Energy supply diversification to China has been at the core of Russia's eastern pivot, while Russian gas is central to China's energy diversification away from the Middle East and Australia.
Russia has become the third-largest natural gas supplier to China, including both pipeline gas and LNG, and is currently its second-largest crude supplier after Saudi Arabia, making Beijing's geopolitical stance -- somewhere between Moscow and Washington -- increasingly important in the ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine.
When the preliminary Power of Siberia gas pipeline deal was signed in 2014, the spot price of LNG was around $10.50/MMBtu. But prices have risen manifold since then, making pipeline gas much cheaper for China. Economics alone will make it tougher for Beijing to cut Russian gas supply.
Still, China will have to consider its options, given its own exposure to the US and global financial systems in the event of secondary sanctions. Alternatively, turmoil in Russia gives Beijing leverage in both energy and financial markets.
PRICES
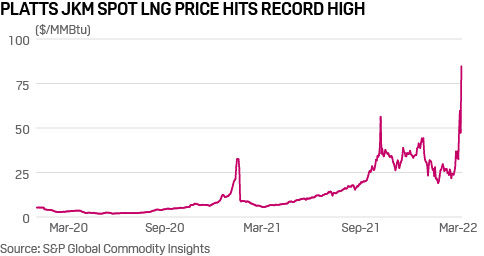
- Spot Asian LNG prices hit a record high twice within a span of a week. On March 3, the Platts JKM for April deliveries touched $59.672/MMBtu. On Mar. 7, Platts JKM rose 79.21% from a day earlier to $84.762/MMBtu, registering the single largest daily jump in the price assessment, according to S&P Global Commodity Insights data.
TRADE FLOWS
- Russia is the third-largest natural gas supplier to China, including both pipeline gas and LNG. Russian natural gas accounted for around 10% of China's total gas imports of 121 million mt in 2021, against 25.9% and 19.8% from Australia and Turkmenistan, respectively.
- Russia exported 12.145 million mt of natural gas, comprising 4.61 million mt of LNG and 7.54 million mt of pipeline gas in 2021, according to China's General Administration of Customs. The total volume rose 51% year on year, with LNG imports falling 9.8%, while pipeline gas imports rose 154%.
- Russia is the second-largest crude supplier to China after Saudi Arabia. It delivered 1.6 million b/d of crude in 2021, customs data showed, down 4.6% year on year. But Russia's share increased slightly to 15.5% from 15.4% in 2020. China cut overall crude imports by 5.1% to 10.3 million b/d in 2021.
- State-owned China National Petroleum Corp (CNPC) and Russia's Gazprom signed a 30-year sales and purchase agreement in May 2014, for 38 Bcm/year of natural gas supplied via the Power of Siberia gas pipeline.
- The Power of Siberia line started supplying gas to China from Dec. 2, 2019, and volume has reached 43 million cu m/day or around 15 Bcm/year since December 2021. Volumes through the pipeline, which is called the China-Russia natural gas pipeline eastern route in China, is expected to reach 38 Bcm/year after the third section of the Chinese portion is completed in 2023.
- Gazprom plans to supply natural gas to China via Mongolia of up to 50 Bcm/year via the Power of Siberia 2 line. The section in Mongolian territory is called the Soyuz Vostok gas pipeline, which will be an extension of Power of Siberia 2. A feasibility study for Soyuz Vostok has been completed, with assistance from Mongolia, Gazprom said Jan. 25.
- On Feb. 4, CNPC and Gazprom signed a long-term SPA for 10 Bcm/year of natural gas to be supplied via the Far Eastern route. At full capacity, Russian pipeline gas to China will reach 48 Bcm/year, Gazprom said.
- On Feb. 25, Novatek Gas & Power Asia, a subsidiary of Russia's Novatek, and China's provincial government owned Shenergy Group signed a 15-year LNG SPA for more than 3 million mt of LNG produced from Arctic LNG 2 on a DES basis.
- On Jan. 11, Novatek Gas & Power Asia and Zhejiang Energy Gas Group, a subsidiary of Zhejiang Provincial Energy Group, signed a 15-year LNG SPA for supply of up to 1 million mt/year LNG from Arctic LNG 2 on a DES basis, following a Heads of Agreement signed on June 2.
- On Dec. 2, Novatek Gas & Power Asia and local state-owned Zhejiang Hangjiaxin Clean Energy signed a framework agreement to ship LNG to the Hibiki LNG receiving terminal, owned by Saibu Gas in Kyushu, Japan. Hangjiaxin will then ship the LNG to its Jiaxing LNG terminal in eastern Zhejiang province using small and medium-sized LNG vessels.
- On Feb. 4, CNPC and Rosneft signed an agreement for supplying 100 million mt of crude oil to northwestern China through Kazakhstan for 10 years.
- CNPC and Rosneft signed a 20-year agreement for supplying 15 million mt/year of crude oil to northeastern China via the Eastern Siberia–Pacific Ocean oil pipeline in June 2009. The project started operations on Jan. 1, 2011. The ESPO pipeline's capacity has been increased to 80 million mt/year, and some 40 million mt/year shipments was reported in 2021.
INFRASTRUCTURE
- China National Oil and Gas Exploration and Development Co (CNODC), a subsidiary of CNPC, bought a 20% equity stake in Russia Novatek's Yamal LNG project in January 2014, giving it LNG equity volume of 3.3 million mt/year. Yamal LNG, which has a production capacity of 16.5 million mt/year, started gas deliveries in May 2018.
- Russia's Novatek sold a 9.9% equity stake in Yamal LNG to China's Silk Road Fund in March 2016. Under the transaction, Silk Road Fund gave a 15-year loan for financing Yamal LNG. A 9.9% equity stake will give the fund 1.6 million mt/year of LNG offtake.
- State-owned CNOOC acquired a 10% interest in Novatek's Arctic LNG 2 project on April 25, 2019, giving it 1.98 million mt/year of LNG offtake at full capacity. Arctic LNG 2 has three LNG trains of 6.6 million mt/year each, scheduled to start production in 2023.
- China's CNODC acquired a 10% interest in Novatek Arctic LNG 2 on June 7, 2019, giving it 1.98 million mt/year of LNG offtake at full capacity.
- On Jun. 5, 2019, state-owned Sinopec, Novatek and Gazprombank signed a Heads of Agreement to set up a joint venture to market LNG and natural gas to customers in China. The venture was approved by the European Commission in March 2020.
- Rosneft and Sinopec have set up a joint mining enterprise, Udmurtneft, for 15 years, with Rosneft holding 51% and Sinopec holding 49%. It currently has oil production of around 6 million mt/year.
- Beijing Gas bought a 20% share in Rosneft subsidiary Vercknechonskneftegas in June 2017, which holds a license to develop the Verkhnechonsk oil, gas and condensate field. The two firms plan to develop a fuel service station network in Russia.
- The Tianwan and Xudapu nuclear power plants, bilateral nuclear energy projects between China and Russia, began construction in May 2021. Deals for units 7 and 8 of Tianwan plant and units 3 and 4 of Xudapu plant were signed in June 2018. When completed and operational, their annual power generation will reach 37.6 billion kWh, equivalent to reducing 30.68 million mt/year of CO2.