Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Our Methodology
Methodology & Participation
Reference Tools
S&P Global
S&P Global Offerings
S&P Global
Our Methodology
Methodology & Participation
Reference Tools
S&P Global
S&P Global Offerings
S&P Global
Jul 17, 2023
For the largest publicly traded US and Canadian electric utilities, overall capital expenditure has increased at a 7% compound annual growth rate since 2010; meanwhile, aggregate capex for this group of companies is expected to continue to rise at a similar rate through the medium term. An examination of company guidance and stated capital investment plans from this peer group indicates that rather than capacity expansion, much of this spending is targeted on infrastructure upgrading and replacement.
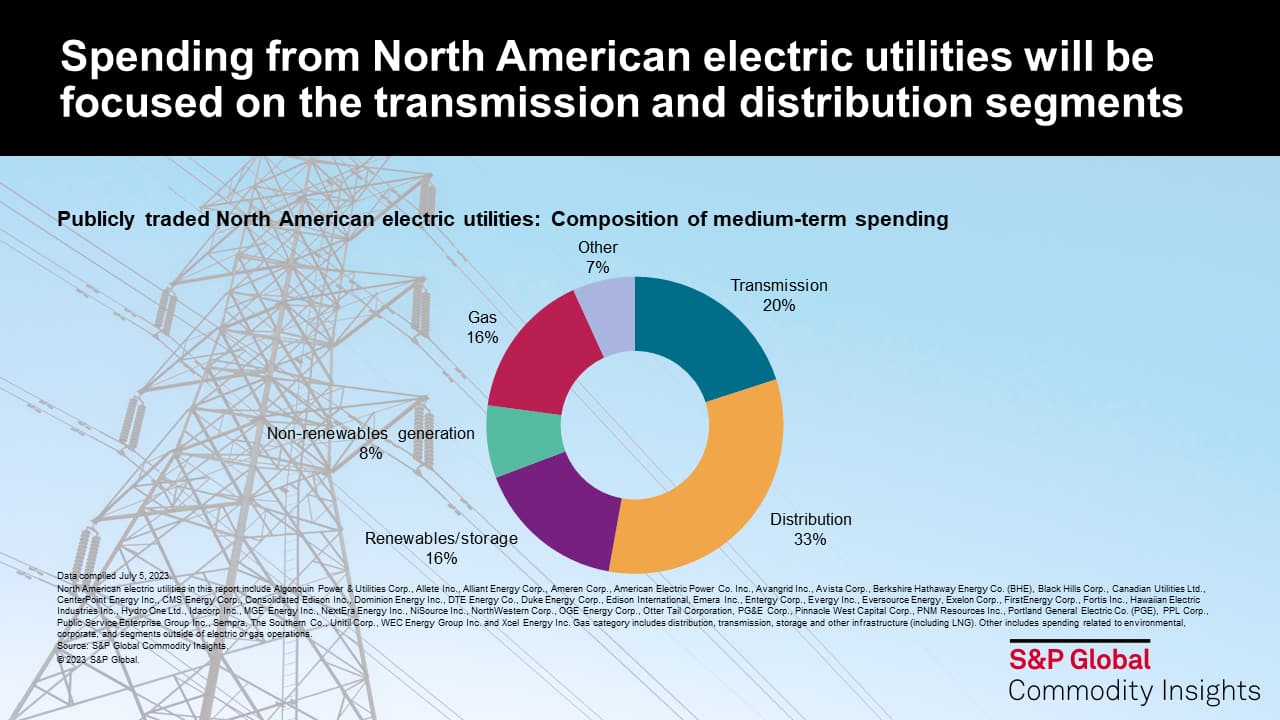
The largest share of budget plans is being directed to distribution, with this segment accounting for approximately one-third of medium-term spending from the peer group, per estimates from S&P Global Energy. In addition to accommodating ongoing customer and demand growth, this spending is aimed at several additional objectives within the distribution segment, including:
Transmission accounts for an additional 20% of expected capital investment from the peer group through the medium term. For this segment, spending is primarily centered on integrating new sources of supply (largely renewables and storage) into the grid via the expansion of transmission lines and line capacity, and the installation of new interconnection facilities and substations. Similar to distribution, transmission-related investments are also focused on infrastructure improvements and enhancements to increase resilience, reliability and efficiency, including via the replacement of aging transmission lines, transformers and circuit breakers.
Outside of T&D, spending in the renewable generation and storage segments collectively accounts for close to 15% of expected capital investment, as utilities look to improve the emissions profile of their generation fleet, achieve progress toward their own corporate sustainability objectives and meet governmental climate targets, while expanding generation capacity and replacing fossil fuel plant retirements. Of note, several companies have indicated increased appetite for spending in this segment following passage of the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) in the United States in 2022. In particular, the legislation provides greater visibility around project economics via the long-term extension of tax credits for low-carbon technologies, broader applicability of the tax credits to a wider range of technologies (including stand-alone storage becoming eligible for the investment tax credit [ITC]), and enhanced optionality around the tax credits (including greater transferability, and the ability for regulated utilities to opt out of normalization accounting for the storage ITC), all of which support further spending by utilities within this segment. Conventional generation accounts for another 8% of spending, centered on both investment in existing facilities and the addition of new gas and nuclear facilities.
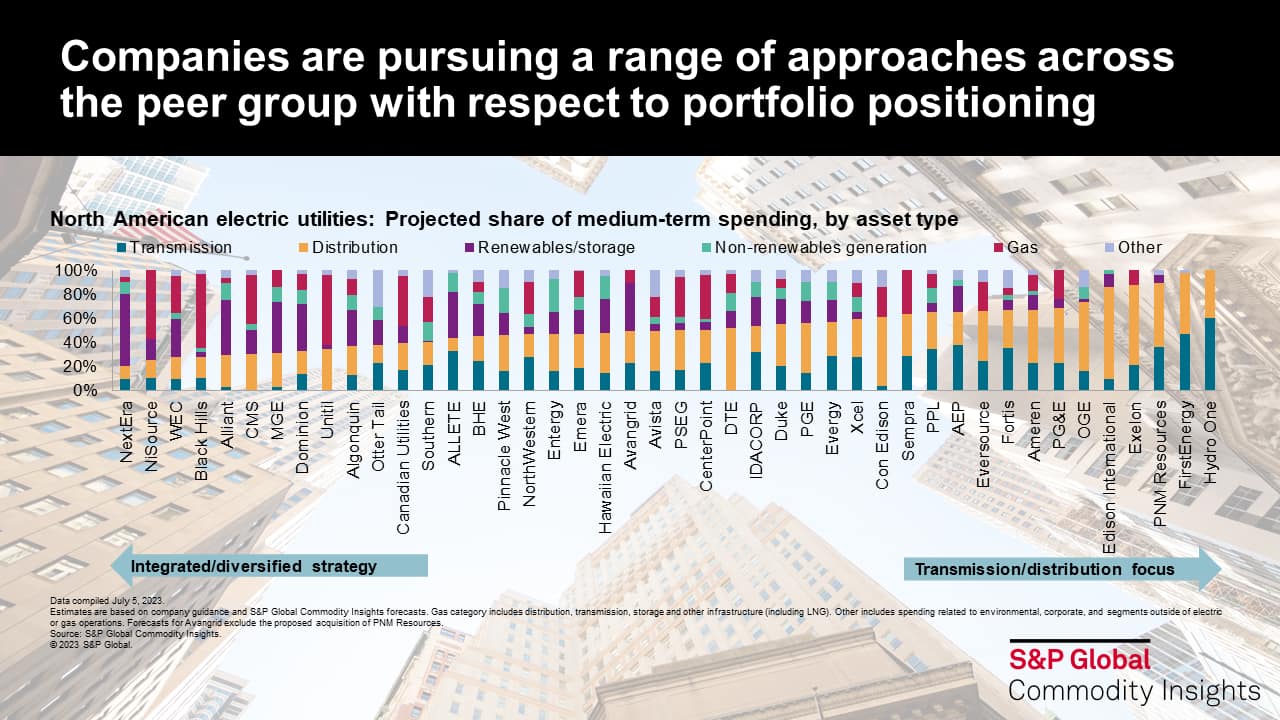
Beyond the high-level spending themes that exist across the industry, an examination of company-specific capex plans highlights the variance in strategic and portfolio positioning across the peer group. For one, this trend exists with respect to the degree of integration, with approaches ranging from fully vertically integrated operations (for those utilities operating in regulated electricity markets) to a primary emphasis on transmission and/or distribution. Beyond regulated power generation, transmission and supply, several companies within the peer group maintain additional means of portfolio diversification. This approach primarily includes segments that leverage complementary skillsets, such as nonregulated generation (with Allete, Avangrid and NextEra as examples of companies pursuing this segment of the market), distribution, transmission and storage of gas (with Black Hills, NiSource and Unitil all allocating over half of medium-term capex to the gas segment) and water distribution (which includes companies such as Algonquin and Eversource). Diversification beyond these areas remains limited, with only a small number of companies (including Berkshire Hathaway Energy via its HomeServices residential real estate brokerage unit, Hawaiian Electric through its American Savings Bank business and Otter Tail via its manufacturing and plastics segments) opting to venture beyond complementary business lines — a trend that is consistent with investor preferences for more streamlined portfolios that are focused on core operating areas.
Looking ahead, an array of emerging technologies and potential high-growth opportunities — such as hydrogen, renewable natural gas, carbon capture and storage, distributed generation and electric vehicle-related infrastructure — are providing these companies with further opportunities for investment within areas that are more aligned with core competencies and expertise. While spending in these areas remains relatively small for now, these technologies provide additional outlets for capex and earnings growth (in some cases aided by policy support), can provide greater resilience of portfolios by accelerating decarbonization of existing infrastructure, while also creating greater prospects for strategic differentiation relative to peers.
Learn more about our Global Power and Renewables service.
Chris DeLucia is a Director at S&P Global Energy with the Global Power and Renewables team, where he focuses on company strategies and competitive dynamics within the power and renewables segment.
Posted 17 July 2023
This article was published by S&P Global Energy and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
