Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Research — Jan 30, 2025
By Adam Wilson and Katherine Nelson, PhD
The Western US solar fleet is amid rapid growth, with the region being home to four of the top five markets in planned photovoltaic capacity. This expansion of solar generation is plummeting daytime energy prices and available solar revenues, driving the need for complementary battery energy storage systems (BESS), as evidenced by rising hybrid solar-plus-storage capacity in interconnection queues. Despite growing developer interest, forecast economics of hybrid systems vary across the West, with California looking most favorable due to robust renewable energy credit (REC) and arbitrage revenues.

– The Western US is experiencing a significant surge in solar development, driven by declining costs of utility-scale photovoltaic projects and federal incentives from the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022. This growth is bolstered by excellent solar resources and increasing energy demand, particularly due to the AI-driven datacenter boom.
– In markets where high solar penetration leads to reduced solar capture ratios, hybrid solar-plus-storage systems are crucial for maintaining grid stability and optimizing energy use. These systems enable efficient energy storage and distribution, ensuring continued resource availability during peak demand periods.
– The development pipeline for hybrid projects is strategically concentrated in designated energy communities, leveraging available tax incentives and enhancing project viability.
– The five key revenue sources for hybrid solar-plus-storage projects — electricity prices, RECs, tax credits, battery storage capacity and arbitrage opportunities — vary significantly across the Western US. While some markets face challenges due to limited market structures and lower REC prices, California ISO stands out as the most favorable market. Its high REC prices and robust arbitrage opportunities make it well positioned to deliver profitable returns for hybrid projects.

Download Commodity Insights' interactive US solar-plus-storage investment outlook and its Excel companion.
Operating and planned solar in the West
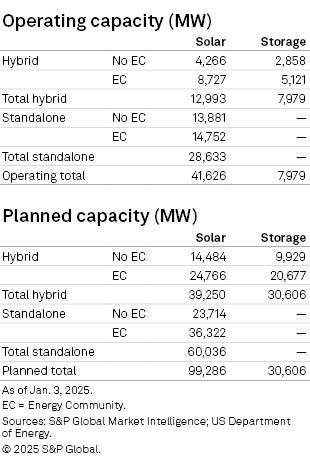
The Western US is comprised of five major power markets: CAISO; Basin (Utah and parts of Nevada); COWY (Colorado and Wyoming); the Northwest Power Pool, now known as the Western Power Pool (Washington, Oregon, Idaho and Montana); and the Southwest Reserve Sharing Group (Arizona, New Mexico and southern Nevada). Together, these markets have 41.6 GW of installed solar capacity, 28.6 GW of which is stand-alone and 13.0 GW colocated with 8.0 GW of battery storage.
By state, California leads the region with 22.2 GW of operating solar capacity — over half the installed base of the West. California led the nation in operating solar generation until 2024, when Texas took over the top spot. Nevada (5.5 GW) and Arizona (5.0 GW) rank second and third, respectively, in the West in installed photovoltaic capacity. New Mexico, Utah, Colorado and Oregon all have more than 1 GW of operating solar as well. About 69% of the operating solar capacity in the West is stand-alone.
|
The pipeline for solar in the West has surged in recent years, as costs of utility-scale photovoltaic projects continue to decline while federal incentives from the Inflation Reduction Act add critical revenue streams for stand-alone and hybrid systems. Combined with excellent solar resources and rising energy demand due partly to the recent AI-driven datacenter boom, the West — along with Texas — will remain a focal point for solar development in the US for the foreseeable future.
Nevada leads the West in planned solar capacity, accounting for over a quarter of the 99.3 GW in development across the region. The state's large swaths of open space eligible for the 10% energy community tax credit adder play a significant role, with 91% of the proposed capacity located in such areas. California ranks second with 17.8 GW of solar in development, with 44% of this capacity having colocated battery storage, according to S&P Global Market Intelligence data. The more speculative interconnection queue in CAISO indicates a move away from — if not a complete abandonment of — stand-alone solar, with 97% of solar capacity in the queue part of a hybrid system. The non-CAISO West is following suit, with over 83% of interconnection queue solar capacity being paired with energy storage.
Financial outlook
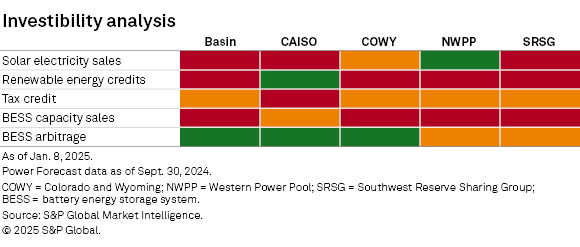
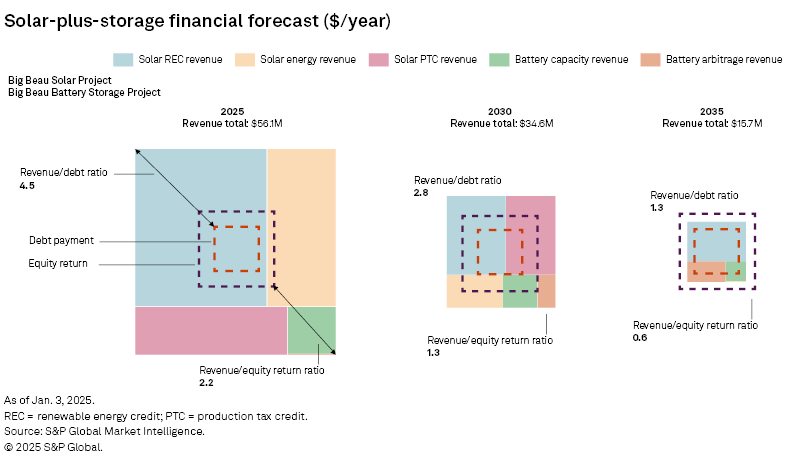
As the Western US continues to expand its solar and storage infrastructure, understanding the financial outlook becomes crucial for stakeholders aiming to capitalize on these developments, ensuring that investments align with evolving market dynamics and potential revenue streams. The financial outlook for hybrid solar-plus-storage plants is based on multiple factors: the electricity price for solar generation, the price of RECs, available income from production and investment tax credits, revenues for battery storage capacity and arbitrage. The five markets in the West have unique opportunities in these five areas.
|
Basin, with high solar penetration, has inverted on- and off-peak pricing and experiences high curtailment, resulting in low prospects for solar electricity sales. Additionally, the lack of compliance-REC and capacity markets further limits revenue potential. However, a high percentage of counties within the Basin market are eligible energy communities with the potential for step-up tax credit revenues, and the spread in hourly prices provides good BESS arbitrage opportunities.
Overall, forecast economics for solar-plus-storage plants are strong in 2025 as the solar market is not yet saturated, resulting in strong energy revenue along with income from the federal Production Tax Credit (PTC). By 2030, solar energy revenue is projected to decrease 90%; by 2035, the PTC expires, which more than offsets rising arbitrage revenue. As a result, projects in the Basin fail to reach the minimum debt service threshold by the end of the period.
The profitability of a hybrid solar-plus-storage plant in COWY is only supported by high BESS arbitrage. Having access to only voluntary REC markets, the lack of a capacity market, moderate solar penetration and only minimal opportunities for tax credit step-ups, a hybrid plant is only able to reach approximately 80% of its equity returns through 2030, and when the PTC expires, it no longer reaches debt payment levels.
With lower solar penetration due to less potent solar resources, NWPP still has strong daytime revenue potential for solar generation. However, no observable REC or capacity markets, fewer opportunities for tax credit step-ups and plentiful hydro generation that keeps battery arbitrage potential low result in a murky financial outlook for hybrid solar-plus-storage. All revenues are forecast to barely meet minimum debt payments and only 60% of equity returns.
Though the SRSG region has similar problems to the NWPP market in terms of RECs, capacity and tax credit revenue potential, solar electricity prices are high in 2025 to support debt coverage. However, high solar penetration reduces solar capture ratios by 2035, and with the expiration of the PTC, plants can no longer make debt payments.
While the financial outlook for hybrid solar projects varies across the Western US due to differing market conditions and revenue streams, CAISO emerges as a standout region, offering unique opportunities for profitability and growth.
Unique opportunity in CAISO
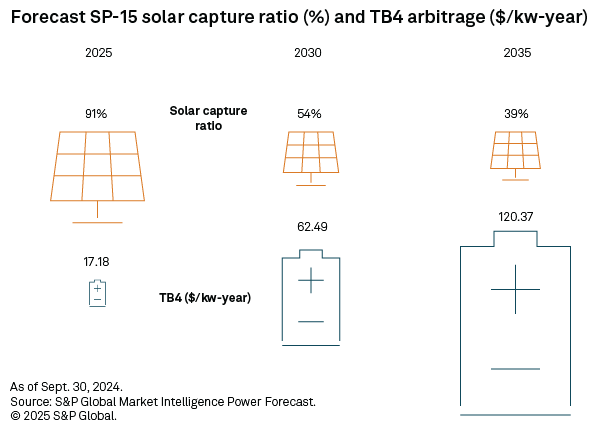
With significant amounts of solar generation on the grid, CAISO faces the strongest "duck curve" in the country as daytime prices plummet and evening prices rise to meet demand. This provides strong arbitrage potential for batteries, as quantified using the difference between the four highest hourly prices in the evening and the four lowest hourly prices midday, called top-bottom 4 (TB4). This quantity is used as a proxy for the revenues that a four-hour battery could acquire when charging at the low-priced hours and discharging at the high-priced hours. TB4 is forecast to more than double from 2025 to 2035, while the solar capture ratio drops to 43% of its 2025 value, highlighting the necessity to colocate storage with any solar added to the CAISO grid.
|
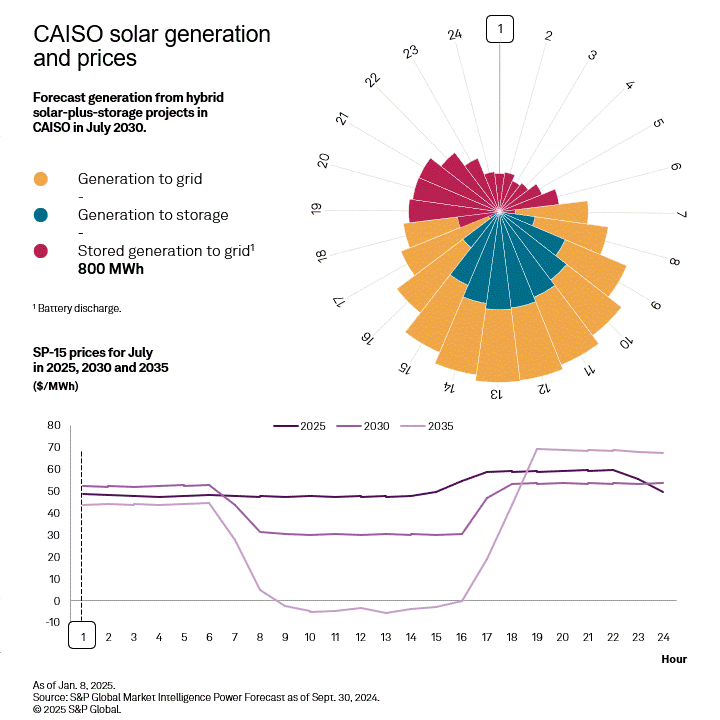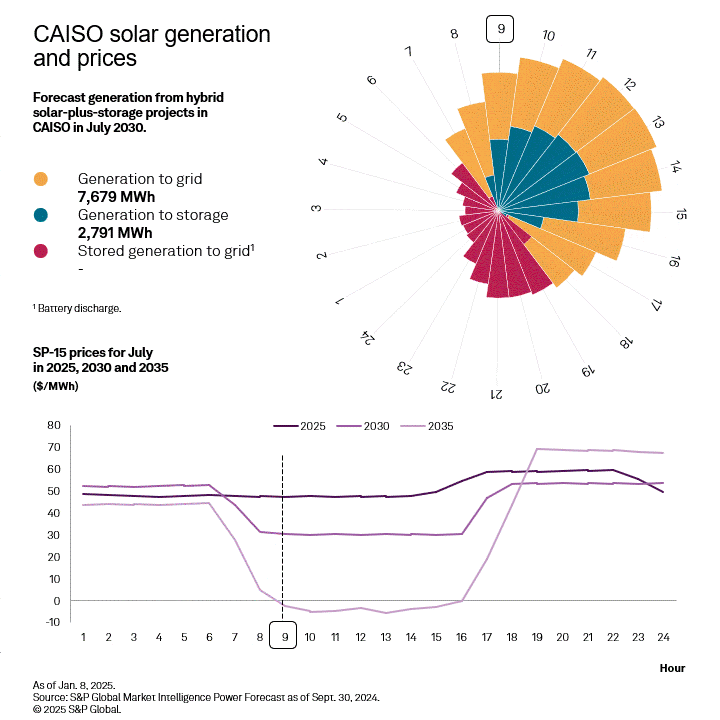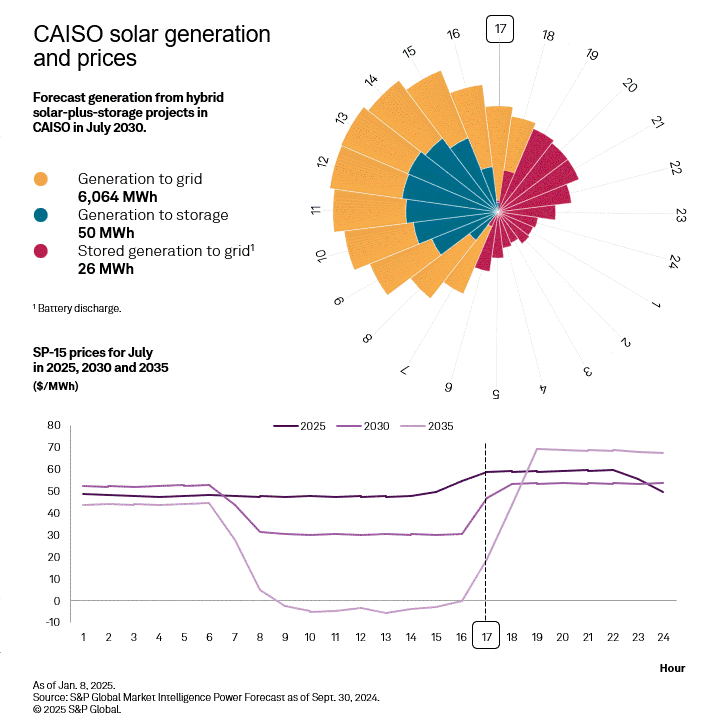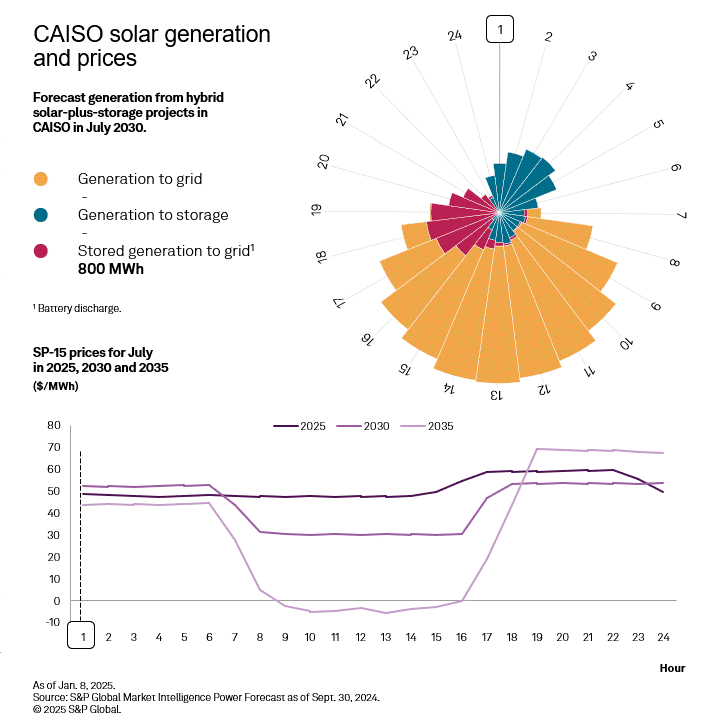
While some generation from the solar portion of a hybrid plant still goes to the grid in daytime hours, the portion stored in the colocated battery provides continued resources during evening hours when energy prices hit their daily peak. Colocated battery storage provides revenue to the generator and a more balanced grid when daytime solar generation ends but energy demand remains high.
|
CAISO is the only region in the West forecast to have positive returns on equity through 2030. Using an indicative 128 MW solar with a colocated 40-MW storage system in CAISO, the market dynamics can be illustrated. Due to the high CA Bucket 3 REC prices and base production and investment tax credit revenue, the total revenues are 130% of the full annualized revenue requirements and plant operating expenses, despite having little potential for tax credit step-ups and a less robust capacity market. However, after the expiration of the 10-year PTC, a hybrid plant will no longer be able to satisfy equity holders, though still meeting debt payments based on strong REC and BESS arbitrage revenues.
|
As the Western US continues to navigate the complexities of solar hybrid development, understanding and leveraging regional dynamics will be pivotal in achieving sustainable profitability and driving the future growth of renewable energy solutions.
Cartography by Leigh Lunas. Data visualization by Allen Villanueva.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
For wholesale prices and supply and demand projections, see the S&P Global Market Intelligence Power Forecast. S&P Global Commodity Insights produces content for distribution on S&P Capital IQ.
Regulatory Research Associates is a group within S&P Global Commodity Insights.
For a complete, searchable listing of RRA's in-depth research and analysis, visit the S&P Capital IQ Pro Energy Research Library.
Theme
Location