Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Research — 26 Apr, 2023
In its monthly Zinc Commodity Briefing Service (CBS) reports, S&P Global Commodity Insights discusses the zinc market within the broader macroeconomic environment and provides rolling five-year supply, demand and price forecasts.
Access the Zinc Commodity Briefing Service April 2023 Databook and March quarter 2023 Slide deck.
Key findings
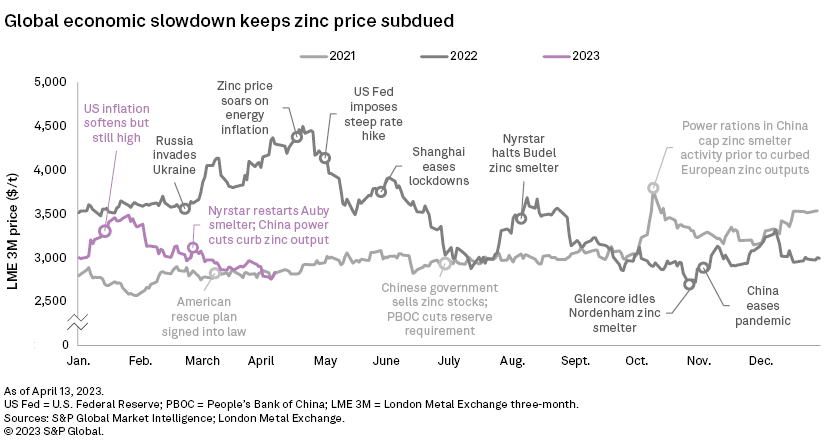
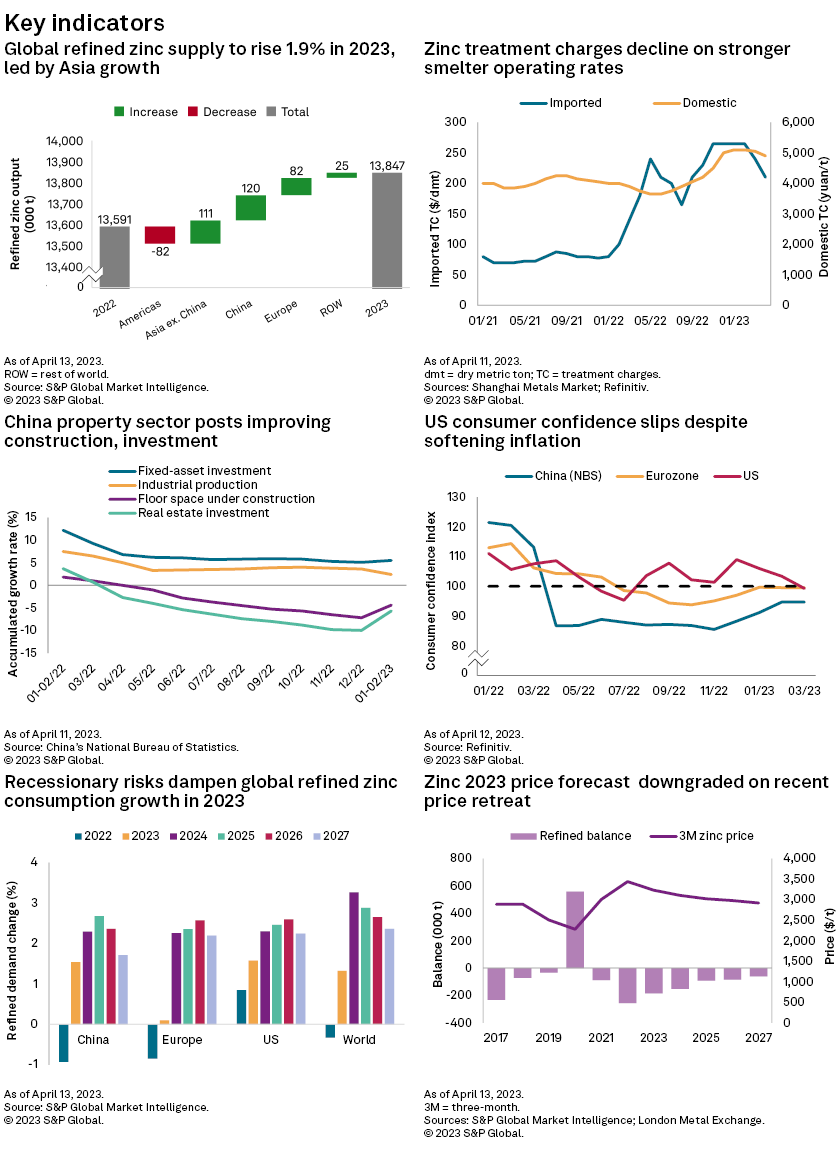
– The London Metal Exchange three-month (LME 3M) zinc price was rangebound throughout March on macroeconomic pressures and constrained supply. For the first quarter of 2023, the average price was down 16.6% year over year.
– China's economic rebound is reflected by its expanding manufacturing activity and improving property sector metrics. Given muted downstream demand, however, we have kept China's zinc demand growth forecast for 2023 at 1.5%.
– Stubbornly high core inflation in Europe and falling consumer confidence in the US have led us to maintain our current global refined zinc growth consumption forecast at 1.3% in 2023.
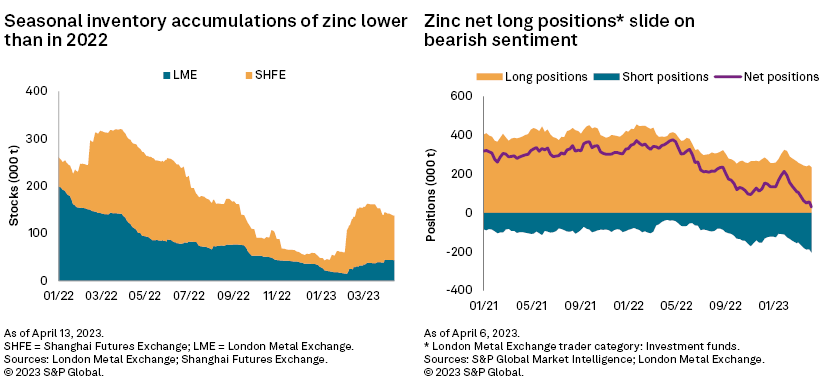
– Despite inventory rebuild at the major zinc exchanges, stock levels remain historically subpar. The spot scarcity mindset quickly faded, however, as net long positions at the LME dropped due to risk-averse investors.
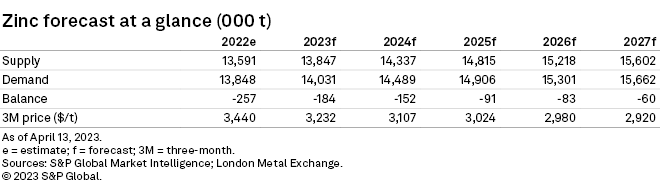
– Given weaker LME prices recently, we have downgraded our average zinc price forecast for 2023 to $3,232 per metric ton, but we still expect a market deficit of 184,000 metric tons, given power curbs in China.

Amid China's rebound and milder US inflation, the zinc price hovered around $2,900/t in March as the downcast global economy stalled demand. We, therefore, expect global refined zinc consumption to only grow 1.3% in 2023. We anticipate power cuts in China to pressure global refined zinc outputs, which are forecast to rise 1.9% in 2023. Our anticipated deficit for 2023 remains 184,000 metric tons, but we have downgraded our LME zinc price forecast to now average only $3,232/t to reflect recently softer prices.

Analyst comment
Despite a weaker US dollar, the LME 3M zinc price hovered around $2,900/t throughout March as macroeconomic uncertainties fueled demand concerns. The price dropped further to $2,757/t on April 11, and net long positions have fallen as recessionary symptoms proliferate despite low zinc inventories. Amid volatile market conditions, the price averaged $3,107/t in the first quarter, down 16.6% year over year.
In China, the National Bureau of Statistics and Caixin purchasing managers' indexes (PMI) moderated to 51.9 and 50.0, respectively, in March as manufactured export orders eased. Accumulated growth rates for real estate investment and floor space under construction for January and February combined showed signs of improvement in the property sector but remained down year over year. Industrial production and fixed-asset investment held steady during the same period, while February vehicle production stood strong. Crude steel production improved, but environmental controls limited consumption by galvanizing and die-cast operations, although these enterprises have been restocking given weaker zinc prices. Moreover, China's refined zinc imports have improved and are now only down 3.0% year over year in February. China is focusing on boosting consumer spending and business investment and improving trade flows and durable infrastructure. We, therefore, still estimate China's refined zinc consumption will rise 1.5% to 7.1 million metric tons in 2023, then 2.3% in 2024, as the government and central bank cooperate to reach economic targets.
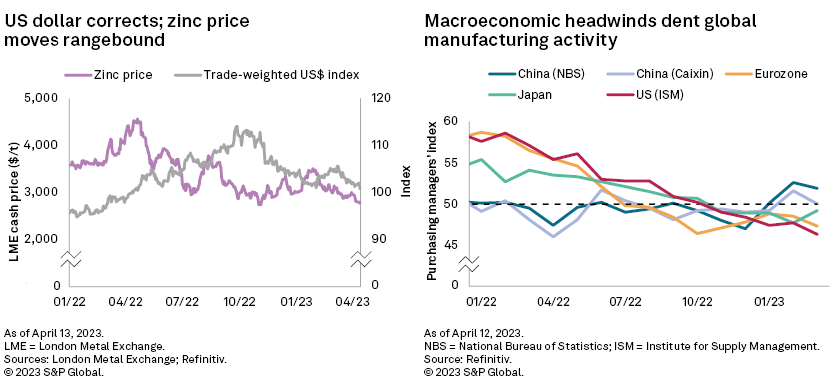
Inflationary pressures in the US have started easing, but the stressed bank sector eroded consumer confidence throughout the March quarter. This also depressed manufacturing activity, with the US Institute for Supply Management PMI stumbling to 46.3 in March — its lowest since April 2020. Industrial production and construction spending in the US and EU declined year over year in February, while domestic auto production in the US and new passenger car registrations in the EU increased. Consumer prices in the bloc remain elevated despite abating energy costs, however. So while the US Federal Reserve slowed its pace of interest rate hikes, persisting high core inflation in the EU is likely to keep the European Central Bank hawkish. As we keep our demand forecasts unchanged for the US and Europe in 2023, we expect global refined zinc consumption to increase 1.3% to 14.0 MMt in 2023, then grow 3.3% in 2024.
Although there have been seasonal accumulations at the major exchanges, zinc inventories at the LME and Shanghai Futures Exchange are lower than in the same period of 2022. Spot scarcity has kept premiums elevated, but economic turbulence led to a sharp reduction in net long zinc positions at the LME in March as investors seek safer securities.
Weaker LME zinc prices have led to higher zinc product and raw material inflows into China. High smelter utilization rates in China, however, have pressured zinc concentrate treatment charges, with the domestic and imported fees at 4,900 yuan/t and $210/t in April, respectively. More recently, Korea Zinc Co. Ltd. and Teck Resources Ltd. settled the benchmark treatment charge at $274/t, up 19.13% compared with $230/t in 2022. The higher fee may encourage zinc smelters to boost outputs, but we expect power stability and environmental trade-offs to challenge such plans.
We, therefore, maintain our 1.9% growth forecast for global refined zinc supply in 2023 to 13.8 MMt. This expectation is underpinned by European smelters further ramping up production given falling energy costs, hydropower shortages curtailing zinc output in Yunnan and maintenance shutdowns elsewhere in China. In 2024, we expect stronger production growth at 3.5% as energy conditions improve.
On the mined supply side, we foresee reserves depletion in China to weigh down mining production. We estimate the global mined zinc supply to only grow 2.6% to 13.4 MMt in 2023, then 2.8% in 2024. We expect shrinking mine output further out in our forecast horizon, compounded by underinvestment in zinc mining projects.
Outlook
The flagging global economy, vulnerable US banking sector and high core inflation in Europe broadly offset the optimism from China's recovery — an overarching sentiment reflected in slumping long investment funds at the LME despite low inventories and refined zinc undersupply.
We maintain our refined zinc deficit of 184,000 metric tons in 2023, given our substantial adjustments to supply and demand from our previous report. We downgraded our average LME 3M zinc price forecast for 2023 to $3,232/t due to weaker prices during the first half. We expect the zinc price to average $3,008/t across 2024–27, supported by narrowing deficits and slow inventory rebuild.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
