Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Language
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
S&P Global — 6 Sep, 2022 — Global
By S&P Global
Start every business day with our analyses of the most pressing developments affecting markets today, alongside a curated selection of our latest and most important insights on the global economy.
A Mixed Record on Carbon Capture
Countries around the world are looking to respond to the threat of climate change by decarbonizing their economies through a combination of renewable energy and carbon capture technology. However, a recent report has cast doubt on the effectiveness of existing carbon capture projects.
Carbon capture is intended either to intercept carbon dioxide directly from emissions streams or to pull carbon from the atmosphere using direct air capture, which accelerates the natural ability of certain minerals to absorb CO2 from the air. Once captured, carbon, typically in the form of CO2, can be sequestered underground or used for industrial purposes. For hard-to-decarbonize industries such as construction or steel, carbon capture and sequestration is essential for reaching net-zero goals. According to some industry groups, the world will need to remove 6 billion to 10 billion metric tons per year of CO2 by 2050 to meet Paris-aligned goals and limit temperature rise to 1.5 degrees C.
The U.S. Inflation Reduction Act supports carbon capture technology by providing subsidies of up to 70% for facilities that capture emissions. According to industry group the Carbon Capture Coalition, government incentives and backing could spur a 13-fold increase in carbon capture deployment by 2035. The act puts the U.S. firmly on the path of privately funded carbon capture, dependent for now on heavy government support.
"The Inflation Reduction Act that just passed the Senate is set to turbo-charge the market for CO2 removal technologies like Heirloom, with significant tax incentives unlike anything we've seen before," Alexa Dennett, head of marketing and communications at Heirloom, a direct air capture company, said to S&P Global Commodity Insights.
According to S&P Global Market Intelligence, the Biden administration is aiming for a 100% clean U.S. power grid by 2035. But a new report from the U.S. Energy Department suggests that this would require a large increase in generating capacity, in part because carbon removal technologies demand a great deal of energy. Advocates suggest that additional energy generation could be offset by cost savings. It will cost an estimated $1.6 trillion to decarbonize the U.S. power sector by 2035, but this could be reduced by $300 billion if some existing natural gas-fired plants are paired with carbon capture technology.
Despite the market interest in carbon capture technology companies and the new government incentives, a recent report by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis concluded that most existing carbon capture projects have failed or underperformed. Of the 13 carbon capture projects the report examined, seven performed below their stated capacities, two failed due to technical issues and one was suspended. But advocates say the technology used in carbon capture is still nascent and fast-developing, and that a study focused on older projects paints an inaccurate picture of the current state of the industry.
With credits now available through the Inflation Reduction Act for every ton of CO2 captured and stored, the economics of carbon capture have certainly changed. Now the market must wait to see if better economics improve the effectiveness of carbon capture technology.
Today is Tuesday, September 6, 2022, and here is today’s essential intelligence.
Written by Nathan Hunt.
Economic Research: U.S. Business Cycle Barometer: As Weakness Continues, Further Spread Would Mean Recession
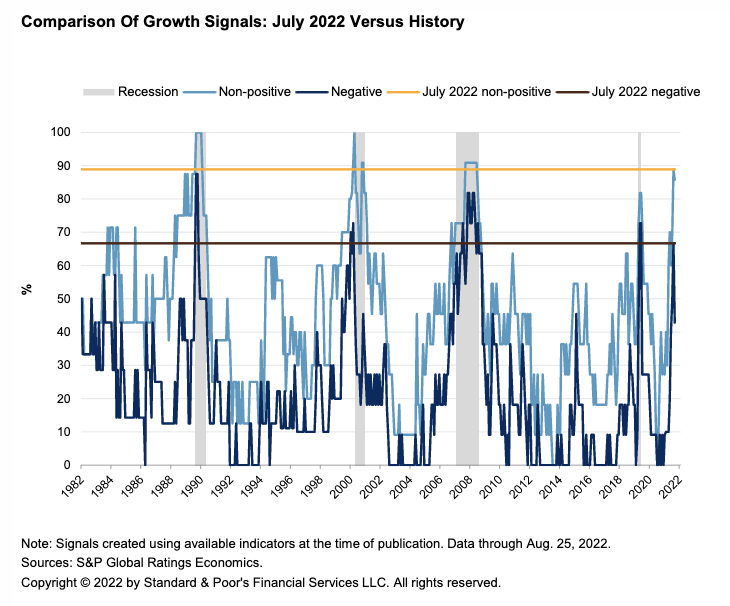
Although U.S. GDP contracted the past two quarters, current conditions indicate that a recession, as defined by the National Bureau of Economic Research, is not here yet — since the NBER's "dispersion" criterion has not been met. But with weakness continuing through August, S&P Global Ratings believes that the worst is not over. Indeed, its dashboard of leading indicators through July signals that U.S. economic momentum has continued to worsen — eight of the nine indicators it tracks sent negative or neutral signals on near-term growth prospects.
—Read the report from S&P Global Ratings
Access more insights on the global economy >
Semiconductors Ripe For Private Equity After CHIPS Act
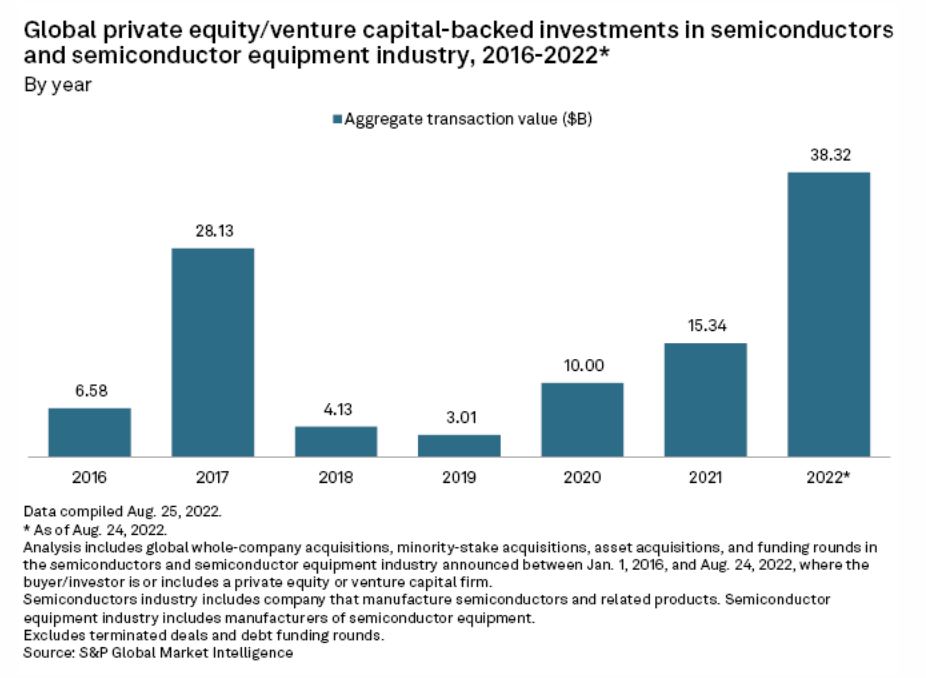
A U.S. effort to bolster domestic semiconductor manufacturing is likely to spur more private equity investment in the capital-intensive industry and the businesses that support it, industry sources told S&P Global Market Intelligence. The CHIPS Act signed into law Aug. 9 by President Joe Biden is expected to channel roughly $280 billion over the next decade into domestic semiconductor science and production, including $52 billion targeted at manufacturing and $200 billion for research. It creates a 25% tax credit for investment in advanced chipmaking facilities.
—Read the article from S&P Global Market Intelligence
Access more insights on capital markets >
Listen: EU Russian Oil Ban: How Are Fuel Oil Supply And Demand Fundamentals Shifting
EU sanctions on Russian fuel oil have dramatically altered supply flows for high sulfur material within Europe, and while there is some trading activity still in the Mediterranean basin, most Russian fuel oil is heading to Singapore and elsewhere in the East. While weaker demand has offset a lack of supply within Europe for now, market uncertainty remains high with the question of where Europe will get its imports from in the future open. In this episode of the Platts Oil Markets Podcast, S&P Global Commodity Insights editors Mary Tiernan and Chloe Davies discuss with John Morley sanctions and market dynamics for high sulfur fuel oil and VGO in Europe.
—Listen and subscribe to Oil Markets, a podcast from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on global trade >
ESG Regulatory Tracker — July 2022

The European Parliament voted on July 6 not to oppose including gas and nuclear in the EU green taxonomy, a framework for defining sustainable activities. The controversial proposal, which drew criticism from the EU’s expert group, was put forward by the European Commission, the EU’s executive arm, earlier in 2022.
—Read the article from S&P Global Sustainable1
South Korea Seeks More LPG To Spike Into LNG To Quell Shortage
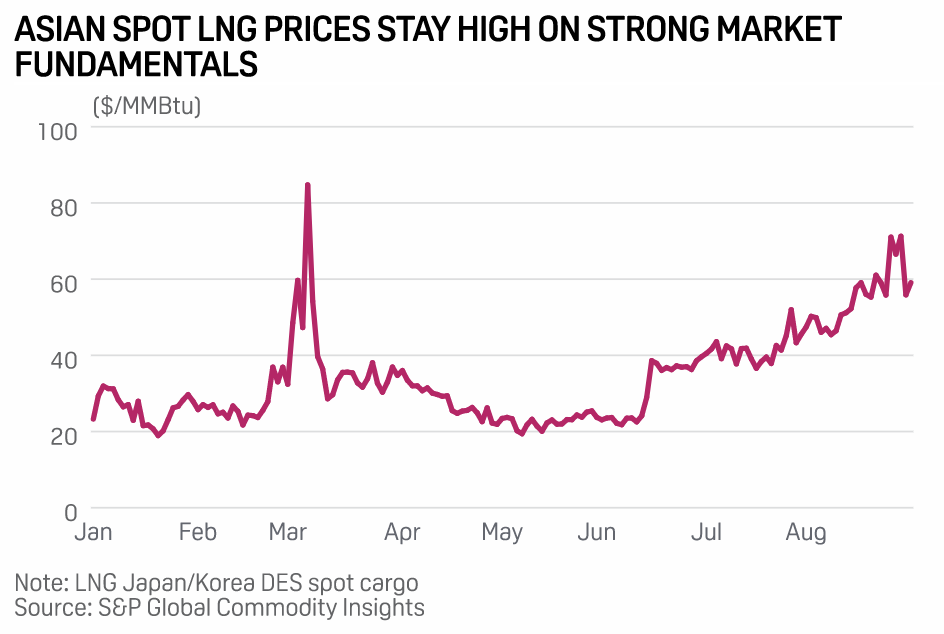
South Korea will likely seek more liquefied petroleum gas in the coming months to add into liquefied natural gas, to boost the calorific or heating value of regasified LNG for use in heavy industries and utilities, trade sources said. The move is prompted by a rise in LNG prices on strong demand from Europe and North Asian buyers gearing up for winter procurement amid limited supplies due to the Russia-Ukraine war as well as other facility outages.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on energy and commodities >
Fuel For Thought - Automotive Marketing Signals: How Inventory And Loyalty Impact Investment
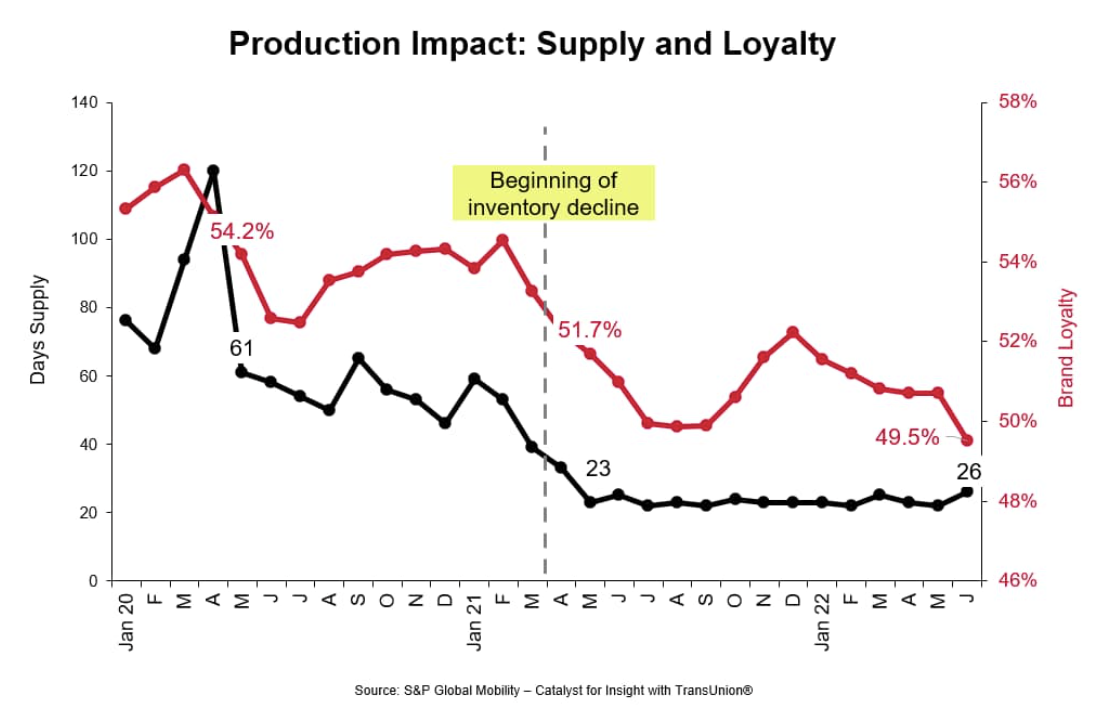
We are in year two of the great supply chain crisis. There are a handful of factors — from chip supply to impacts from climate and conflict — as to when "normal" production will return. Here is what we know now: profit margins are near historic highs for OEMs while consumer loyalty scores are near historic lows.
—Read the article from S&P Global Mobility
Access more insights on technology and media >

