Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Research — 5 Apr, 2023

By Alice Yu
In its monthly Lithium and Cobalt Commodity Briefing Service (CBS) report, S&P Global Commodity Insights discusses the lithium and cobalt markets within the broader macroeconomic environment and provides rolling five-year supply, demand and price forecasts.
Key findings
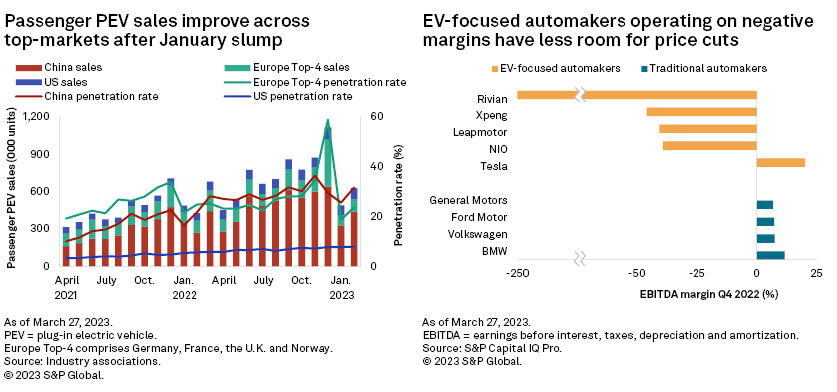
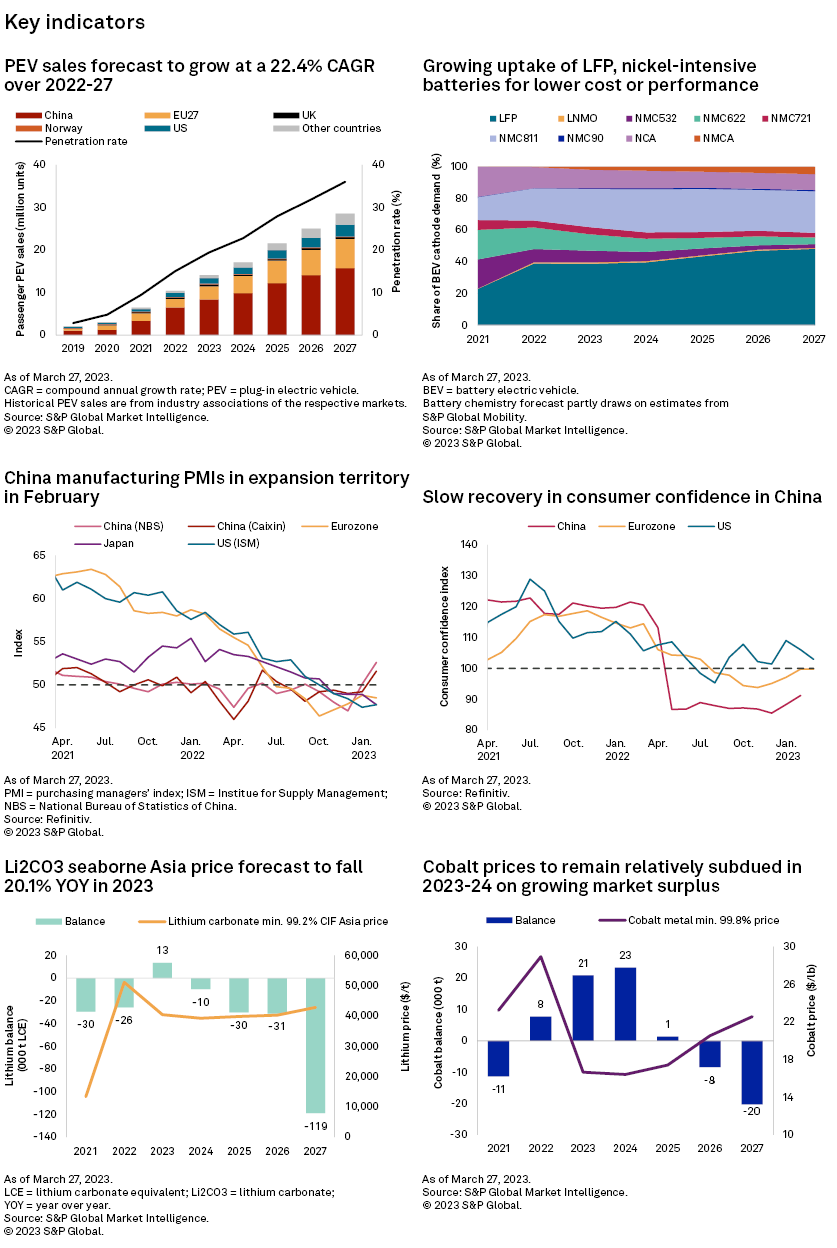
– Passenger plug-in electric vehicle (PEV) sales across the top markets rose 27.7% month over month in February, although the impact of subsidy drops still lingers in China and Europe.
– Vehicle price discounts, including internal combustion engine (ICE) and PEV models, are more rampant and broad-based in China, the only market where some models are being discounted.
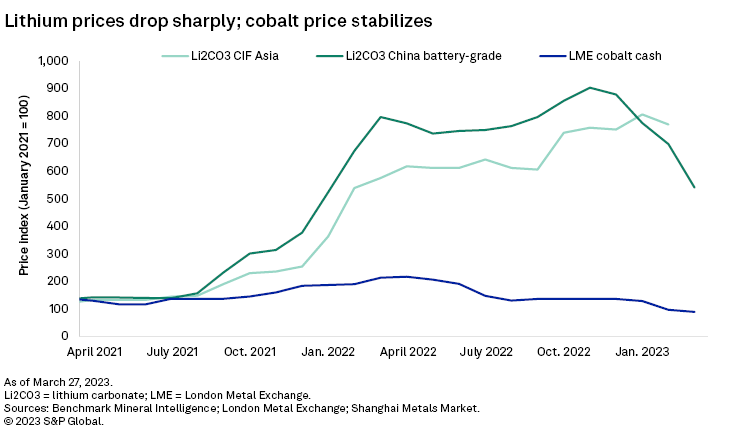
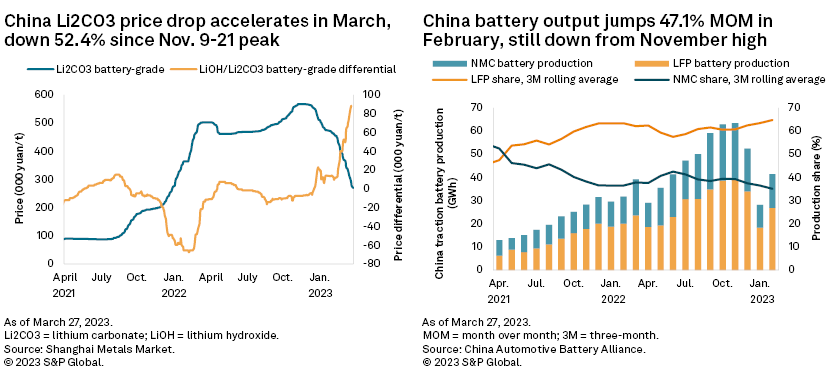
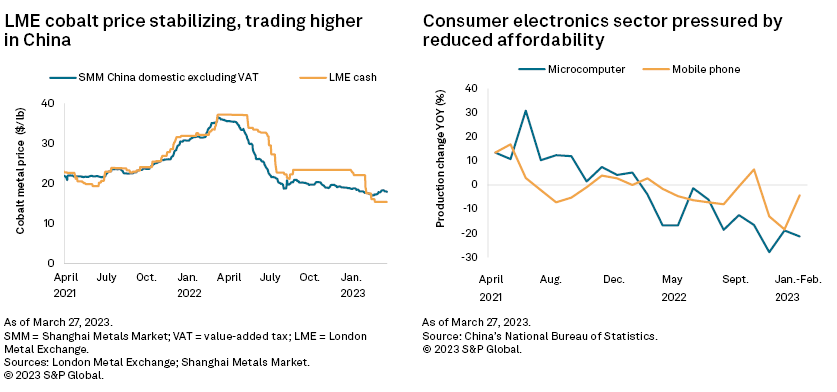
– China's battery-grade lithium carbonate price decline accelerated, dropping 29.0% month-to-March 27 to 270,000 yuan per metric ton ($34,773/t excluding value-added tax). Prices have dropped 52.4% since peaking Nov. 9-21, 2022.
– Product inventory at lithium refineries is rising on weak demand, accentuated by a lack of restocking by downstream consumers in the battery supply chain. Lithium refineries reliant on spodumene purchased from the spot market are currently loss-making.
– The cobalt metal price decline paused in March, with the London Metal Exchange (LME) cobalt cash price stabilizing between $15.31 per pound and $15.32/lb in March-to-date. China's cobalt metal price rose 4.5% March 1–13 before pulling back 5.9% by March 27 on a lack of support for a sustained price increase.
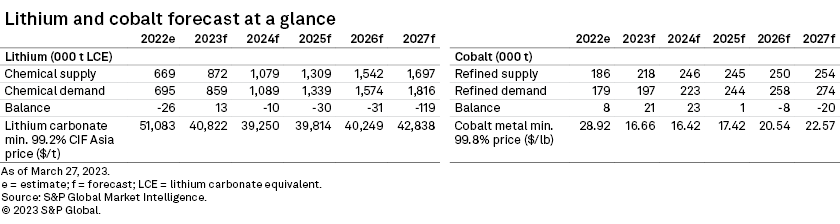
– We now expect a steeper decline in the lithium carbonate CIF Asia price — a 20.1% drop year over year in 2023 compared with 15.9% in our previous report — as more drastic discounts on ICE vehicles could slow the PEV sales recovery in China.
– We expect a subdued cobalt metal price throughout the year, from weak demand at present, and that supply additions will offset the impact of more noticeable demand improvements in the second half.
Access the Lithium and Cobalt Commodity Briefing Service March 2023 Databook.

The impact of subsidy reductions still lingers across major PEV markets, including China, Germany and Norway. Demand weakness accelerated the decline in China's battery-grade lithium price, dropping 29.0% month-to-March 27. Cobalt metal prices stopped falling, with the LME price stabilizing and prices in China fluctuating around a near-term price floor.
Since the beginning of March, rampant price cuts to ICE vehicles in China have spilled over to PEVs. Global car makers appear to be more readily offering discounts on PEVs in China than in other markets. Steep discounts in China's ICE vehicles could nonetheless pressure the PEV sales share in the short term and further moderate the pace of the country's PEV sales recovery.
A declining price environment — from vehicles to batteries and for lithium and cobalt — provides greater opportunities for low-cost, integrated producers to gain market share while being much more challenging for others.
We expect the lithium carbonate CIF Asia price to decline 20.1% year over year in 2023 and the cobalt price to correct 42.4% over the same period.

Plug-in electric vehicles
Passenger PEV sales across top markets rose in February as recovery is underway from the January slump. Sales in China rebounded 32.8% month over month in February, although the recovery is far from complete, with the full PEV sales potential capped by weakness in the broader car market, which was down 19.8% year over year in the first two months. In the Europe Top-4 markets, passenger PEV sales rose in France and the UK from growing confidence in the auto sector and supply-chain improvements, though sales declined in Germany and Norway due to a step change in subsidies and taxes.
Tesla Inc.'s global price cuts in January spurred a wave of price drops, mainly by EV-focused producers in China and traditional automakers' all-electric models that are in direct competition. These include price cuts on Ford Motor Co.'s Mustang Mach-E sold in North America and China and limited-time offers on Toyota Motor Corp.'s bZ4X and Nissan Motor Co. Ltd.'s Ariya in China. These price reductions provide consumers cost savings from supply chain improvements and lower lithium prices. The tougher competition will nonetheless pressure automakers' margins or revenue.
The price competition is fiercer in China. The provincial government in Hubei surprised the market in early March by offering subsidies that slashed prices by up to 90,000 yuan ($13,000) for the purchase of vehicles. The discounts benefit foremostly ICE vehicles, which face weak demand, high inventory and stricter emissions regulation starting in July. The provincial-level cut subsequently spurred broad-based discounts, with momentum spilling over to PEVs. On March 17, SAIC Volkswagen Automotive Co. Ltd. announced a temporary promotion across PEV and ICE models through to end-April.
The battery maker Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Ltd. is also offering discounts to its key automaker customers in exchange for volume, securing supply of at least 80% of each customer's battery needs for the next three years. The deal is only offered to selected auto customers and is a form of profit-sharing in times of challenging market conditions by easing automakers' cost and margin pressures. When the news was first reported in mid-February, the offer was equivalent to a 53.6% reduction in the spot lithium prices used to determine battery prices. The spot lithium price has since dropped, narrowing the effective reduction, but the deal still provides automakers with cost stability at below-market rates.
The latest PEV price cuts are disruptive but should not be surprising, as the industry relied on long-term PEV demand being underpinned by increasing price competitiveness as battery costs fall on improving technology, efficiency and scale.
Lithium
China's battery-grade lithium carbonate price decline accelerated, dropping 29.0% month-to-March 27 to 270,000 yuan/t ($34,773/t excluding value-added tax). The price has lost 52.4% since peaking at 567,500 yuan/t Nov. 9–21, 2022.
The lithium chemical price slump points to a sluggish global PEV sales recovery, reduced consumer capability to pay for lithium as some battery and automakers actively lower their prices, expected lithium supply additions and inventory build-up. Product inventory is rising at lithium refineries due to weak demand coupled with low willingness to restock by precursor and battery makers.
In a falling price environment, producers throughout the lithium supply chain face the added pressure of cost-to-price mismatch: lithium units are more expensive at time of purchase than when sold as refined and processed products. The uncertainties over the timing of the demand recovery under a bearish price environment make for testing times for lithium producers.
Refineries relying on spodumene purchased from the spot market are loss-making with an implied battery-grade lithium carbonate cost of 315,467 yuan/t, 16.8% higher than the spot price on March 27. Integrated lithium refineries are still very profitable under current prices. Under a consensus price scenario, the highest-cost integrated carbonate producer has a total cash cost of $11,650/t in 2023, one-third of the spot price on March 27.
Cobalt
The cobalt metal price decline paused in March. The LME cobalt cash price stabilized, trading at $15.31/lb-$15.32/lb between Feb. 22 and March 27. China's cobalt metal price rose 4.5% between March 1 and March 13 to 316,000 yuan/t ($18.28/lb excluding value-added tax) as spot availability decreased, with refineries honoring deliveries to China's state reserve. There was otherwise limited demand support to sustain a price increase, and prices subsequently pulled back 5.9% to 297,500 yuan/t ($17.38/lb excluding value-added tax) March 27.
Cobalt demand from the PEV sector remains subdued as the recovery across PEV sales and traction battery production is still incomplete. China's traction battery production is 34.6% lower than peak production in November 2022, despite rising 47.1% month over month in February. The consumer electronics sector has been and will remain depressed this year as consumers curtail discretionary spending amid ongoing macroeconomic challenges and still recovering consumer confidence in China.
PEV subsidy reduction in China is expected to accelerate the trend of lower cobalt usage in battery chemistries for cost benefits. A falling lithium price further increases the cost-saving benefit of lithium-iron-phosphate batteries that contain no cobalt over that of cobalt-containing batteries.
Outlook
China's passenger PEV sales will likely continue recovering, supported by positive signs from the country's manufacturing sector, with purchasing manufacturing indices rising in February. The PEV penetration rate could nevertheless experience setbacks in the short term due to comparatively more rampant ICE vehicle discounts.
Lithium prices could take longer to bottom out due to a sluggish-paced PEV sales recovery, rising lithium chemical inventory and lithium supply additions. We expect more greenfield projects to commission this year as they overcome delays. Sayona Mining produced its first spodumene concentrate at the company's North American Lithium project this month and expects first shipment in July. Huayou Cobalt started trial production at the Arcadia project. The supply progress will further weigh on sentiment and prices during a period of relatively weak demand.
We have downgraded the lithium carbonate CIF Asia price forecast for 2023 and expect the price to drop 20.1% year over year, compared with a 15.9% decline in our previous report. Downstream consumers' capability to pay for lithium has also drastically decreased amid PEV price drops, fierce competition and broadly lower subsidies in Europe and China than in 2022.
We forecast the cobalt market surplus to widen this year from a higher mine supply increase of 24.8% year over year in 2023, compared with the 19.5% increase in 2022. We expect a subdued cobalt metal price to persist throughout the year from depressed demand at present, higher supply growth offsetting the impact of more noticeable PEV demand improvements in the second half and a lack of upsides from the consumer electronic segment.
Potential upsides to both lithium and cobalt demand will depend on policy outcomes. Policymakers ex-China are refining terms that would boost the PEV sector. The EU is delaying a key vote on the 2035 ICE ban to consider the inclusion of carbon-neutral fuels. The EU and the US have agreed to begin talks on including critical minerals processed in the EU as trade-friendly material that would qualify for the US EV tax credit as part of the Inflation Reduction Act, which could broaden the subsidy base. Eyes are also on the imminent release by the US Treasury of detailed criteria to qualify for the full $7,500 tax credit, which will determine if effective consumer subsidies are higher or lower than in 2022. In China, the government has repeatedly touted consumption as a pillar for economic recovery, and any major policy measure could be a significant boost.
Key Indicators
Notes
Historical lithium carbonate CIF Asia prices refer to Benchmark Mineral Intelligence's assessments. Historical cobalt metal prices refer to the London Metal Exchange's cobalt cash prices; historical refined cobalt supply figures draw partly on the work of the Cobalt Institute.
S&P Global Commodity Insights and S&P Global Market Intelligence are owned by S&P Global Inc.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.