Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Research — 22 Aug, 2024
By Alexander Johnston and Melissa Incera
The past month has brought an explosion of new large language models from OpenAI LLC, Mistral AI SAS, Alphabet Inc.'s Google, Runway AI Inc. and Meta Platforms Inc., among others, alongside a demo of Apple Inc.'s 4M model. In particular, Meta has drawn significant attention with Llama 3.1, its 405 billion-parameter flagship open-source release that is said to have performance comparable with leading closed-source models such as GPT-4 Omni and Claude 3.5 Sonnet. This report also examines other notable product and funding announcements over the past few weeks, including investment rounds by Cohere Inc. and Vectara Inc., and OpenAI's acquisition of Multi Software Co., as well as updates on the politics of AI.

The debate between open-source and closed-source large language models has been influenced by the dominance of leading frontier models, which are typically closed. However, with the release of Llama 3.1 405B, the gap between open and closed LLMs seems to have narrowed, providing organizations with more control over their models. Meta is not the only player in the "open" AI space; Mistral unveiled its new flagship model, Large 2, just a day later, and Google released Gemma 2 shortly before. None of Meta's Llama 3.1 405B, Mistral's Large 2 or Google's Gemma 2 is open source in the purest sense, as Large 2, for example, requires a separate license for commercial use. However, these models are open weight, allowing developers to access the pretrained parameters. This enables organizations to run models locally on their own hardware, gain better insight into model decision-making and customize models with less reliance on third parties.

Product releases and updates
OpenAI announced GPT-4o mini, a smaller and supposedly more cost-efficient model than flagship GPT-4o. The company emphasizes the model's performance in mathematical reasoning and coding, as well as its ability to help reduce costs per call. OpenAI suggests the cost of using GPT-4o mini is more than 60% cheaper than GPT-3.5 Turbo.
A Mistral AI and NVIDIA Corp. partnership has brought us Mistral NeMo 12B. The model is available under a permissive license, and has a 128K context length, which allows the model to process high volumes of text relative to competing models. The model will be available as a packaged microservice via NVIDIA Inference Microservices.
Mistral also announced Large 2, a 123 billion-parameter model that also has a 128K context window. Large 2 outperforms the previous flagship, Mistral Large, in coding tasks and boasts enhanced instruction handling. According to the startup, Large 2 delivers superior performance relative to its cost than competing models.
LLM evaluator Patronus AI Inc. open-sourced a model, Lynx, designed to detect hallucinations. Lynx is a fine-tuned Llama 3 model designed to check and catch errors in LLM responses. Patronus AI suggests it outperforms other open-source models applied to the same task, as well as GPT-4.
Google released 9 billion- and 27 billion-parameter Gemma 2 models. These models are both smaller than many leading foundation models but have a permissive license allowing fine-tuning, redistribution and commercial use. The models are available through the Google AI Studio, a developer platform built around its generative AI models.
Runway announced Gen 3 Alpha, a video-generation model that the startup suggests offers improvements in sharpness and depicting motion. The company indicates that its development road map will provide more controls to tailor videos, and a new set of safeguards.
Meta's Llama 3.1 saw a major update with a new 405 billion-parameter version coming online, joining the 8 billion and 70 billion variants introduced in April. The model launched with support for English, Portuguese, Spanish, Italian, German, French, Hindi and Thai, with its multilingual capabilities also now extended to the smaller previous versions. In addition, as with Mistral's new models, the announced context window of 128,000 tokens has generated interest.
Meta also introduced Meta Large Language Model Compiler, a set of pre-trained models leveraging foundation model Code Llama that can be applied to compiler optimization. Compiler optimization is important in improving the performance of compiled code — ensuring code can run faster and use fewer resources. The LLM compiler was made available on Hugging Face.
Another project made available on Hugging Face Inc. over the last few weeks is a demo of Apple's 4M model. 4M: Massively Multimodal Masked Modeling is a research project that Apple announced in December 2023, developed alongside the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, an any-to-any framework for generating content across different content types. The demo showcases the ability to provide an RGB image input and for the model to predict metadata, object depth and captions, among other features.
Adobe Inc. has expanded its AI-powered Firefly tools for Photoshop and Illustrator, allowing users to generate images and textures with simple prompts. The updates aim to boost creativity and efficiency for designers. It is also offering generative credits to Creative Cloud subscribers to incentivize use. Illustrator also includes new non-AI features like dimension measurement and logo mockup tools.
Funding & M&A
In late June, OpenAI acquired Multi Software, a video collaboration platform for peer programming, in its third publicly announced acquisition so far this year. Deal details were not disclosed, although Multi Software's five employees will join OpenAI.
Cohere formally announced its $500 million series D. The foundation model company, which centers its offering on enterprise search, includes AMD Ventures, Cisco Investments, Fujitsu Limited, NVIDIA and Salesforce Ventures among its investors. The startup's post-money valuation is $5.5 billion.
Harvey, an AI-powered legal assistant, has secured $100 million in funding to expand its platform at a $1.5 billion valuation. Investors include Kleiner Perkins, Sequoia Capital, SV Angel and OpenAI (which is also an important technology partner for the company). The startup plans to invest in training domain-specific models and team growth to enhance its legal research and document drafting capabilities.
Anthropic PBC and Menlo Ventures have teamed up to create a $100 million Anthology Fund to invest in startups using Anthropic models. Startups are granted $25,000 in credits to access Anthropic models, and investment starts at $100,000.
Vectara, a generative AI startup that offers "retrieval-augmented generation as a service" announced a $25 million series A round. This builds on the $28.5 million seed the startup announced in 2022, led by Race Capital. Its series A was led by FPV Ventures and saw the return of key backers such as Race.
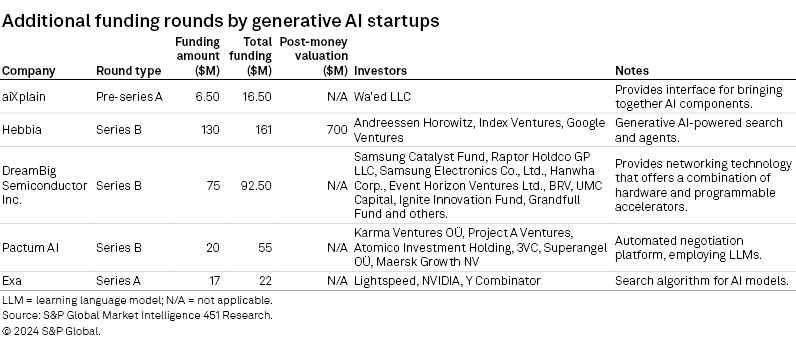
Politics & Regulations
The clock has started to tick on AI developers having to respond to the EU AI Act's provisions, with the final text of the AI Act published in the Official Journal — the publication that contains official information on the EU's acts, making it binding. The law will officially come into force at the start of August, two years after which all provisions will be fully applicable. The European Data Protection Board has established the AI Auditing project, which is designed to help ensure models align with General Data Protection Regulation, and built a framework for supervision to assess accordance with the EU AI Act.
A draft artificial intelligence bill is under review in Turkey. The first step in establishing a distinct law or regulation for AI in Turkey, the bill centers on the need for risk assessments during model development and is perceived to be designed to align with the EU AI Act in classifying "high risk" systems.
Regulation of AI companies featured in the King's Speech — a speech written by the UK government and delivered at the opening of Parliament. The speech showcases upcoming bills expected to be introduced to Parliament and represents the direction of travel for the incoming Labour government.
Meta is denying access to its generative AI tools in Brazil while it attempts to engage with Brazil's National Data Protection Authority around the use of data for training. Brazil's ANPD had rejected an update of privacy terms by Meta, which provided permission to use public social media content for model training, suggesting that these changes did not align with Brazil's General Personal Data Protection Law.
Microsoft proactively gave up its observer seat on OpenAI's board, a spot it had pushed for following the failed ousting of Sam Altman as CEO in November 2023. The move is an effort to get ahead of antitrust actions that have sprouted in the UK and US, although the company claims to be giving up the spot, given its regained confidence in the company's direction. Relatedly, this was followed by news of a formal merger inquiry from the UK's Competition and Markets Authority into Microsoft's hiring of Inflection's AI team earlier this year.
451 Research is a technology research group within S&P Global Market Intelligence. For more about the group, please refer to the 451 Research overview and contact page. This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.