Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Language
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
S&P Global — 26 Jan, 2024 — Global
By S&P Global
Start every business day with our analyses of the most pressing developments affecting markets today, alongside a curated selection of our latest and most important insights on the global economy.
China’s Steel Exports Point to Underlying Issues
As exports of Chinese steel return to the high-water mark of 2015, it is tempting to believe that the Chinese steel industry is operating from a place of strength. But increasing exports of Chinese steel are partly a function of weakness in China’s domestic demand for steel due to significant ongoing shifts in property markets and infrastructure projects. Chinese steel manufacturers cannot afford to cut back further on production, so offering steel at lower prices to other countries may be the best path forward. Fortunately, the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) offers ready and sympathetic markets for Chinese steel in other countries.
Much of Chinese government debt exists at the local government level. Revenues for local governments in China have been impacted by a weaker property sector since land sales and taxes and fees related to new residential projects are a significant source of revenue for local governments. In response to concerns about excess local debt, the central government has directed 12 Chinese provinces and municipalities to downsize or halt some state-funded infrastructure projects. Infrastructure construction drives steel consumption. The slowing rate of growth in infrastructure spending is believed to be tied to lower steel demand in these 12 regions. The property and infrastructure sectors combined accounted for about 45%-50% of China's total steel consumption in 2023, down from about 55% in 2020, according to S&P Global Commodity Insights.
Normally, lower demand for steel would lead to lower levels of steel production. But, based on data from the China Iron and Steel Association and National Bureau of Statistics, China's crude steel output was up 16 million metric tons for 2023. The reason for the growth in steel output is that China’s many newly commissioned steelmaking facilities need to keep production high to keep production costs low and generate cash flows. Economies of scale for large steel production facilities only work if steel output remains high.
With lots of steel and reduced domestic demand, China’s steel manufacturers are looking overseas for customers. From January to November 2023, China’s net steel exports increased 35.6% year over year, according to China's General Administration of Customs. According to S&P Global Commodity Insights, high steel production in China and sluggish domestic demand can be expected to continue through 2024, which would benefit exporters.
Fortunately for these steel exporters, China’s investments in the BRI account for a significant share of China's steel exports. The top 10 countries that received the largest percentage of nonfinancial BRI investments from January to June 2023 were Singapore, Indonesia, Malaysia, the United Arab Emirates, Vietnam, Thailand, Laos, Kazakhstan, Cambodia and Russia, according to China's Ministry of Commerce. Many of these countries have also become leading customers for China’s steel exports. In 2023, China's steel exports to Laos grew 196.7%, while its exports to the UAE increased 72.6% and to Vietnam rose 57.2%. Because many BRI infrastructure projects are entrusted to Chinese firms, they often adhere to Chinese construction standards, making Chinese steel a natural fit.
Today is Friday, January 26, 2024, and here is today's essential intelligence.
Written by Nathan Hunt.
UK Economy Starts 2024 On Stronger Footing, But Red Sea Shipping Delays Drive Prices Higher
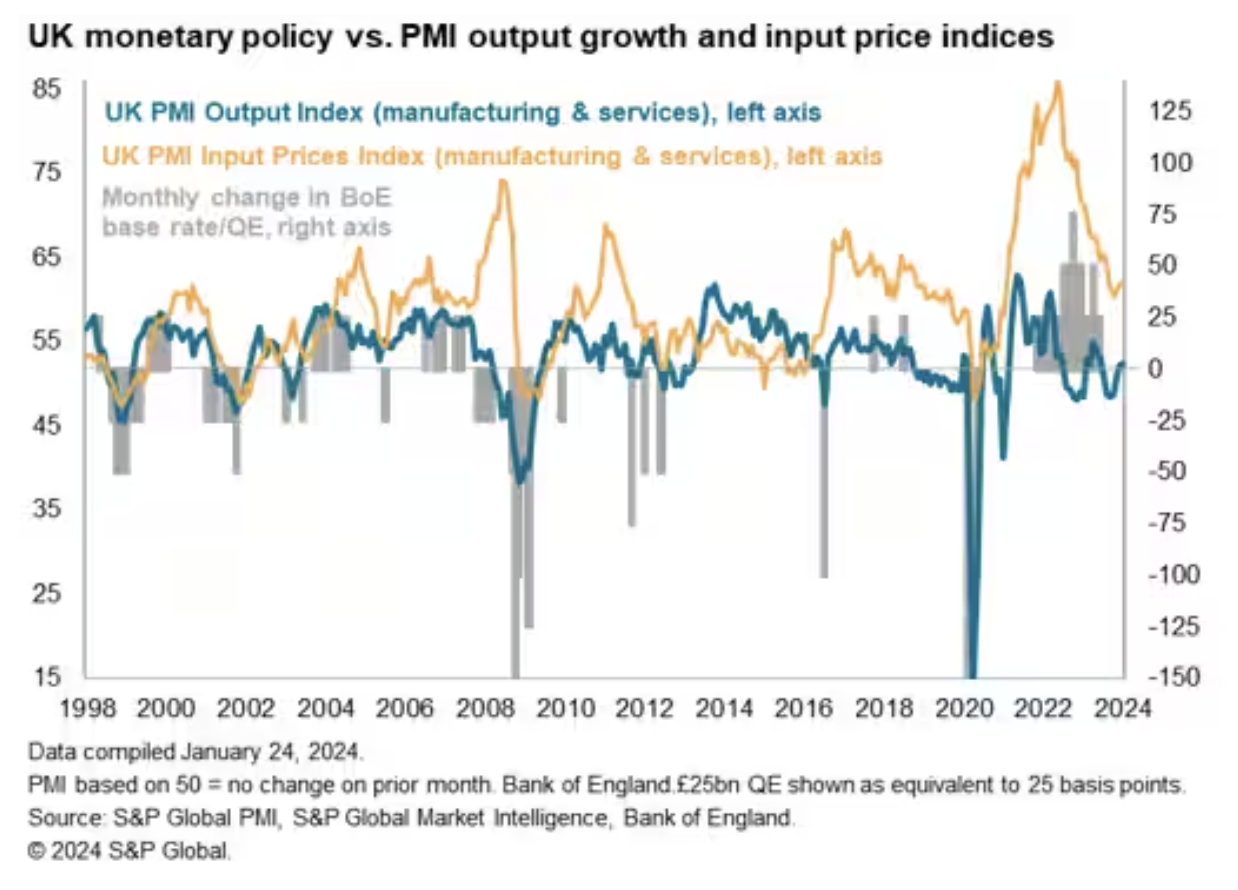
UK business activity growth accelerated for a third straight month in January, according to early PMI survey data, marking a promising start to the year. The survey data point to the economy growing at a quarterly rate of 0.2% after a flat fourth quarter, therefore skirting recession and showing signs of renewed momentum. Businesses have also become more optimistic about the year ahead, with confidence rebounding to its highest since last May. Business activity and confidence are being in part driven by hopes of faster economic growth in 2024, in turn linked to the prospect of falling inflation and commensurately lower interest rates.
—Read the article from S&P Global Market Intelligence
Access more insights on the global economy >
Japan Banking Outlook 2024: BOJ Hikes Will Widen Disparities
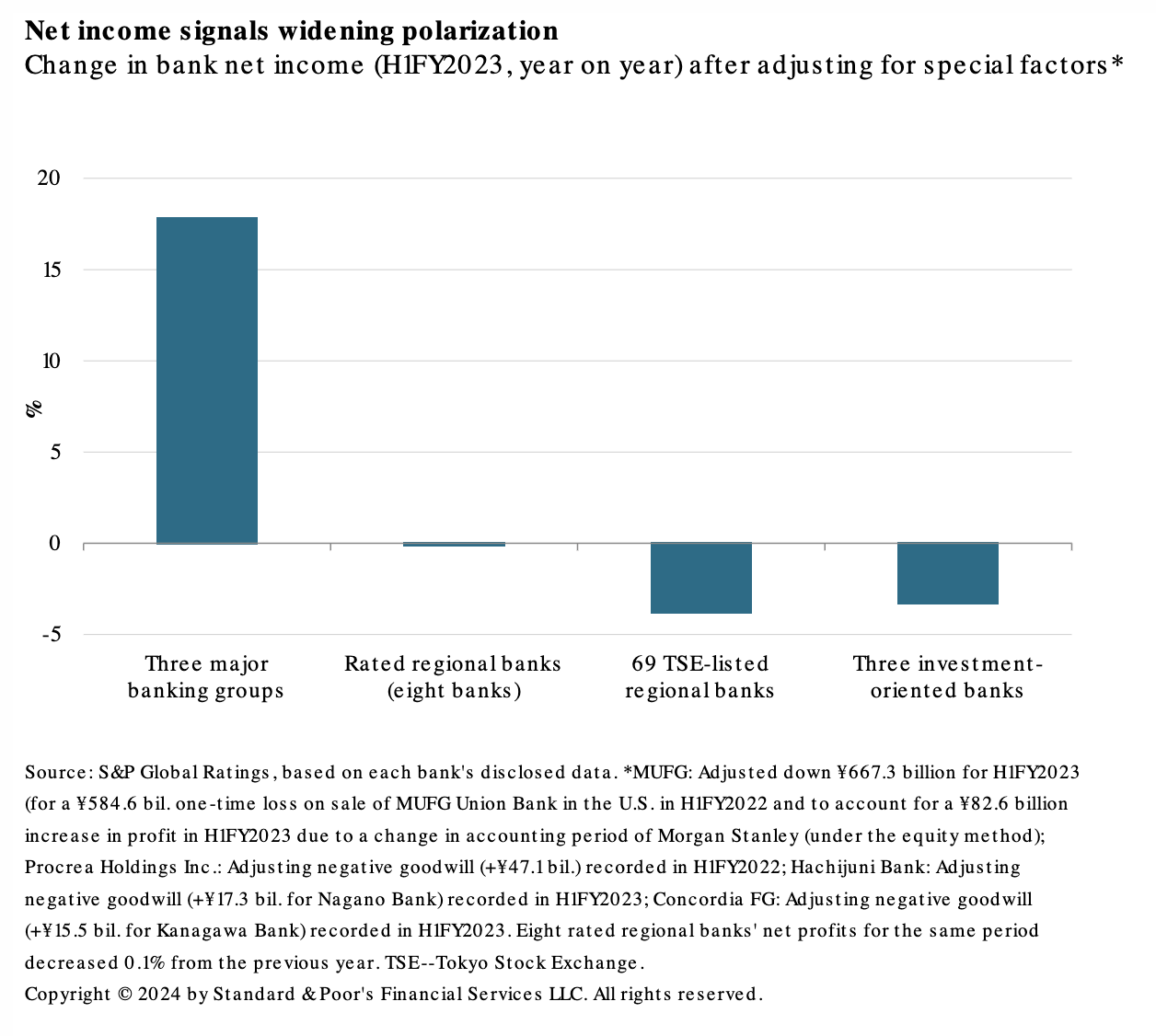
Rising interest rates will separate the strong from the weak. S&P Global Ratings anticipates Japan's short-term policy interest rate will increase gradually in 2024. It expects it to rise about 0.1 of a percentage point this year and about another 0.25 of a percentage point in 2025 from -0.1% now. S&P Global Ratings does not expect an accompanying sharp deceleration in economic growth, which is affected by changes in monetary policy.
—Read the report from S&P Global Ratings
Access more insights on capital markets >
US Nuclear Plants, Uranium Miners Prepare For Possible US Ban On Russian Uranium
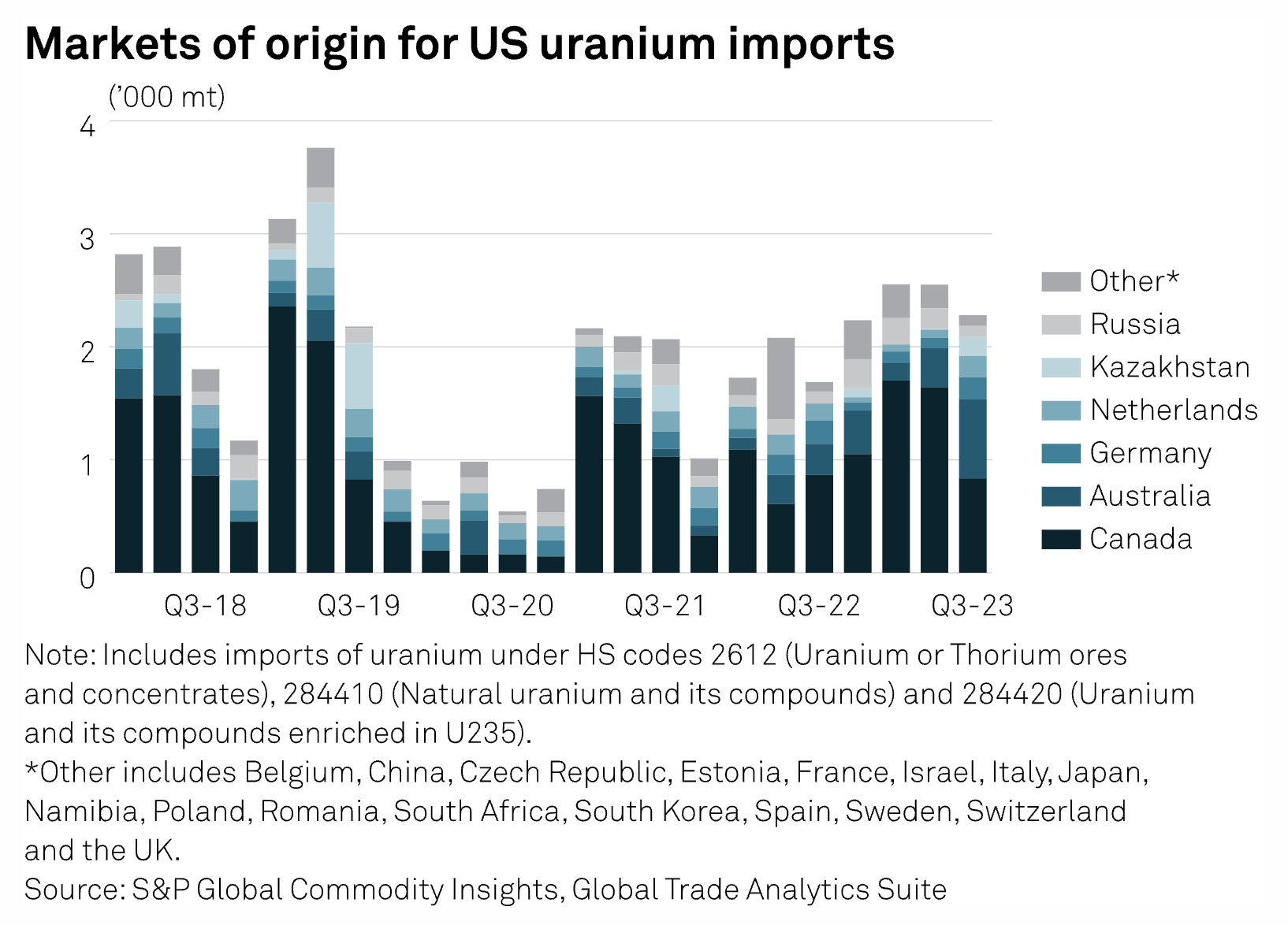
A bill in the US Congress to restrict imports of Russian uranium is stalled in the Senate, but uranium miners and nuclear power providers are already changing their buying habits, analysts told S&P Global Commodity Insights. The US Prohibiting Russian Uranium Imports Act, which passed the House on Dec. 11, has bipartisan support, but it has been held by Senator Ted Cruz, a Texas Republican, over unrelated matters.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on global trade >
California Vehicle Decarbonization With Hydrogen Faces Roadblocks
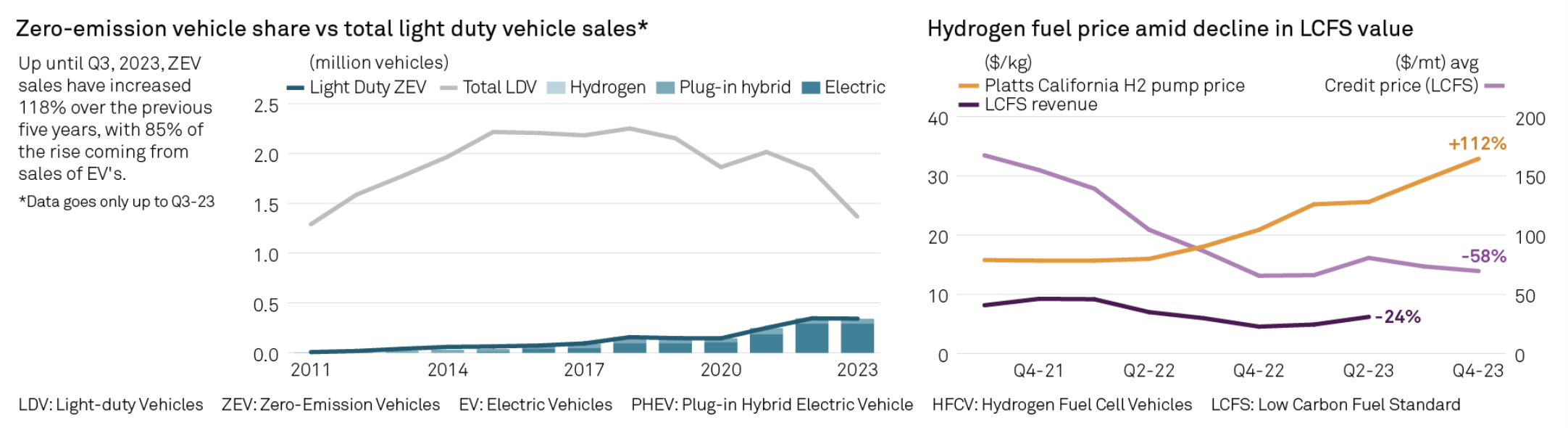
California has faced challenges in decarbonizing its transportation sector using hydrogen as a zero-emission vehicle (ZEV) fuel option. At the heart of it are a lack of reliable infrastructure and prolonged elevated hydrogen prices at fueling stations, according to an analysis by S&P Global. As part of the progress made, ZEV sales reflected 118% growth from 2018-2023, with electric vehicle sales making up most of the volume.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on sustainability >
US Public Power And Electric Cooperative Utilities 2024 Outlook: Mandates Rising Costs And Diminishing Affordability
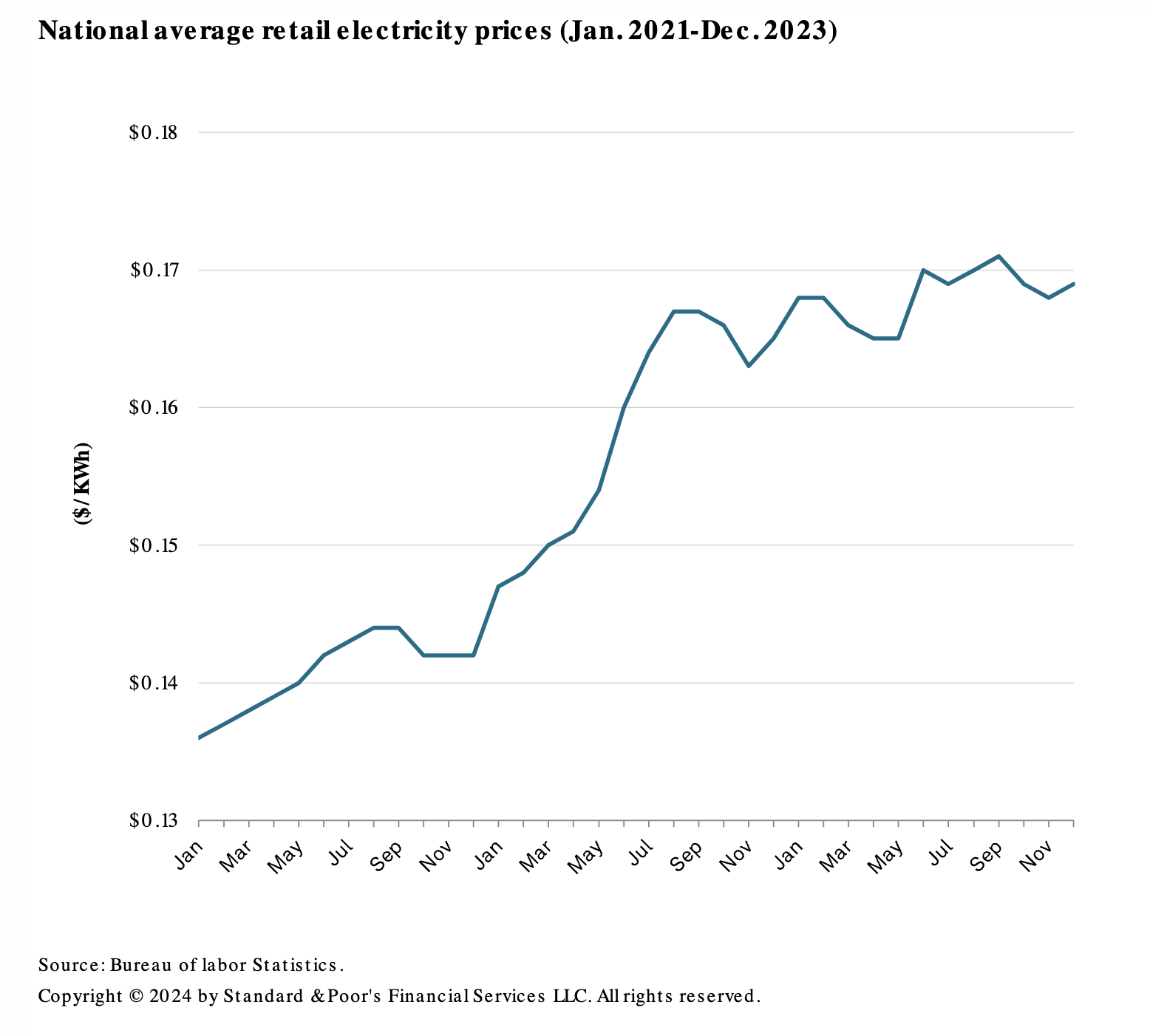
The financial performance of, and ratings on, US public power and electric cooperative utilities could weaken in 2024, owing to a confluence of inflation, reduced consumer wherewithal to pay utility bills, the sensitivity of rate-setting bodies to economic conditions and a developing trend of weakening financial margins. Exacerbating inflation-related affordability pressures are legislative and regulatory mandates that S&P Global Ratings expects will trigger substantial utility spending on clean generation resources and generation additions needed to support load growth from electrification directives. However, utilities could maintain credit quality if they're able to recover costs in a timely manner and at levels sufficient to preserve sound financial margins — commensurate with S&P Global Ratings’ existing ratings.
—Read the report from S&P Global Ratings
Access more insights on energy and commodities >
Tech Demand Indicator Rises To Near Two-Year High
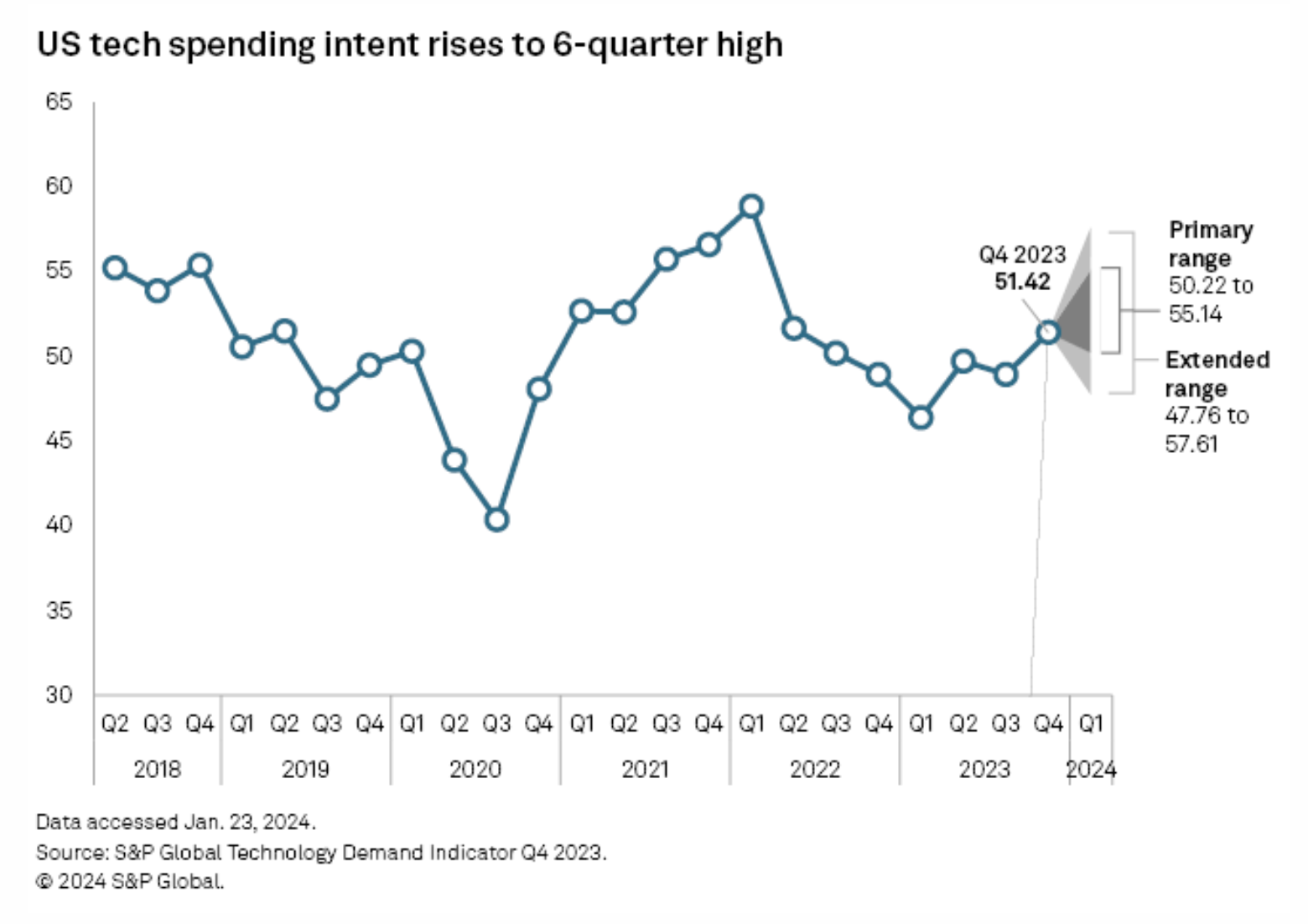
Consumers and corporations ended 2023 more willing to spend on technology as emerging tech such as generative AI and growing threats around cybersecurity pushed buyers to loosen their purse strings. In the fourth quarter of 2023, S&P Global's US Technology Demand Indicator (TDI) rose to the highest level seen since the second quarter of 2022, when central banks around the world began raising interest rates. The TDI is a survey-backed composite of US intent to spend on technology and typically predicts revenue performance for tech vendors by up to a few months.
—Read the article from S&P Global Market Intelligence
Content Type
Location
Language
