Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Blog — 21 Sep, 2022
By Sidiq Dawuda and Nursultan Turdubaev
This article is written and published by S&P Global Market Intelligence; a division independent from S&P Global Ratings. S&P Global Ratings does not contribute to or participate in the creation of credit scores generated by S&P Global Market Intelligence. Lowercase nomenclature is used to differentiate S&P Global Market Intelligence PD credit model scores from the credit ratings issued by S&P Global Ratings.
Bankruptcy Summary:
Business Description:
Christopher & Banks Corporation, founded in 1956 and headquartered in Minnesota, operated as a specialty retailer of private-brand women’s apparel and accessories in the United States. The company designed and sold women’s apparel and accessories to a mature client base.
As of September 11, 2020, the company operated 452 stores in 44 states. It also operated christopherandbanks.com, an e-commerce website for its Christopher & Banks and CJ Banks brands. The company was formerly known as Braun’s Fashions Corporation and changed its name to Christopher & Banks Corporation in July 2000.
Fundamental Probability of Default Analysis
Probability of Default (PD) Model Fundamentals is a statistical model that produces a PD, that is trained using default indicators and incorporates both financial and business risk. Available via our desktop solution Credit Analytics, API, and data feed, PD Model Fundamentals (PDFN) includes a pre-scored universe of more than nine million public and private companies extracted from the S&P Global Market Intelligence database, representing 99% of global market capitalization.
The PDFN score showed a distressed outlook for Christopher & Banks even before the pandemic at above 30% (implied credit score of ‘ccc-‘) compared to the Country/Industry median of 3% (see Figure 1).[1] That is largely due to Christopher & Banks becoming unprofitable a few years before the pandemic, and the crisis exacerbating its already weakened position.
Figure 1: PDFN Score Escalation (FY2015-FY2020)
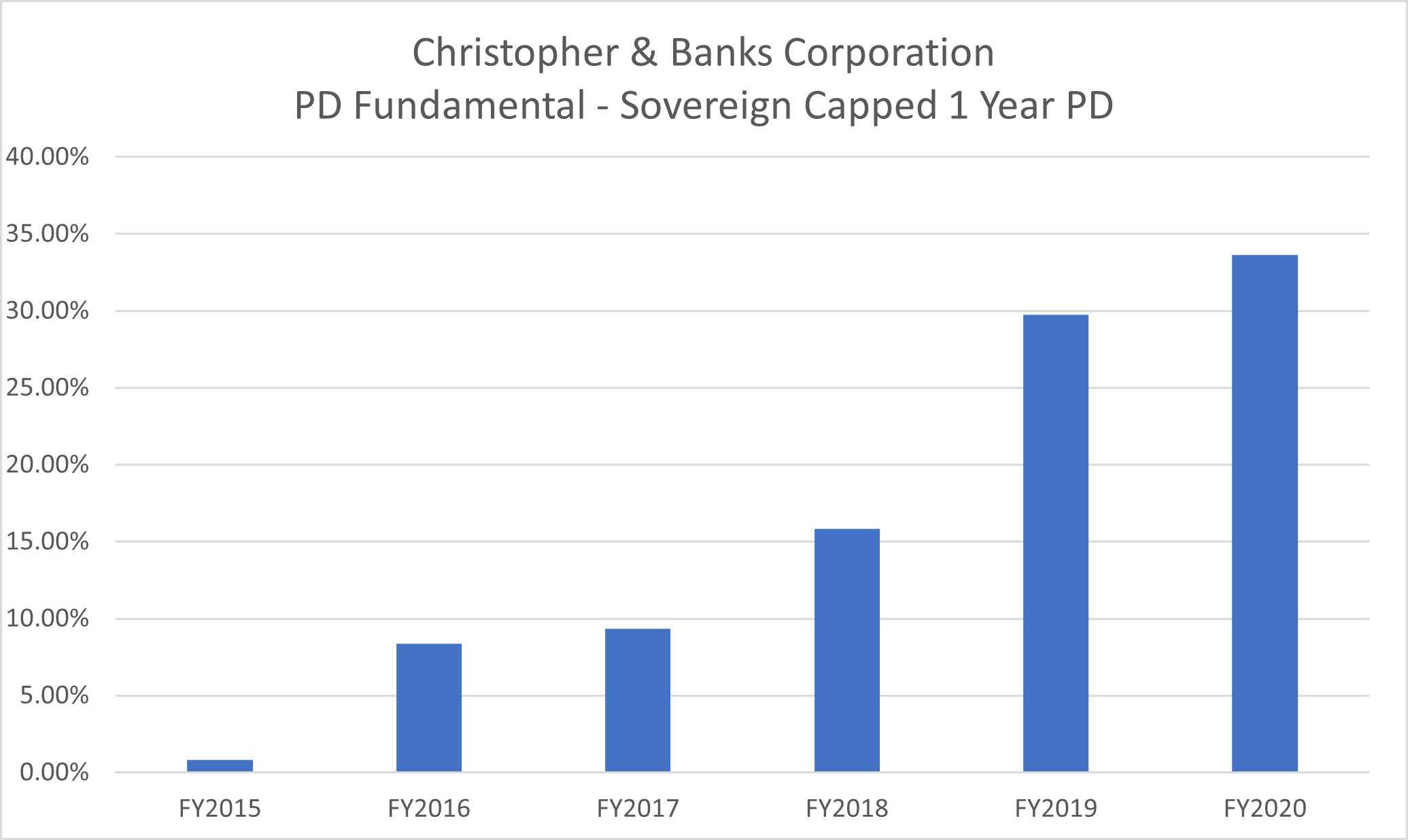
Source: S&P Global Market Intelligence, as of August 23, 2022. For illustrative purposes only
The PDFN score rapidly jumped from 0.8% to 8.3% in 2016 due to a disappointing 2015. Christopher & Banks made a net loss of $49.1 million compared to a net profit of $47.1 million) for the previous year.
Figure 2: Revenues and Net Income
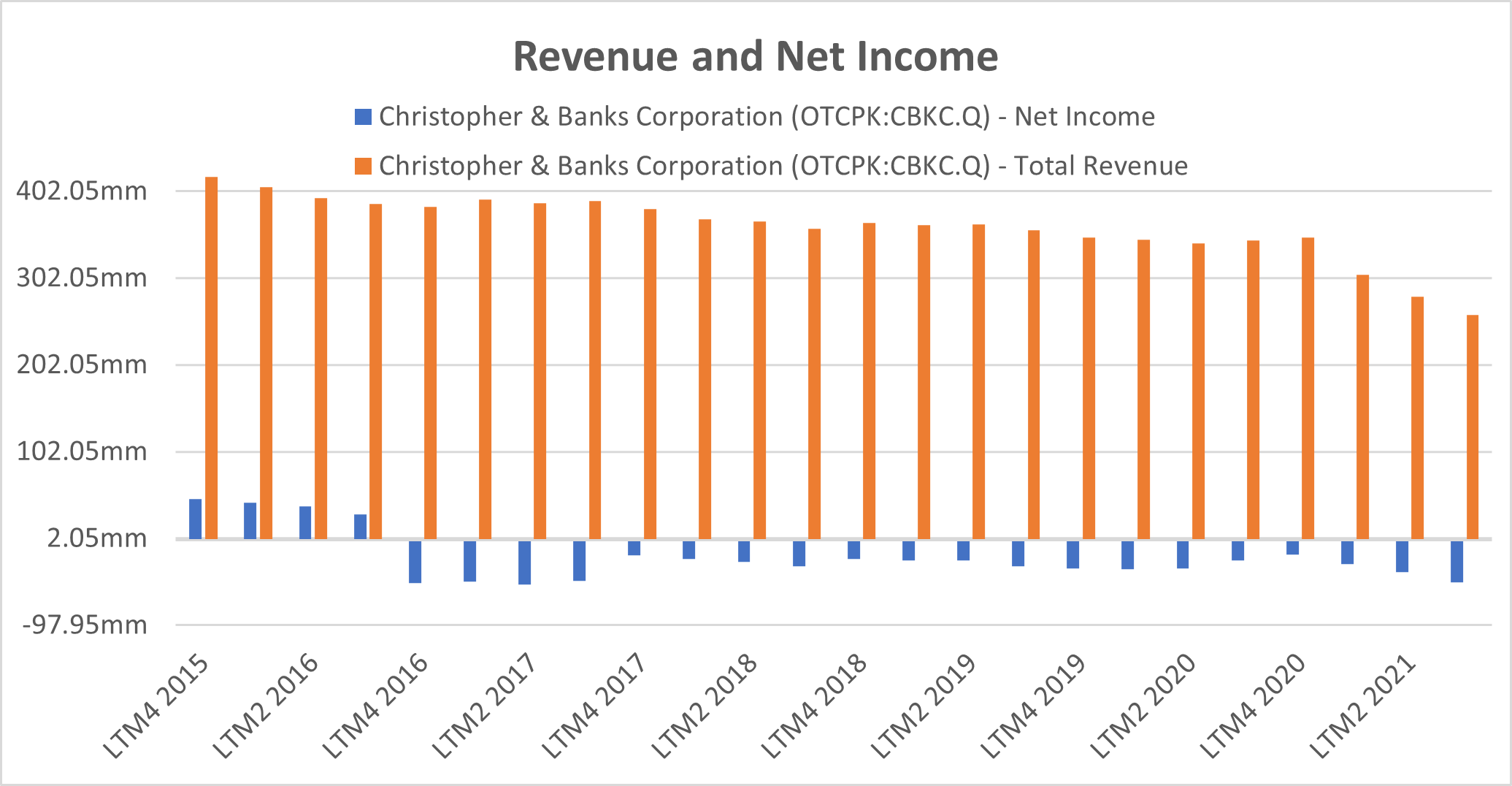
Source: S&P Global Market Intelligence, as of August 23, 2022. For illustrative purposes only
Lower sales, driven by a competitive retail-apparel environment, and operating inefficiency associated with higher costs turned a highly profitable firm into a loss-making machine.
Christopher & Banks showed weaker financials every year, with decreasing sales and consistent losses with an average loss of $31 million a year, implying higher business risk and a higher PD, represented by the increasing PDFN score.
As the COVID-19 pandemic swept across the world at the beginning of 2020, many high-street retail companies found themselves vulnerable. Forced to close its stores, Christopher & Banks’s revenues plummeted.
After the company announced its earnings for the first quarter of 2020, the PDFN score drastically jumped from 33.62% to 63.43% (implied credit score of ‘cc’).
Figure 3: PD Fundamental Escalation

Source: S&P Global Market Intelligence, as of August 23, 2022. For illustrative purposes only
The most significant factors impacting the PD were total equity, profitability (EBIT margin), and liquidity (Cash/Current Liabilities), revealing that the company had high business and financial risk factors.
As the pandemic forced the company to halt operations, the company earnings dropped by more than 50% between FQ2020 and FQ2021, going from $88M to $40M, with a subsequent decline of 41%, ultimately ending with a negative profit margin of -18.11%. As revenue growth for Christopher & Banks slowed, the company became increasingly leveraged.
If you would like to learn how you can track early-warning signals of credit quality deterioration, contact us here
[1] S&P Global Ratings does not contribute or participate in the creation of credit scores generated by S&P Global Market Intelligence. Lowercase nomenclature is used to differentiation PD and credit model scores from the credit ratings issued by S&P Global Ratings.