Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
ECONOMICS COMMENTARY
Oct 09, 2020
Chinese economic recovery sustained as trade gains momentum
- Caixin PMI signals further solid growth in output
- Order books continue to rise strongly, supported by solid export sales, with goods export growth at a three-year high
- Employment increases further as outlook remains upbeat
Caixin PMI data indicated a strong end to the third quarter for the Chinese economy, with business activity maintaining a solid pace of expansion during September. The recovery was sustained by robust inflows of new business, with a jump in goods export growth in particular providing a welcome boost.
Rising demand helped to generate further jobs growth as capacity pressures rose steadily. Business sentiment about the year-ahead outlook remained upbeat, boding well for mainland China as the economy heads into the fourth quarter.
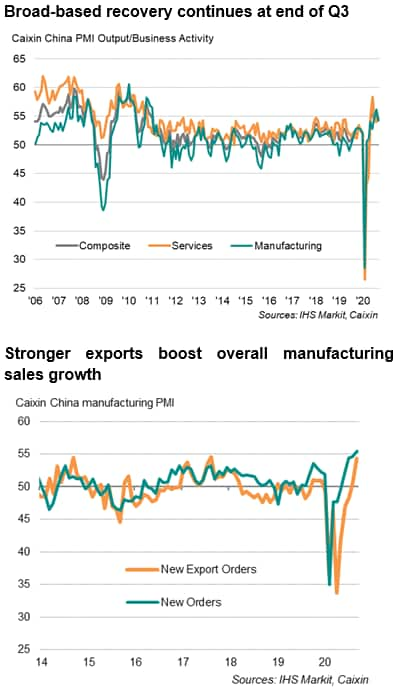
China PMI shows steady recovery
The Caixin headline Composite PMI for mainland China, compiled by IHS Markit and covering manufacturing and services, dipped to 54.5 in September, down slightly from 55.1 in August, but nevertheless indicated a further steady improvement in business conditions. The survey added to evidence that the Chinese economic recovery was solid in the third quarter. At 54.7, the average PMI reading in the three months ending September was above the 52.6 recorded in the second quarter.
Moreover, the increase in overall order book volumes also held up well, with the latest expansion supported by a stronger rise in new export orders. Backlogs of work continued to increase, albeit more modest when compared to the rise in new orders. This is likely due to strong output growth as firms continued to respond to increased demand following the easing of pandemic restrictions earlier in the year.
The recovery remained broad-based, with manufacturing and services driving the expansion in business activity. Manufacturing output rose for a seventh straight month in September, though the rate of increase moderated from the over nine-year high seen in August. Similarly, services business activity expanded for a fifth month in a row, in part reflecting a sustained recovery in consumer demand. Seen among the best performers were automakers and producers of household goods, linked to improved consumer behaviour and reopened retail businesses as the pandemic has been brought under control. Activity at financial services and technology services also continued to increase.
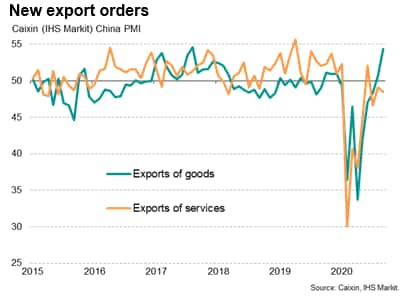
Goods exports rise at steepest rate for three years
The upturn in business activity was driven by a further strengthening of demand conditions, with the manufacturing sector registering the stronger rise in new orders than services.
A key development driving growth in manufacturing sales was a surge in merchandise export sales. Overseas orders of Chinese manufactured products increased at the fastest rate for three years during September after marginal growth in August. This strong expansion in exports reflected an increase in the number of countries reopening their economies and moving towards more normal market conditions.
On the other hand, new business in the service sector was fuelled primarily by the domestic market, with external demand continuing to deteriorate as many countries still maintained some international travel restrictions despite a recent loosening of border controls in parts of the world.
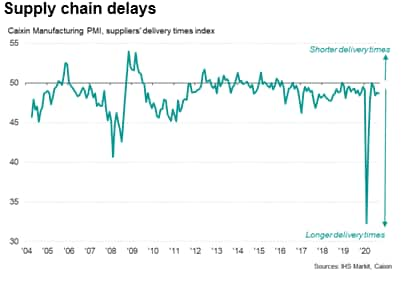
Supply chains still under pressure
The restoration of supply chains remained under way, but the combination of demand revival and stock shortages at distributors (linked to reduced capacity) continued to affect the ability of suppliers to make timely deliveries. While the lengthening of delivery times was modest, and much improved from February, at the height of the pandemic in mainland China, a persisting issue with input availability could impact the extent to which manufacturers can raise production volumes.
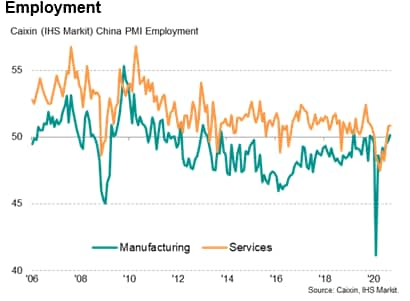
Job creation
The sustained recovery in Chinese business activity and rising demand saw a second straight month of job creation in September. The service sector reported net jobs growth for a second month running while manufacturing employment stabilised after an eight-month period of job cuts.
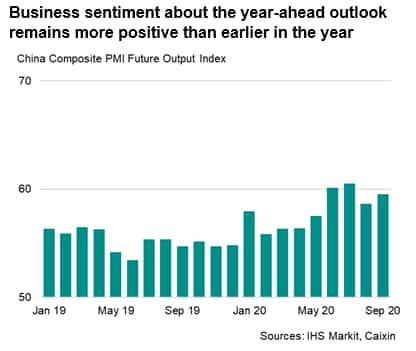
Can the recovery continue?
Business sentiment among Chinese firms remained positive at the end of the third quarter. The PMI's Future Output Index, a gauge of confidence, rose from August and was slightly above the long-term trend. Optimism reflects expectations of further improvement in economic conditions and greater strengthening in client demand once the global pandemic is brought under control. Further export growth will also add to the sustainability of the recovery, alongside greater relaxation of travel restrictions.
Bernard Aw, Principal Economist, IHS Markit
Email: bernard.aw@ihsmarkit.com
© 2020, IHS Markit Inc. All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole
or in part without permission is prohibited.
Purchasing Managers' Index™ (PMI™) data are compiled by IHS Markit for more than 40 economies worldwide. The monthly data are derived from surveys of senior executives at private sector companies, and are available only via subscription. The PMI dataset features a headline number, which indicates the overall health of an economy, and sub-indices, which provide insights into other key economic drivers such as GDP, inflation, exports, capacity utilization, employment and inventories. The PMI data are used by financial and corporate professionals to better understand where economies and markets are headed, and to uncover opportunities.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fchinese-economic-recovery-sustained-as-trade-gains-momentum-Oct2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fchinese-economic-recovery-sustained-as-trade-gains-momentum-Oct2020.html&text=Chinese+economic+recovery+sustained+as+trade+gains+momentum+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fchinese-economic-recovery-sustained-as-trade-gains-momentum-Oct2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Chinese economic recovery sustained as trade gains momentum | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fchinese-economic-recovery-sustained-as-trade-gains-momentum-Oct2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Chinese+economic+recovery+sustained+as+trade+gains+momentum+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fchinese-economic-recovery-sustained-as-trade-gains-momentum-Oct2020.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}




