Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Research — 16 Aug, 2022
By Monica Hlinka and Russell Ernst
Learning is a perpetual process, and this is true for individuals new to the utility sector and those with established ties to it. Utility issues are dynamic, and stakeholders can gain valuable insight through exposure to a variety of informative research pieces.
Regulatory Research Associates, a group within S&P Global Commodity Insights, has published extensively on issues related to state-level electric, natural gas and water utility regulation as well as key aspects of the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission's oversight of interstate electric transmission assets and gas pipelines and wholesale market functions.
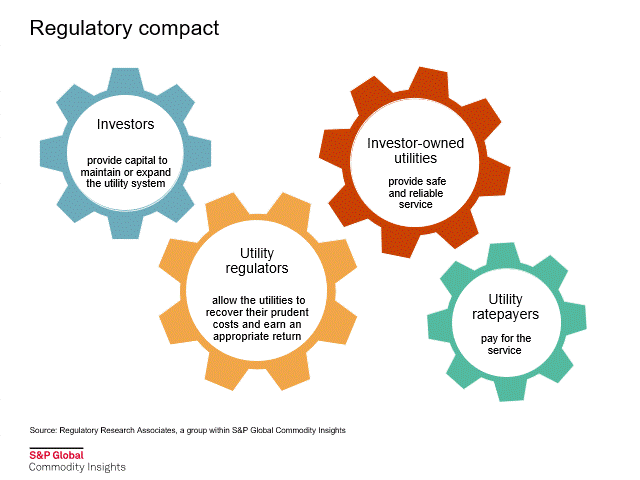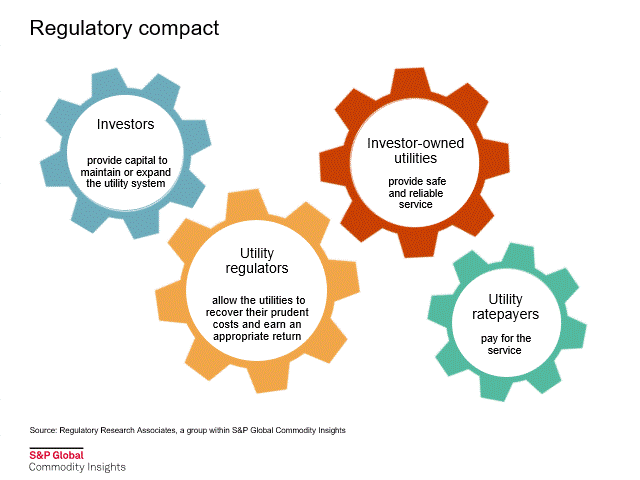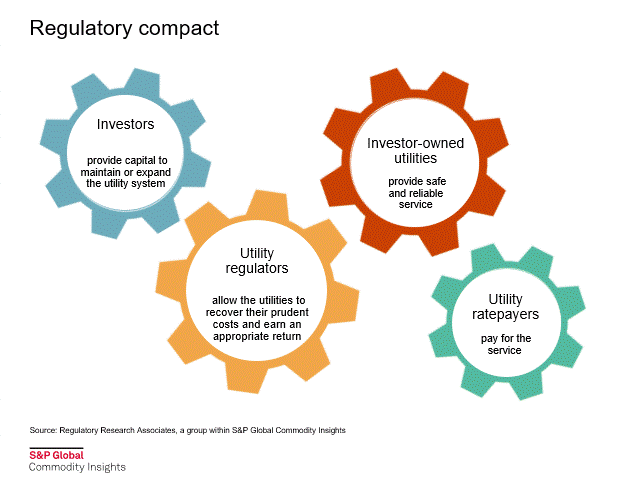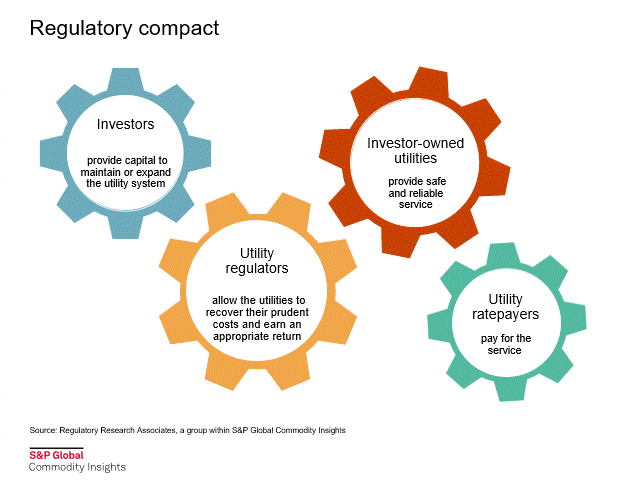
Rate case process
Utilities are natural monopolies that have very significant capital costs and high barriers to entry. As such, they do not operate without ample oversight. State utility commissions were created to regulate the rates charged by the utilities.
In a recent report, "The rate case process: a conduit to enlightenment," RRA discusses the key aspects of a typical rate proceeding, including the determination of an appropriate return on equity.
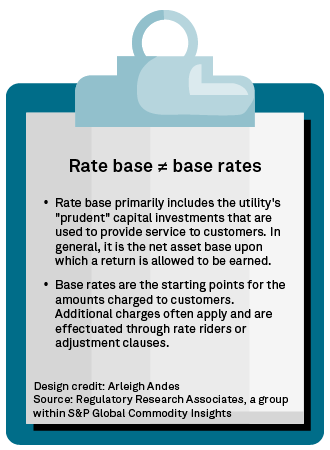
Rate base
One of the most misunderstood concepts in the utility industry is rate base, a term unique to the utility realm. Rate base is essentially the company's prudent capital investment as determined by the applicable regulatory authorities, net of accumulated depreciation and other adjustments. Rate base is the net asset base of an electric, gas or water utility upon which an allowed rate of return, usually the company's weighted-average cost of capital, is applied. The rate base value is a key variable that regulatory bodies use in a rate case to determine a utility's revenue requirement.
RRA's recent report "Rate base: How would you rate your knowledge of this utility industry fundamental?" is an excellent resource for anyone interested in learning more about the mechanics of the rate base calculation.
FERC
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission plays a critical role in the nation's energy industry through economic regulation of the electric power and gas sectors, ensuring companies in these sectors have a reasonable opportunity to earn a fair return on their investments while providing safe and reliable service at just and reasonable rates to their customers.
Climate change and the clean energy transition are presenting regulated electric and gas companies with unprecedented challenges and growing regulatory uncertainty. Evolving state and federal policies and transformational changes in the nation's generation portfolio mix are introducing new complexities and testing current regulatory frameworks, including the challenge of integrating an increasing amount of non-traditional resources into the electric distribution and transmission system while maintaining reliability and grid security.
In light of the many challenges and uncertainties in the current regulatory environment, RRA examines FERC's important role in a new report, "An Overview of FERC Regulation." Among other things, the report analyzes FERC's functions and responsibilities, the role of federal and state regulators, FERC's electric and gas industry jurisdiction, the commission's processes and ways to access public information about commission proceedings.
Water
The water utility sector is experiencing growth via municipal acquisitions and is seeing heightened interest from environmental, social and governance investors. Water and wastewater systems have been ripe for consolidation for decades due to a lack of investment.
In a recent report, "Intro to Water Utilities — Current Trends & Growth Drivers," RRA examines how the prevalence of legislation enabling acquirers to utilize market value for municipal system transactions has served as the catalyst to consolidate this fragmented sector and inject needed investment into the country's deteriorating water infrastructure.
Settlements
There are often clear incentives for utilities and parties with vested interests in the utility sector to embrace compromise. Utilities often obtain settlement benefits in the form of key utility policy objectives and more favorable rate case outcomes than would otherwise be achievable. Although black box settlements are often used to resolve all outstanding matters in rate cases, settlements can also be focused on a narrow set of issues. Partial settlements can be used to reduce the number of issues that need to be discussed at a hearing and ultimately adjudicated by the commission.
Deferrals
Utility accounting deferrals are an interim ratemaking technique designed to help reduce "regulatory lag." Allowing the utility to defer recovery of increases in specific costs until the commission can address them at a later date leaves the company's earnings unaffected by the increased costs, as the increases are offset from an accounting perspective by the creation of a regulatory asset that would likely be recovered through customer rates in the future.
Once the commission determines that the costs were prudently incurred and are "extraordinary" in nature, recovery will generally take place over a multiyear period and the commission may or may not permit the utility to earn a return on the unamortized balance during the recovery period. However, these deferrals do nothing to mitigate any cash flow constraints that might exist.
Intervenors
Intervenors play an important role in utility regulatory proceedings and serve to advance the interests of a variety of constituents. Regardless of whether they are involved in base rate cases, plant preapproval proceedings, service quality review dockets or other matters, these parties ensure that the commissions hear from a broad group of stakeholders.
While some may have interests aligned with utilities, an intervenor's participation in a proceeding will often expose areas of concern related to customer service and affordability.
Adjustment clauses
Adjustment clauses facilitate the timely recovery of certain utility costs, including those that are rising and volatile. A defining characteristic of an adjustment clause is that it effectively shifts the risk associated with the recovery of an expense from shareholders to customers. If the clause operates as designed, the company can change its rates to recover its costs on a current basis without any negative effect on the bottom line and without the expense and delay accompanying a rate case filing.
In a recent report, "Adjustment clauses: a state by state overview," RRA highlighted the adjustment clauses that are more prevalent than others.
Frequently asked questions
Utility regulation can be quite confusing. Terminology that is unique to the utility space often causes anxiety for newcomers to the industry and even those that have devoted a considerable amount of their careers to following the industry.
In a recent report, "Frequently Asked Questions," RRA discusses some of the more noteworthy issues causing confusion among industry practitioners.
Regulatory Research Associates is a group within S&P Global Commodity Insights.
Lillian Federico, Lisa Fontanella, Dan Lowrey, Jason Lehmann, Brian Collins, Jim Davis, Jim O'Reilly and Heike Doerr contributed to this article.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
Like our content?