCE in the third quarter. We revised up our forecast for third-quarter real PCE growth by 7.6 percentage points to 37.9%. Data revisions show that core retail sales initially breached their pre-pandemic February level in June before improving to 2.3% above that mark in July.
- In July, business restrictions were targeted toward restaurants and bars, which still managed a 5.0% increase in sales but remained 19.7% below the February level. Retail sales at food and beverage stores increased 0.2% in July from an already-elevated level and were 11.5% above February.
- Pandemic-induced shopping trends are firmly in place elsewhere in the retail industry. Relative to the pre-pandemic February levels, nonstore retailers (+21.9%), sporting goods and hobby stores (+17.6%), and building material and garden supply dealers (+8.7%) are all benefitting from social distancing as consumers divert spending from services to home and recreational goods.
- Auto dealers (+3.4%) are also seeing stronger sales as Americans avoid air travel and public transportation.
- Retail sales generally improved in July but at a slower pace,
as some states paused or rolled back reopening plans.
High-frequency credit- and debit-card data show that spending
stalled throughout the month, setting up for a potentially soft
next couple months, as questions remain about additional stimulus
and income support from the federal government.
- The University of Michigan US Consumer Sentiment Index edged up
0.3 point (0.4%) to 72.8 in the preliminary August reading,
remaining effectively unchanged a mere 1.0 point above its April
trough. The reading is consistent with our expectation for slowing
growth in consumer spending. (IHS Markit Economists David Deull and
James Bohnaker)
- The current conditions index fell 0.3 point in early August to 82.5, while the expectations index increased 0.6 point to 66.5. Relative to April, views on current conditions were notably (8.2 points) higher in early August, but the index of expectations was 3.6 points lower, having worsened in May.
- Despite the relative prevalence of COVID-19 cases, the South maintained the highest level of consumer sentiment at 77.6, while sentiment for the Northeast, North Central, and Western regions were clustered within two points of the 70.0 mark.
- Consumer sentiment rose 3.1 points to 70.3 among households earning less than $75,000 a year but fell 1.5 points to 74.4 among households with earnings above that threshold.
- Perceptions of buying conditions barely changed in early August. The index of buying conditions for large household durable goods increased 1 point to 107, while that for vehicles fell 2 points to 122 and for homes was unchanged at 133, just shy of the 2019 average.
- The expected one-year inflation rate was unchanged at 3.0%, while expected five-year inflation ticked up 0.1 percentage point to 2.7%.
- As congressional gridlock became apparent, the net percent of respondents approving of the government's economic policies fell in early August to -21%, the lowest since January 2016.
- Despite a partial recovery in consumer spending since the depths of the COVID-19 shutdowns, consumer sentiment has remained stubbornly depressed and may not recover until there is a fundamental shift in the dynamics of the disease or an effective vaccine becomes widely available.
- Total US industrial production (IP) rose 3.0% in July, the
third monthly increase following sharp declines over March and
April. The level of IP in July, though, remains 8.4% below the
pre-pandemic (February) level. (IHS Markit Economists Ben Herzon
and Lawrence Nelson)
- The details in this report that bear on our GDP tracking added 0.1 percentage point to our forecast of third-quarter GDP growth, which now stands at 26.1%.
- July is usually the month that automakers shut down for a week or so for retooling; the seasonal factor expects this and boosts NSA auto output in July to smooth it out. This is part of the reason July auto IP, seasonally adjusted, was so strong, as automakers generally were ramping up rather than retooling.
- Bearing this in mind, seasonally adjusted vehicle assemblies and IP of motor vehicles and parts each posted healthy increases in July, and each have regained their pre-pandemic levels.
- The pace of NSA auto assemblies was roughly 4% above industry production schedules issued earlier this month, the pace we assumed in our base forecast. As a result, we responded to this report by raising our forecast of third-quarter motor vehicle output and inventory investment.
- Outside of motor vehicles and parts, nearly every major industry posted a gain in July.
- IP of electric and gas utilities rose 3.3% in July, while mining IP rose 0.8%. The latter was the first increase since January 2020. IP of electric and gas utilities rose 4.2% in June, reflecting increases in both electric power (4.6%) and natural gas (2.1%).
- US productivity (output per hour in the nonfarm business
sector) rose at a 7.3% annual rate in the second quarter. Hours
worked fell at a 43.0% annual rate while compensation per hour
surged at a 20.4% pace. (IHS Markit Economists Ken Matheny and
Lawrence Nelson)
- The large second-quarter swings in productivity, hours, and compensation per hour were in the vicinity of our estimates. Unit labor costs rose at a 12.2% pace in the second quarter, 1.8 percentage points less than we estimated.
- For the first quarter, productivity growth and compensation per hour were each revised up. Hours were revised to show a slightly larger decline.
- First-quarter growth in unit labor costs was revised up 4.7 percentage points, more than accounted for by the upward revision to compensation per hour.
- The reference period for the source data the Bureau of Labor Statistics used in estimating first-quarter productivity predated most COVID-19-related job losses, which surged beginning in the week ending 21 March. To capture these losses, adjustments were made to March employment based on non-seasonally adjusted data for initial claims from the second half of March. There were no such adjustments made for BLS's preliminary estimate of second-quarter productivity. Further information is contained here.
- Data on productivity and costs have been severely impacted by the fallout from the COVID-19 pandemic, so the implications of the latest quarterly data for longer-run trends are unclear.
- Productivity growth had been firming prior to the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. During 2019, productivity rose 1.9%, up from 1.2% over the three years through 2018. Over the first two quarters of 2020, productivity rose at a 3.4% annual rate. We expect productivity growth to ease in coming quarters.
- During 2019, compensation per hour rose at a moderate pace of 3.3%, up from 2.6% during 2018. Over the first two quarters of 2020, it surged at 14.8% rate.
- We anticipate that growth in compensation per hour will moderate as employment recovers in lower-wage occupations over the next few years. This will support a moderation in growth of unit labor costs.
- The US state of Michigan plans to establish a 40-mile corridor between the cities of Detroit and Ann Arbor that will be dedicated to connected and autonomous vehicles, reports Bloomberg. The project will be led by Cavnue, a subsidiary of Sidewalk Infrastructure Partners, working with partners including Ford, General Motors (GM), Argo AI, Arrival, BMW, Honda, Toyota, TuSimple, and Waymo. Michigan Governor Gretchen Whitmer said, "We are taking the initial steps to build the infrastructure to help us test and deploy the cars of the future". In the first phase of the project, the companies will focus on testing technology and exploring the viability of a highway dedicated to such vehicles that is expected to last about two years. The goal would be to create a corridor "that allows for a mix of connected and autonomous vehicles, traditional transit vehicles, shared mobility and freight and personal vehicles". (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Locomation has completed an eight-day trial of autonomously transporting commercial freight in partnership with Wilson Logistics, reports VentureBeat. During these trials, Locomation deployed its autonomous relay convoy (ARC) technology in the trucks, which enables one driver to pilot a lead truck while the following truck operates in tandem. This allows the driver in the following truck to log off and rest. The pilot scheme was conducted on a 420-mile route from Portland, Oregon to Nampa, Idaho, along the I-84 highway. The trucks covered approximately 3,400 miles and operated autonomously roughly half of the time, delivering 14 commercial loads. Dr Cetin Mericli, CEO and co-founder of Locomation, said, "The successful kickoff of this commercial agreement with Wilson Logistics is a significant milestone for our teams. Despite the threat of COVID-19, we delivered real world results for the most advanced, efficient, and safest solution to make commercial autonomous trucking a reality. Most importantly, the pilot strongly proved that our autonomous technology can be integrated seamlessly and deployed within a real trucking operation in a sustained fashion." Locomation was founded in 2018 by experts in autonomous technology from the National Robotics Engineering Center of the Robotics Institute at Carnegie Mellon University. The company expects full commercialization of its technology by 2022. The company says that its technology can reduce the operating cost per mile by 33% and fuel costs by 8%. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- The University of Tennessee is investigating the microbiome of cattle and its influence on feed efficiency. As part of a new three-year project, researchers will aim to determine the microbes and microbial interactions in the rumen of Angus cattle. The scientists will also look at how these microbes affect the conversion of low-quality feedstuffs into usable energy. In addition, the experts will work to estimate the heritability of the rumen microbes and their features and identify host genomic markers that ensure heritability. Phillip Myer - lead investigator, assistant professor and microbiologist in the university's department of animal science - said: "The overarching hypothesis of this project is that host beef cattle genetics are associated with the variation of microbes in the rumen, producing an individualized rumen microbiota among animals." He believes if certain rumen microbes play a key role in feed efficiency, disease resistance and other traits in cattle, they have significant potential to rapidly improve beef cattle nutrition and influence growth. The research has been awarded $0.5 million by the USDA's National Institute of Food and Agriculture. It is one of 23 projects focused on animal nutrition, growth and lactation to receive funding. (IHS Markit Animal Health's Sian Lazell)
Europe/Middle East/ Africa
- European equity markets closed lower across the region for the second consecutive day; France/UK -1.6%, Spain -1.3%, Italy -1.1%, and Germany -0.7%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed mixed; France/UK flat, Italy -3bps, and Germany/Spain -1bp.
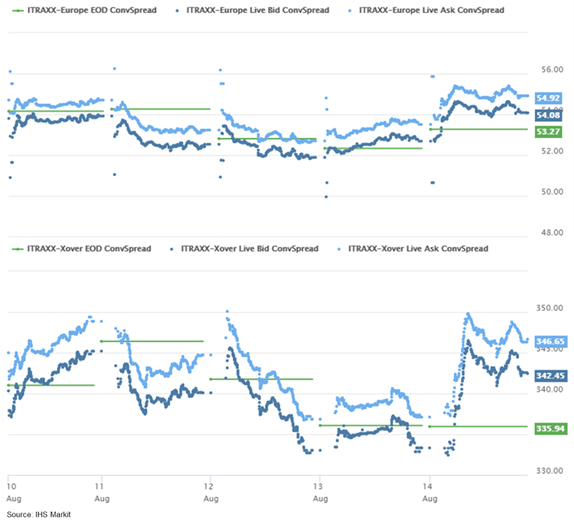
- iTraxx-Europe closed +1bp/55bps and iTraxx-Xover +9bps/345bps,
ending almost flat and +5bps week-over-week, respectively.
- Brent crude closed -0.4%/$44.80 per barrel.
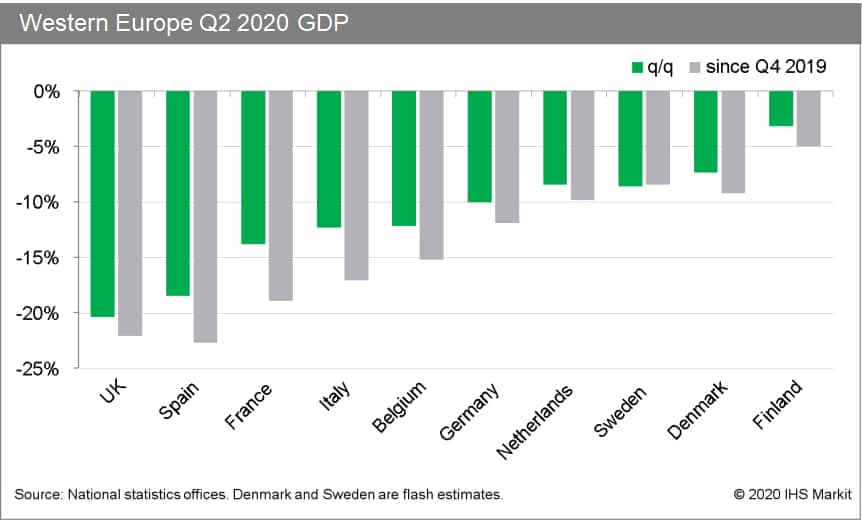
- Eurostat has published its "second flash" GDP estimate for the
second quarter. It is still based on the data of 16 of 19 member
states, covering 93% of eurozone GDP, and reports that seasonally
adjusted GDP decreased by 12.1% quarter on quarter (q/q) in the
second quarter, unchanged from the first release. We believe that
private consumption, business investment, and exports crashed
during the quarter. (IHS Markit Economist Raj Badiani)
- This implies that the region was in technical recession (defined as two successive quarters of q/q decline) for the first time since early 2013, after the economy shrank by 3.6% q/q in the first quarter of 2020.
- On a year-on-year (y/y) basis, GDP dropped by 15.0% in the second quarter following a decline of 3.1% in the first.
- The unprecedented circumstances of the COVID-19 virus pandemic point to future GDP revisions, with the next update being a breakdown by expenditure component of second-quarter GDP on 8 September.
- Meanwhile, Eurostat also reports that eurozone employment shrank for a second straight quarter in the second quarter, falling by 2.8% q/q, the sharpest decline since the time series started in 1995. This came after employment fell by 0.2% q/q in the first quarter, the first decline since the second quarter of 2013.
- In annual terms, employment in the second quarter was 2.9% lower than a year earlier.
- Sharp employment losses during the second quarter are not fully reflected in the latest unemployment rate developments. The eurozone seasonally adjusted unemployment rate was a surprisingly low 7.8% in June, up from 7.7% in May 2020 and 7.5% in June 2019.
- The lower-than-expected unemployment rate during the height of the COVID-19 virus-related lockdowns is partly because of the rising inactivity rate in some member countries, with an increasing number of people neither working nor looking for work. Many laid-off workers stopped looking for jobs during the national lockdowns, and were classified as inactive rather than unemployed.
- There has been a marked upward shift in growth momentum recently in line with the steady easing of the COVID-19 virus-related restrictions, signaled by healthier surveys and reviving "hard" data. This spells the end of the eurozone's technical recession.
- A second "flash" estimate released by Statistics Portugal shows
GDP declining by 13.9% q/q during the second quarter, revised from
a previous estimate of -14.1% q/q. (IHS Markit Economist Diego
Iscaro)
- Portuguese output had waned by 3.8% quarter on quarter (q/q) during the first three months of 2020.
- On a year-on-year (y/y) basis, GDP is now estimated to have fallen by 16.3% during the second quarter. As a reference, the largest y/y decline in GDP during the financial and sovereign debt crises was 4.5% during the fourth quarter of 2012.
- The economy has now declined by 17.3% during the first half of 2020, and output levels during the second quarter were the lowest since the first quarter of 1999.
- The statistics office did not release a full breakdown alongside the second "flash" figures (this will be published with the detailed release on 31 August). However, its media statement mentions that domestic demand was the main drag on activity in the quarter, shredding 10.7 percentage points from the total change in demand. Next, external trade made a sizeable, but smaller, negative contribution of 3.2 percentage points.
- This is in line with high-frequency indicators, which suggest that private consumption was the main factor behind the large decline in activity, while investment spending is also likely to have fallen substantially. While exports are also expected to have contracted markedly, declining imports are also likely to have moderated the negative contribution of net foreign trade to the change in demand.
- Denmark's economy is among the best performers in Western
Europe in Q2 according to "flash" estimate, despite record
contraction. (IHS Markit Economist Daniel Kral)
- The Danish statistics office (Statistics Denmark) released the first estimate for GDP growth in the second quarter of 2020. It points to a contraction of 7.4% quarter on quarter (q/q), the largest on record, which implies a contraction of 8.5% year on year (y/y).
- Despite the record contraction, Denmark's economy performed better than most of its peers. This is consistent with relative outperformance in retail sales and industrial production, following a rebound in the latter half of the second quarter.
- There is no detailed breakdown available, but Statistics Denmark notes that large negative contributions came from the private production of services, especially trade, transport, hotels and restaurants, as well as culture and leisure. On the other hand, agriculture, raw material extraction, finance and construction have been less affected.
- "Flash" estimates of Danish GDP are subject to significant
revisions even during normal times. In the context of the COVID-19
virus pandemic, Statistics Denmark notes considerable uncertainty
regarding its estimate, since many of the usual sources of data,
such as VAT returns, have not been available. It is also not
straightforward to construct the relationship between revenue and
value added, as production inputs have diverged from output, due to
closures.
- The Volkswagen (VW) Group's Financial Services unit has posted
a 9.8% year-on-year (y/y) decline in operating profit in the first
half of the year to EUR1.16 billion (USD1.37 billion), according to
a company statement. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
- The unit incurred a COVID-19 virus-related decline in first-half new financing contracts of 17.4% y/y to 3.4 million units.
- The overall number of contracts under management rose by 1.8% y/y to 21.3 million. CFO of VW Financial Services Frank Fielder said, "As a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, we have had to accept a substantial drop in new contracts during the first half of the year. In addition, the operating result is adversely impacted by higher risk costs for credit and residual value risks, which are affecting the entire portfolio."
- The unit announced this week that it was making extra provisions of EUR500 million in order to take into account the decline of the book value of its assets and contract defaults.
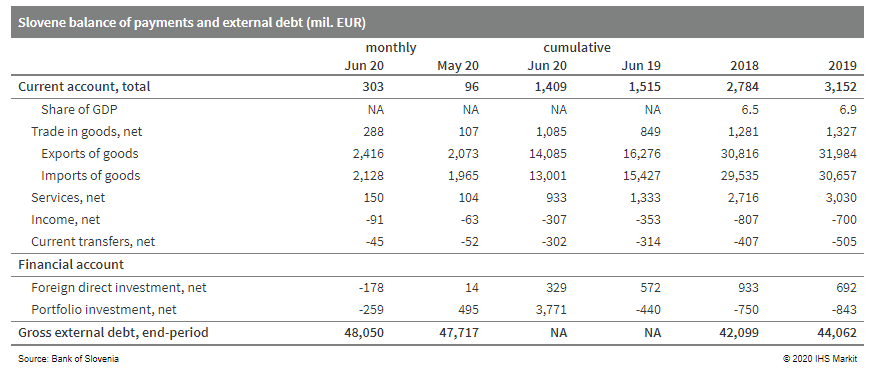
- Slovenia's current-account surplus shrank in the first half of
2020 as compared to the same period of 2019, by just over EUR100
million. (IHS Markit Economist Andrew Birch)
- In January-June 2020, the services surplus plunged by EUR400 million year on year (y/y), brought low by a sharp drop-off of service exports. In the first half of the year, travel service exports plunged by EUR685 million y/y and transport service exports dropped by EUR157 million y/y, as the Europe-wide restrictions to counter the spread of the COVID-19 virus deeply disrupted movement across the continent.
- The merchandise trade, income, and transfers balances all improved in January-June 2020 as compared to a year earlier. While the loss of merchandise exports undermined demand for domestic productive output, it did not reduce the trade surplus because of an even greater drop-off of merchandise imports.
- After serving as a safe haven for capital as a member of the
eurozone in March and April, portfolio capital flowed back outward
in June as global markets have shifted back towards searching for
higher yields.
- On 12 August, the Russian Ministry of Finance (MOF) said that
federal budget deficit had reached USD20.7 billion over
January-July 2020, with the July deficit rising 85% month on month.
(IHS Markit Country Risk's Alex Kokcharov)
- According to MOF data, between January and July the federal budgets expenditures reached 60.6% of the amount budgeted for the full-year 2020, while revenues only reached 50.5% of the full-year target.
- Tax revenue amounted to USD84.8 billion in January-July or 47.2% of the target for 2020, while custom duty revenues reached USD32.6 billion or 43.6% of the annual target.
- On 2 July Deputy Finance Minister Vladimir Kolychev said the total budget deficit in 2020 could reach 5% of GDP, versus a federal budget surplus of 1.8% of GDP in 2019.
- Russia's worsening budgetary position was triggered by the triple shock from sharply lower global crude oil demand, a 23% oil production reduction under the OPEC+ deal, and deep declines in private consumption and fixed investment reflecting the COVID-19 virus pandemic and associated lockdowns, which restricted economic activity.
- According to IHS Markit economics, the combined impact of these developments will lead to an 8.5% contraction of Russian real GDP in 2020. IHS Markit assesses that the growing budget deficit in 2020 is likely to lead to revision of state contracts in 2021-22, and efforts to improve tax collection.
- Moneyweb reported on 14 August that South Africa's FirstRand and Absa Bank have warned the market of expected earning declines for the end of June. FirstRand and Absa expect earnings to decline by up to 45% and 85%, respectively. It follows an announcement from Standard Bank (the country's biggest bank by assets) in July, noting that it expected earnings to reduce by up to 50%, compared with the same period. The main reason cited by banks for the decline in earnings is the increase in impairments because of the challenging macroeconomic conditions. In addition, banks have had to restructure loans, grant temporary holiday payments, and provide other debt-relief measures to support borrowers; the low interest rate environment has put pressure on the sector's earnings. Standard Bank, FirstRand, and Absa are the three biggest banks in South Africa, accounting for about 67% of the sector's total assets. (IHS Markit Banking Risk's Banking Risk)
Asia-Pacific
- APAC equity markets closed mixed; South Korea -1.2%, India -1.1%, Hong Kong -0.2%, Japan +0.2%, Australia +0.6%, and Mainland China +1.2%.
- China's industrial value-added grew 4.8% year on year in July,
unchanged from the reading in June. Meanwhile, the month-on-month
growth softened to 0.98%, the second consecutive month of slowdown.
The year-to-date contraction at 0.4% y/y narrowed by 0.9 percentage
points from a month ago. (IHS Markit Economist Yating Xu)
- Of the surveyed sectors, 25 out of 41 surveyed sectors year-on-year production growth in July, compared to 26 reported in June.
- Manufacturing growth picked up, while utilities moderated and mining slip into contraction partially due to the disruption by flooding.
- Auto, equipment and high-tech manufacturing led the headline growth, with year-on-year expansion of 21.6%, 13.0% and 9.8% respectively.
- Consumer goods production remained weak as agricultural products and food production stayed in contraction and textile production growth moderating.
- By products, auto and infrastructure-related products such as construction machinery, crude steel and iron ore gained continuous improvement.
- Auto production rose 26.8% year on year, up 6.4 percentage points from June. However, power generation growth slowed by 4.6 points to 1.9% in July.
- All ownerships reported slower industrial value-added growth from a month ago, except an acceleration in foreign-invested firms, reflecting the recovery in exports.
- Service production index rose 1.2 percentage points to 3.5% in July, while the year-to-date index remained in 4.7% y/y contraction. The headline services growth was entirely driven by strong growth in information, financial and real estate sectors. However, wholesale and retail, catering and accommodation remained in contraction.
- The year-to-date fixed asset investment (FAI) declined 1.6% year on year in July, narrowing by 1.5 percentage points from June. M/m FAI growth continued to slow to 4.9% in July from a 5.9% m/m expansion in June. The estimated de-cumulative FAI growth accelerated to 6.1% y/y.
- Thanks to the ongoing credit expansion, housing sales market regained strength in July. Decline in the floor space of commercial housing sold continued to soften to 5.0 % year on year through July and the estimated de-cumulative figure recovered to a 9.8% year-on-year expansion.
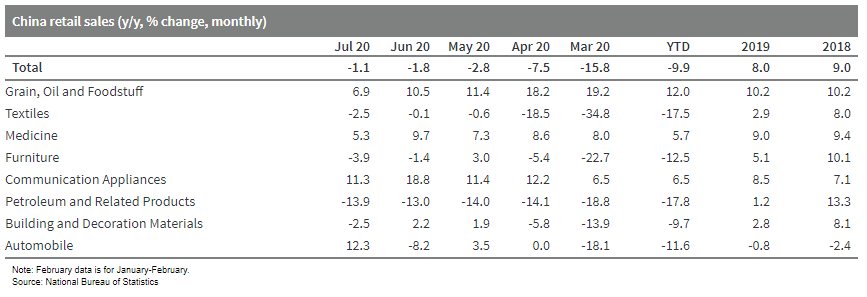
- Nominal retail sales contracted by 1.1% y/y in July, up 0.7 percentage points from June. Catering sales improved but remained in double-digit contraction while good retail sales improved to expansion.
- Consumption softened in all commodities except auto and jewelry. Auto sales jumped from an 8.2% year-on-year contraction in June to 12.3% year-on-year expansion in July.
- Retail sales excluding auto declined 2.4% year on year, deteriorating from a 1.0% year-on-year contraction a month ago.
- Clothes, furniture, and oil products sales declined further, food sales growth slowed despite rising consumer price index (CPI), and home appliance and construction materials deteriorated from expansion to contraction.
- Online retail sales growth accelerated to 9.0% year on year through July, accounting for 30% of total retail sales.
- Surveyed unemployment rate reported at 5.7%, unchanged from a
month ago. It is worth noting that surveyed unemployment for youth
rose, suggesting continuous pressure for the 8.74 million graduates
this year.
- Tesla has established an insurance brokerage in China with a registered capital of CNY50 million (USD7.2 million), reports China Daily, citing the National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System. The company was registered in Lingang New Area of the China (Shanghai) Pilot Free Trade Zone, where Tesla's Shanghai Gigafactory is located. Tesla is expected to soon expand its services in China to cover insurance-related services. The establishment of an insurance brokerage will allow Tesla to design an insurance product that better suits the needs of electric vehicle (EV) drivers. In September 2019, the US EV maker has begun offering an insurance product in the United States, initially only available to owners in California. According to the automaker, the insurance it offers in the US market is designed to provide Tesla vehicle owners with rates that are up to 20% lower, and in some cases as much as 30%. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Abby Chun Tu)
- According to China's General Administration of Customs (5 August 2020), Gansu province shipped its first ton of olive oil to South Korea. This is important as China is an important net importer of olive oil. It is reported that Gansu's Longnan City has the most suitable climate to cultivate olive for crushing in the whole country. The quality of the oil is said to be comparable to Italian and Greek imports. The planted area is 20,000 hectares. It is an important revenue stream for the local poor farmers. In the year to June 2020, China imported 19,895 tons of olive oil (HS codes 15099000 and 15091000), down by 2% compared with the year before, at an average price of USD3,149 per ton cif, down by 16%. Virgin olive oil accounted for 72% of total volume. Shipments from Chile rose by 322% to reach 380 tons, at an average price of USD3,075/ton, down by 23%. Olive oil from Australia, Portugal, Cyprus and the UK also increased significantly. In the same period, the export volume halved from last year to 14 tons. South Korea is the key destination, at an average price of USD5,730/ton, down by 14% compared with last year. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Hope Lee)
- Malaysian GDP contracted by 16.5% quarter on quarter in
second-quarter 2020, as the impact of the protracted Movement
Control Order (MCO) hit industrial production and consumer
expenditure. (IHS Markit Economist Rajiv Biswas)
- On an industry sector basis, only agriculture recorded positive growth, increasing 1% y/y in second-quarter 2020.
- The construction sector was the worst-affected, with output falling by 44.5% y/y in second-quarter 2020, as almost all construction activity ceased during April, and then only gradually restarted during May as the MCO was eased.
- The services sector recorded a 16.2% decline y/y in output during second-quarter 2020, as most retail outlets remained closed during April, although conditions improved during May and June as the MCO was eased. The tourism and commercial aviation sectors were very badly hit during second-quarter 2020 by the impact of domestic and international travel restrictions.
- Manufacturing output also fell sharply, down 18.3% y/y in second-quarter 2020, as the lockdown measures resulted in the shutdown of many plants and factories during April. Mining output also showed a large decline, with output down 20% y/y in second-quarter 2020 as production of oil and gas fell sharply owing to the impact of the MCO on operations.
- Domestic demand declined by 18.7% y/y in second-quarter 2020, as private consumption spending fell 18.5% y/y owing to the impact of the MCO on retail activity. Gross fixed capital formation declined by 28.9% y/y, with private investment falling by 26.4% y/y.
- Medical device manufacturer Medtronic (US/Ireland) has reportedly entered into a collaboration agreement with Vingroup (Vietnam), whereby the latter will produce components for use in ventilator equipment manufactured and assembled mainly in Europe and the US. The collaboration agreement aims to take advantage of the benefits of a free trade agreement between the European Union and Vietnam. The deal is one of the first substantial European investment projects in Vietnam's medical device manufacturing sector following the ratification of the European Union-Vietnam Free Trade Agreement (EVFTA) by the European Parliament at the start of 2020, followed by Vietnam's National Assembly later in the year. This should build confidence in Vietnam's strategy of developing an alternative manufacturing hub for the European and US markets and away from a dependency on China. In the long term, this is likely to help increase Vietnam's importance in the global supply chain system for medical equipment in the long term. (IHS Markit Life Sciences' Eóin Ryan)
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-14-august-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-14-august-2020.html&text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+14+August+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-14-august-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Daily Global Market Summary - 14 August 2020 | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-14-august-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+14+August+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-14-august-2020.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}




