Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Our Methodology
Methodology & Participation
Reference Tools
S&P Global
S&P Global Offerings
S&P Global
Our Methodology
Methodology & Participation
Reference Tools
S&P Global
S&P Global Offerings
S&P Global
Aug 02, 2023
In 2022, China's LNG demand fell 16 million metric tons (MMt) year over year owing to weak domestic gas demand and high global spot prices. As a result, China Oil and Gas Pipeline Corp.'s (PipeChina) terminals utilization rate dropped to 49% from 68% in the prior year. Non-national oil company (NOC) imports via PipeChina's terminals decreased 83% year over year to only 300,000 metric tons.
On the other hand, PipeChina's Hainan terminal, which is mostly used for reloads, exported nine cargoes totaling 500,000 metric tons in 2022. The majority of imported cargoes through the Hainan terminal were priced at oil-indexed levels for term contracts, and the export price roughly followed the trend of global spot price, leading to an average spread of $13/MMBtu in 2022.
In the first half of 2023, as China's LNG imports returned to growth, the service volumes at PipeChina's LNG terminals increased by 12% year over year. Growth concentrated in the second quarter at 40%, with volumes by NOCs and non-NOCs rising by 24% and 751%, respectively, year over year. During the same period, there were 7 reexport cargoes out from PipeChina's Hainan terminal for 400,000 metric tons, with the majority occurring during the first quarter of 2023. As global spot price declines, profitability of reexports becomes increasingly uncertain. Consequently, there was a wave of cancellations of slot usage at the Hainan terminal for June, July and August deliveries.
PipeChina's terminal utilization is expected to rise in 2023 but remain below the 2021 levels. China's demand for gas has returned to growth but will still be limited from weak economic rebound and surging coal and renewable capacity. Continued growth in domestic production and ramping delivery from Russian pipeline imports will also constrain LNG import growth. As of the July spare capacity announcement, PipeChina's terminals are only 41% booked for September through December 2023, although slot reservation and cancellation will continue to change based on LNG demand (see Figure 1). The current spare capacity indicates around 24-25 slots are still available each month.
Figure 1
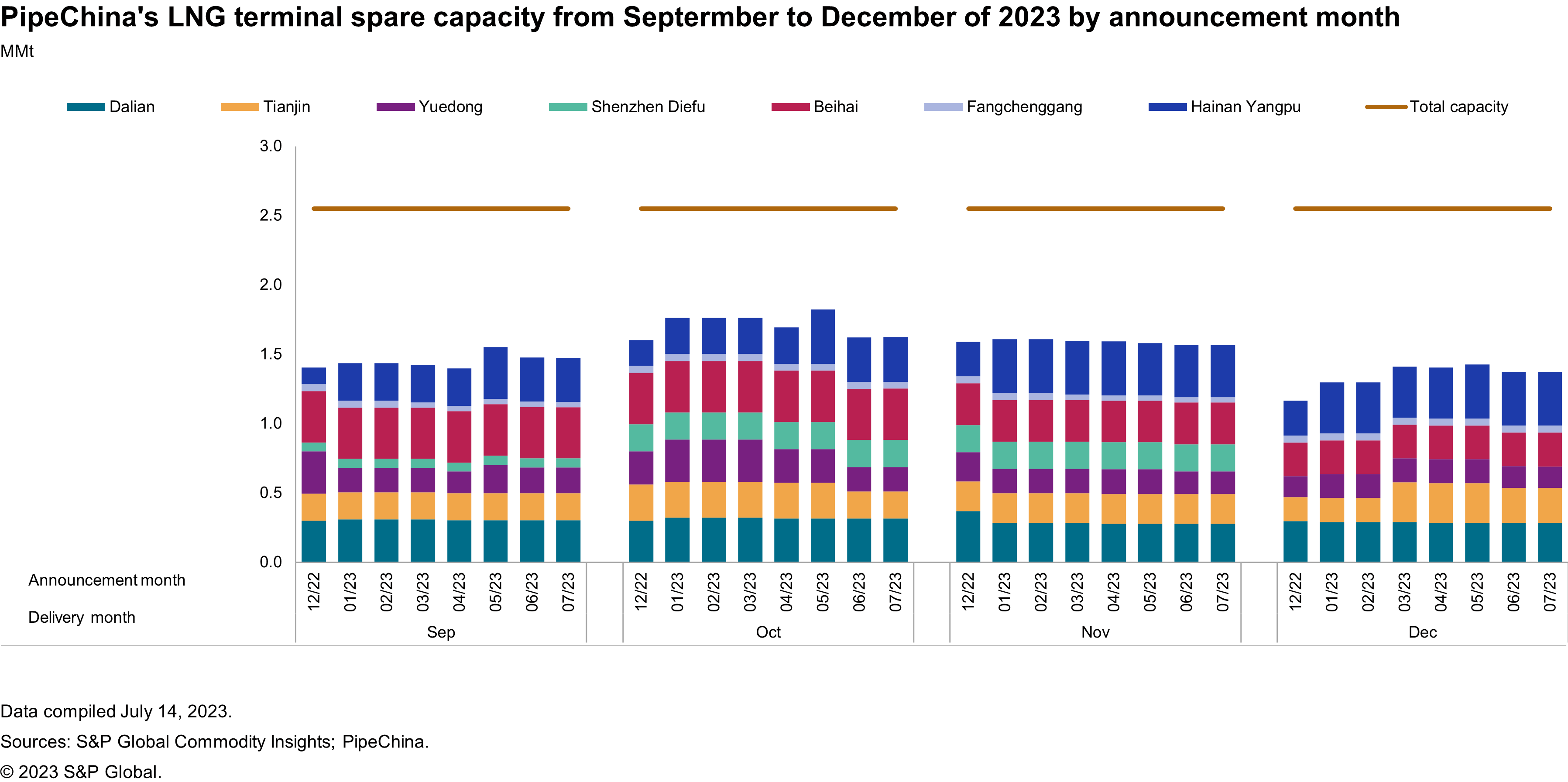
The NOCs are expected to be the main users at PipeChina's terminals throughout the remainder of 2023. This is primarily driven by their requirement to secure capacity in advance to meet long-term contractual obligations and ensure supply security during the winter season. In contrast, non-NOCs, many of them having their own terminals, may take advantage of lower spot prices during the summer season to import cargoes but the anticipated global price increase in the 2023-24 winter season may still keep them out of the market.
This report is part of our research series, "Natural gas in Asia Pacific: Balancing supply security and energy transition."
Learn more about our Asia-Pacific energy research.
Tianshi Huang is an Associate Director covering Greater China's gas and LNG markets.
Posted 2 August 2023
This article was published by S&P Global Energy and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
