Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Blog — 15 Jul, 2020
Highlights
China's digital economy will reach $9.130 trillion (60 trillion Chinese yuan) by 2025, with the ICT sector bringing in $1.978 trillion (13 trillion Chinese yuan).
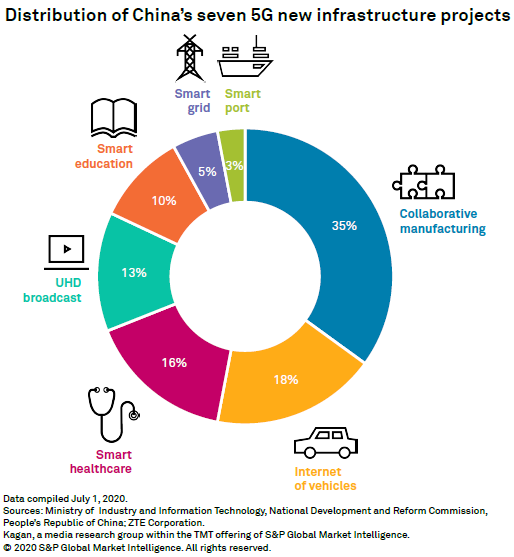
Collaborative manufacturing and internet of vehicles currently have the most established 5G ecosystem, forming 35% and 18%, respectively, of all 5G initiatives across China.
"New infrastructure" and "digital transformation" have become buzzwords in the mobile industry, especially with the advent of 5G, according to panelists at the New Infrastructure and Business Digitalization Forum at GSMA Thrive held June 30.
While MWC Shanghai last year focused on preparations for 5G, its online event this year titled GSMA Thrive set its eye on the digital transformation that the mobile industry needs to achieve to meet the new requirements and unlock the potential of 5G to transform numerous industries.
Moving beyond connectivity
According to panelists in the forum, China's digital economy will reach $9.130 trillion (60 trillion Chinese yuan) by 2025, with the ICT sector bringing in $1.978 trillion (13 trillion Chinese yuan). At the center of this path toward a digital economy is 5G.
"5G significantly improves the experience of connectivity, expanding 4G's people-centered connections to a full range of scenarios that span not only smartphones," said Gan Bin, chief marketing officer for wireless network solutions at Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.
Chengzhi Yu, deputy general manager of government and enterprise service development at China Mobile Ltd. agreed and said that "the 5G era is not just an era of connectivity but an era of empowering industries." According to Yu, the expanding role of 5G entails the development of new infrastructure that is better than the current ones we have for 4G and earlier networks. This new infrastructure, however, is not meant to replace existing infrastructure but augment it as "5G+4G."
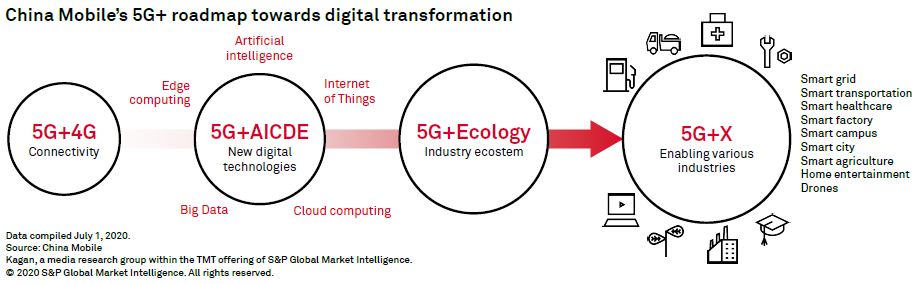
Experts in the forum argued this new infrastructure needs to be virtual, intelligent and cloud-based. It should blur the lines between the physical and online world by using intelligent applications power by cloud networks to deliver solutions to real-life problems. To achieve these requirements, 5G should be combined with new digital technologies, specifically artificial intelligence, internet of things, cloud computing, big data and edge computing, which Yu collectively called "5G+AICDE."
5G on its own will provide the foundation of virtual new infrastructure as the latest generation of wireless technology. 5G's high data capacity and massive connectivity features will trigger an explosion of data, opening opportunities for artificial intelligence and big data applications. Gan mentioned 5G could potentially add $1 trillion to China's AI industry by 2025.
Cloud computing is part of the ongoing trend of software-defined networks. When asked about its main advantage, speakers in the summit had one word to say: agility. Unlike physical infrastructure that was too rigid, software-defined networks provides operators the ability to easily and swiftly customize networks to fit the differing requirements of various 5G uses cases.
Panelists also said 5G needs edge computing for three reasons. First, it will help deliver 5G's promise of ultra-low latency by bringing network traffic closer to the end user and reducing the distance that data needs to travel. Second, it frees up backbone network resources for high-bandwidth 5G applications such as video streaming. Lastly, it allows operators to process data locally and introduce custom security requirements for various 5G use cases.
Most in the conference believed new infrastructure should be open sourced, or disaggregated into numerous vendors that build interoperable platforms. Open sourcing will allow for easy customization of networks while keeping costs low. Telefónica SA in Peru, Rakuten Inc. in Japan and Reliance Jio Infocomm Ltd. in India are some operators that have jumped into open sourcing for their mobile infrastructures.
Collaboration toward a digital economy
Open sourcing will eventually lead to the cultivation of a 5G ecosystem, or "5G+Ecology" as called by Yu, both downstream and upstream in the supply chain with operators as the focal point.
On the supply side, panelists said that better coordination among operators, equipment and device manufacturers and government regulators is necessary to deliver various 5G use cases. While enhanced mobile broadband and fixed wireless access still form the bulk of current 5G applications, industrial application will soon start increasing so operators and vendors alike should share experiences and capabilities to create good industrial 5G solutions.
Yu asserted that a similar level of cooperation is need on the demand side. According to him, mobile operators and vendors should identify the demands and requirements of various industries and jointly develop new solutions and products in cooperation with them. "Only by deep cooperation with industrial partners can 5G become an accelerator for industrial transformation and development," Yu said.
In March, China's Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and National Development and Reform Commission promoted building new infrastructure across seven industries to form the foundations of China's digital economy. These seven new infrastructure projects include: (1) the construction of a 5G smart medical system for major public health emergencies, (2) building 5G virtual private networks for collaborative manufacturing, (3) implementing the large-scale application of 5G smart grids, (4) large-scale application of cellular vehicle-to-everything Internet of vehicles, (5) application of 5G on smart education, (6) construction of 5G smart port systems and (7) construction of 5G, 4K or 8K ultra-high definition broadcasting systems.
According to the panelists, collaborative manufacturing and internet of vehicles currently have the most established 5G ecosystem, forming 35% and 18%, respectively, of all 5G initiatives across China. They also noted the current pandemic highlighted the importance of integrating 5G with smart education and smart healthcare.
In our recent article about China's 5G solutions in fighting the coronavirus pandemic, we saw real-life examples of 5G smart healthcare, ranging from thermal imaging and disinfecting 5G robots to remote 5G operation and COVID-19 diagnosis, as well as 5G UHD broadcast.
The close cooperation among mobile operators China Mobile, China Unicom (Hong Kong) Ltd. and China Telecom Corp. Ltd., technology vendors Huawei and ZTE Corp. and industry verticals Tencent Holdings Ltd. and China Central Television in these examples certified Yu's argument that a healthy ecosystem of collaboration is necessary for enabling digital transformation.
"5G is not just for operators but also for thousands of industries. Let us jointly create a new era of digital economy and build a new future of industrial development together," said Yu.
Wireless Investor is a regular feature from Kagan, a media market research group within S&P Global Market Intelligence's TMT offering, providing exclusive research and commentary.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
Webinar
Blog
